1) The document discusses the opportunities and challenges presented by India's large youth population and growing digital landscape.
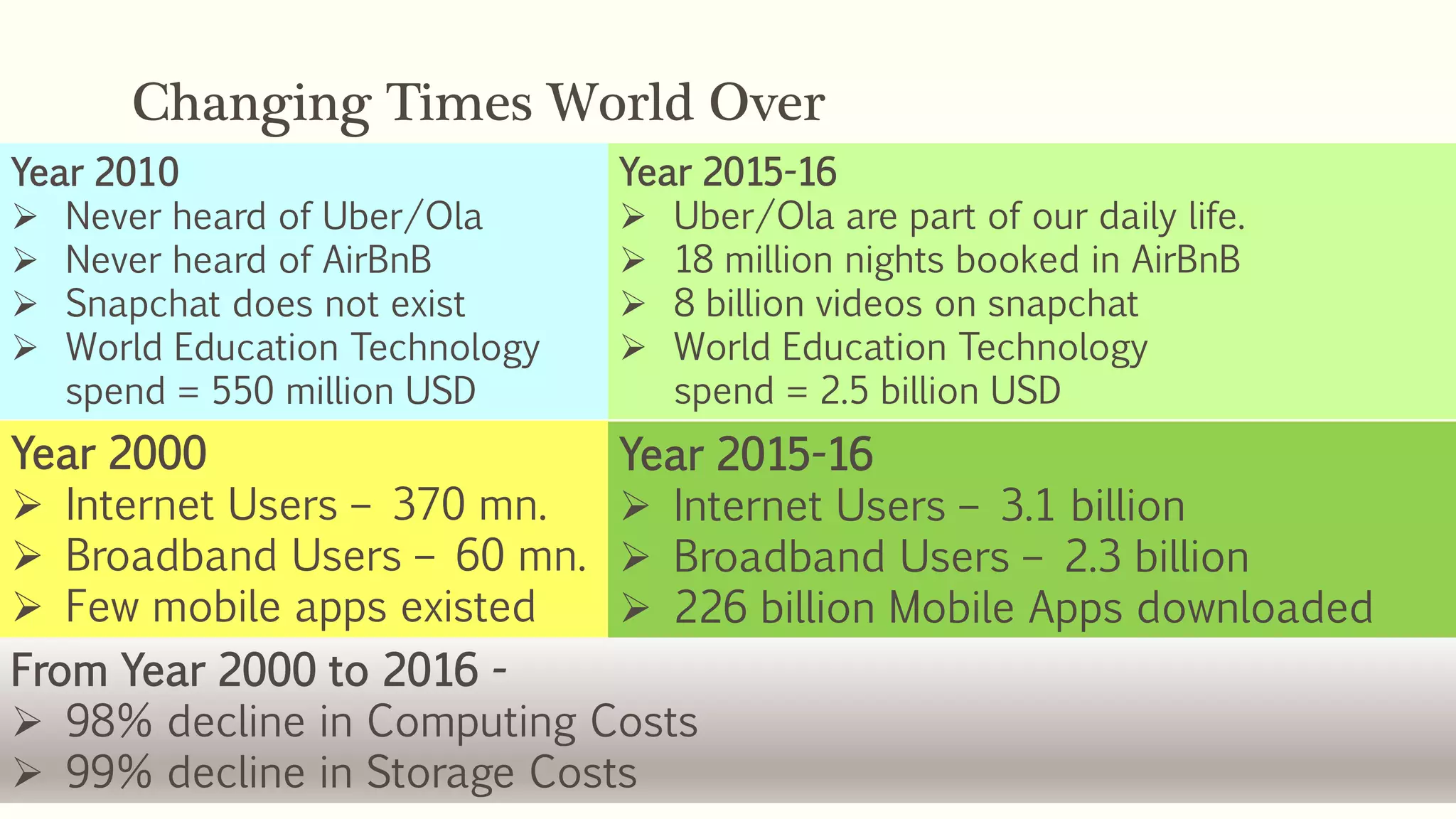
2) It notes that 48% of India's population is between 15-65 years old, making it potentially economically productive. The 13-24 year old segment is very active digitally.
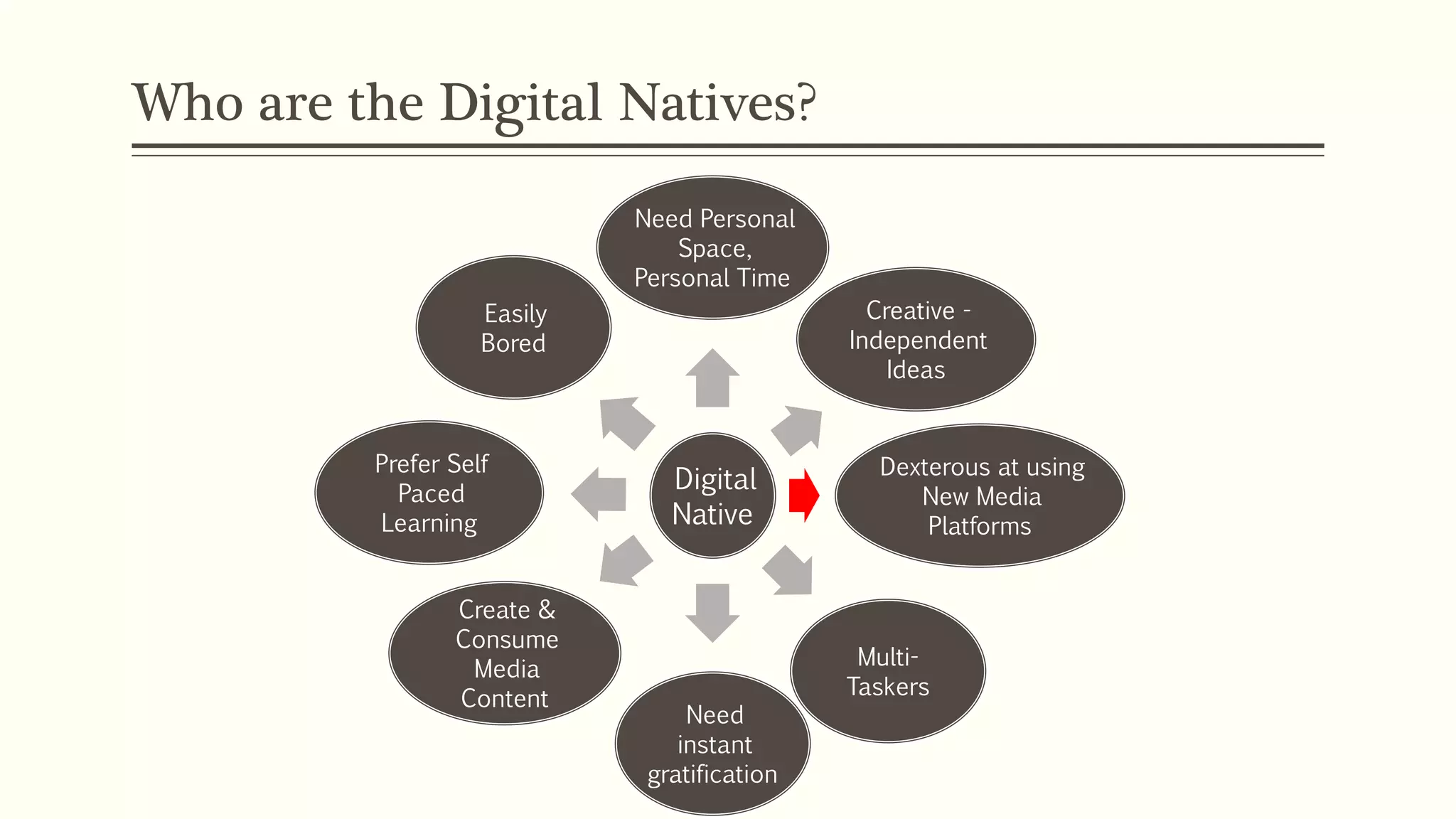
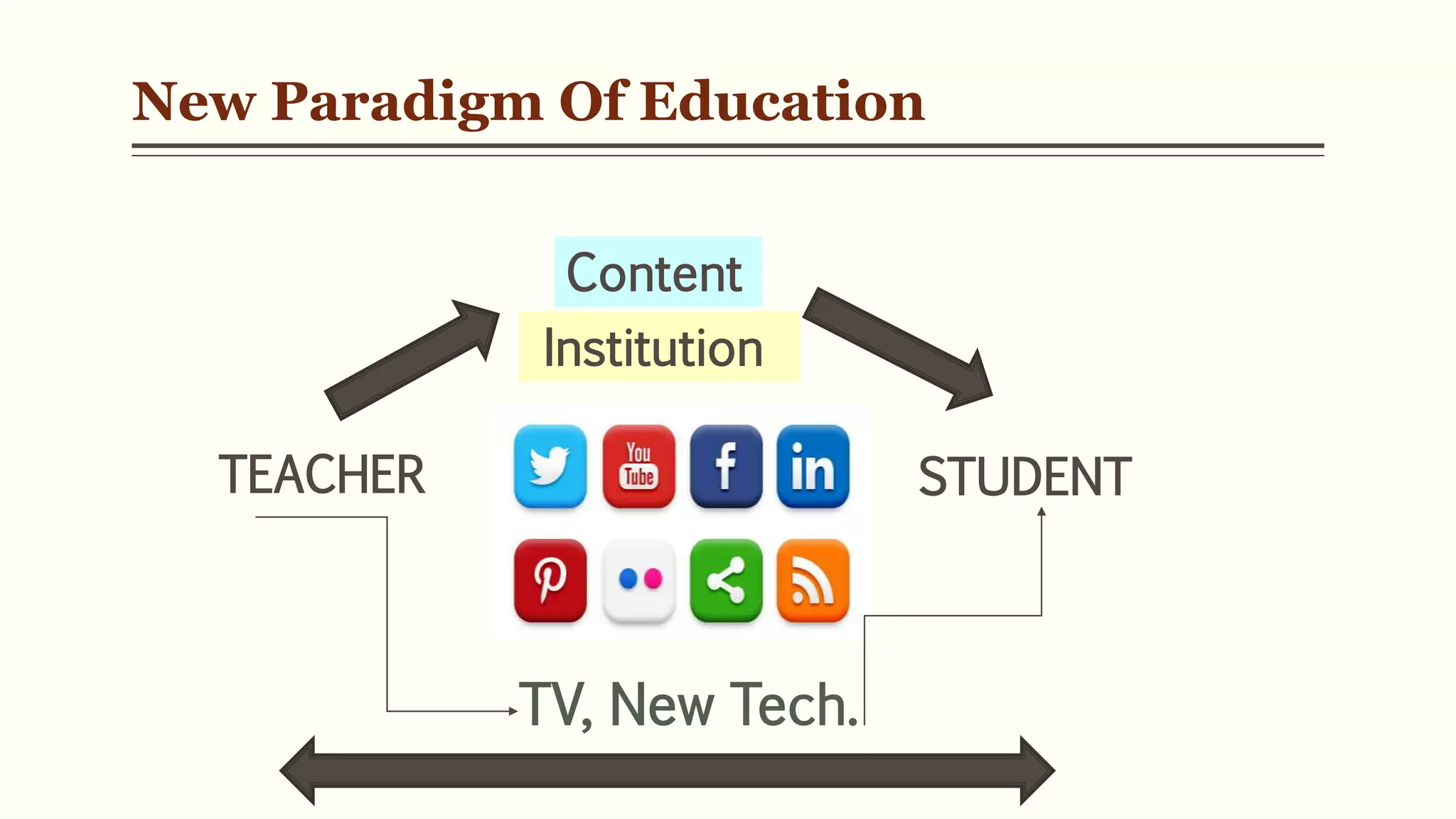
3) This "digital native" generation prefers multimedia and self-paced learning over text. Education must move from rote learning to applied knowledge to engage them.
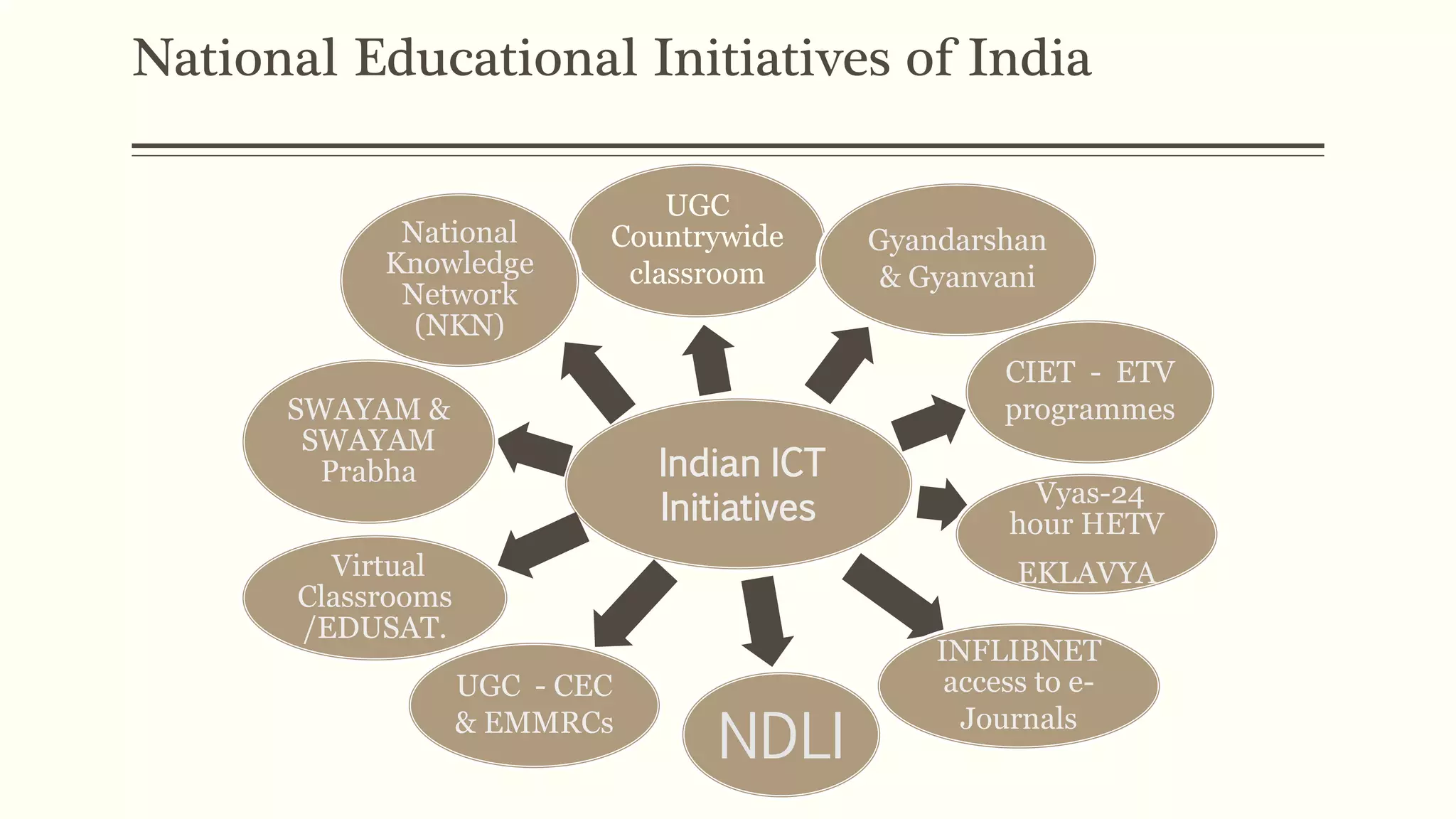
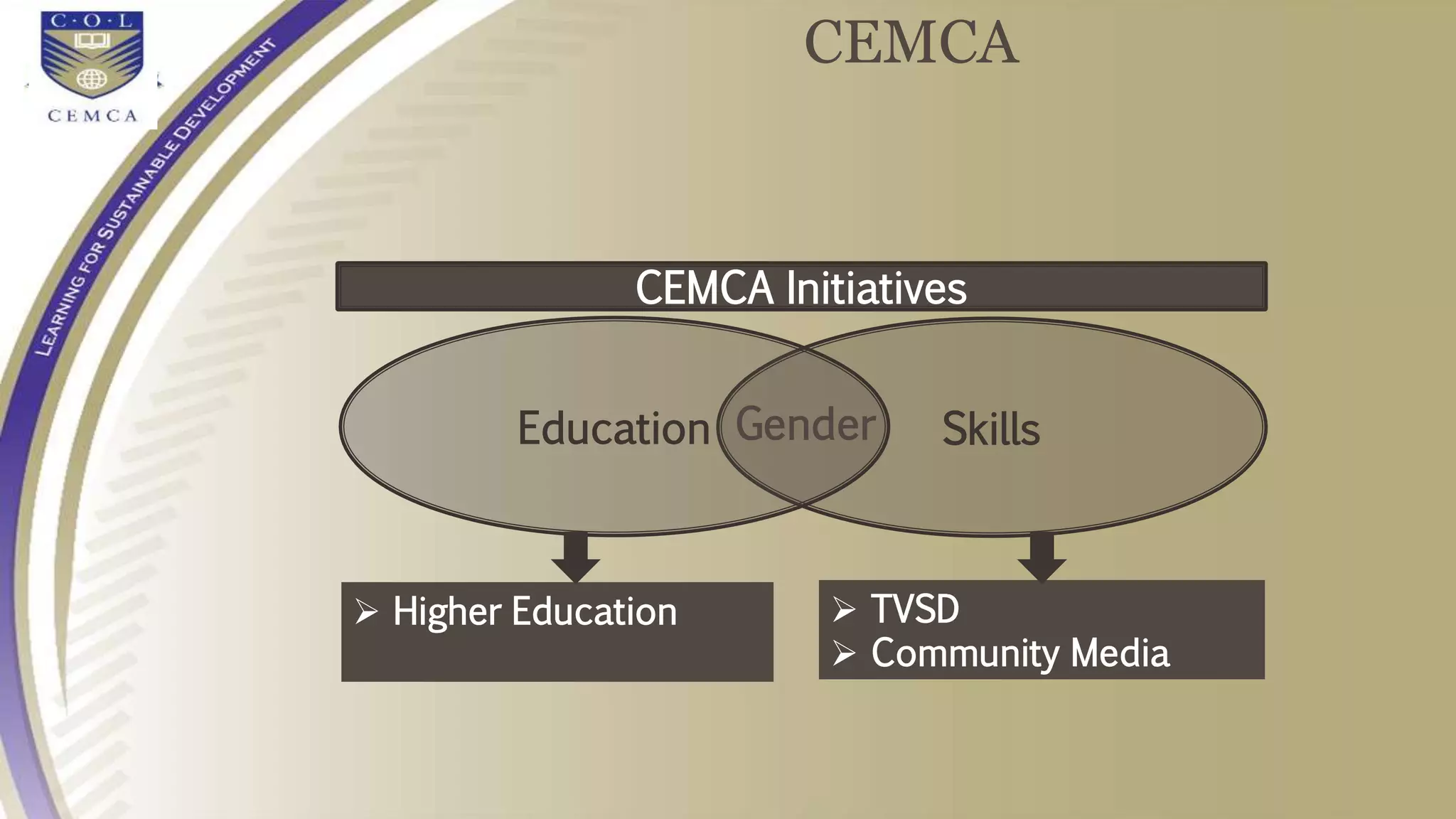
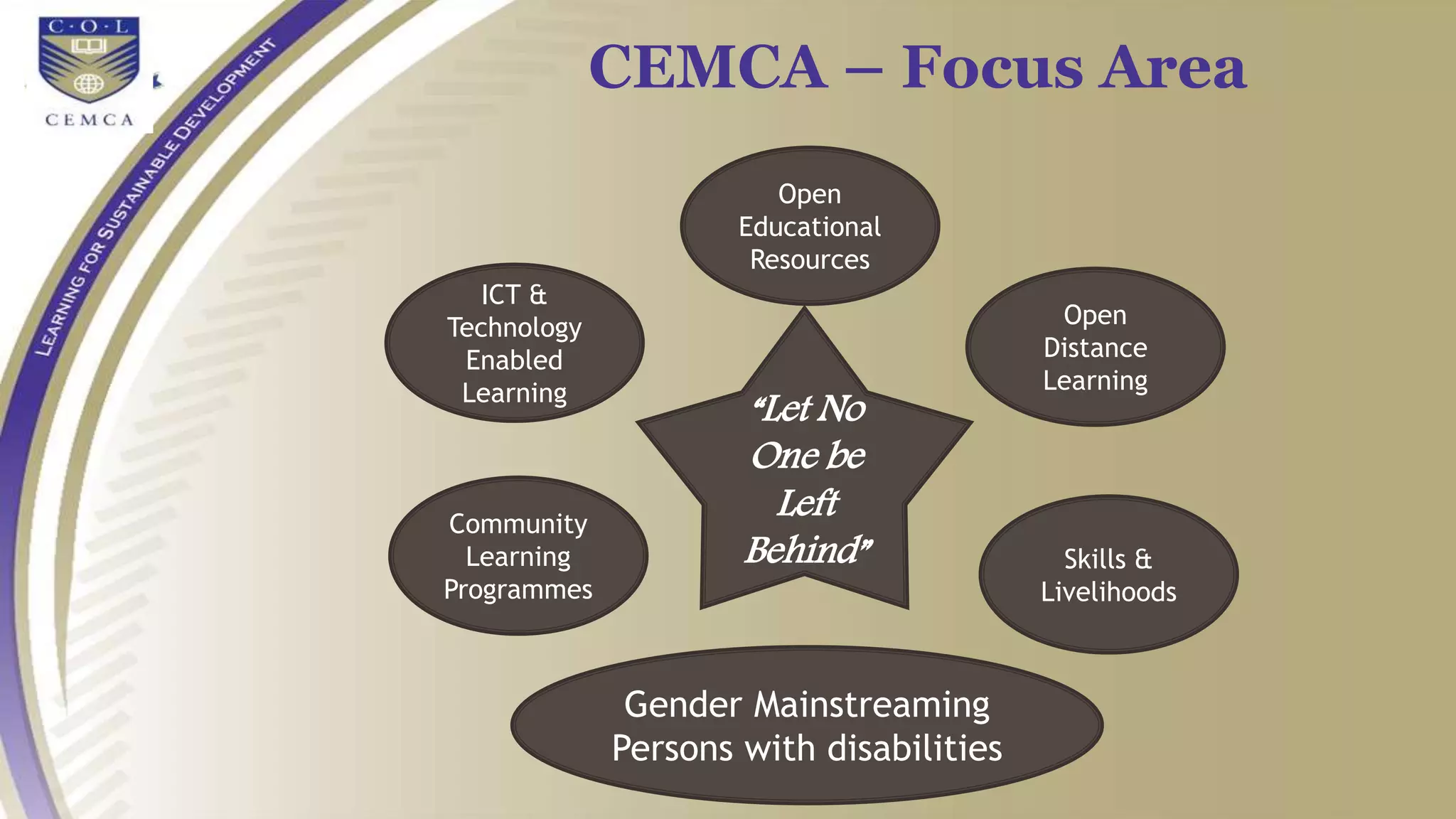
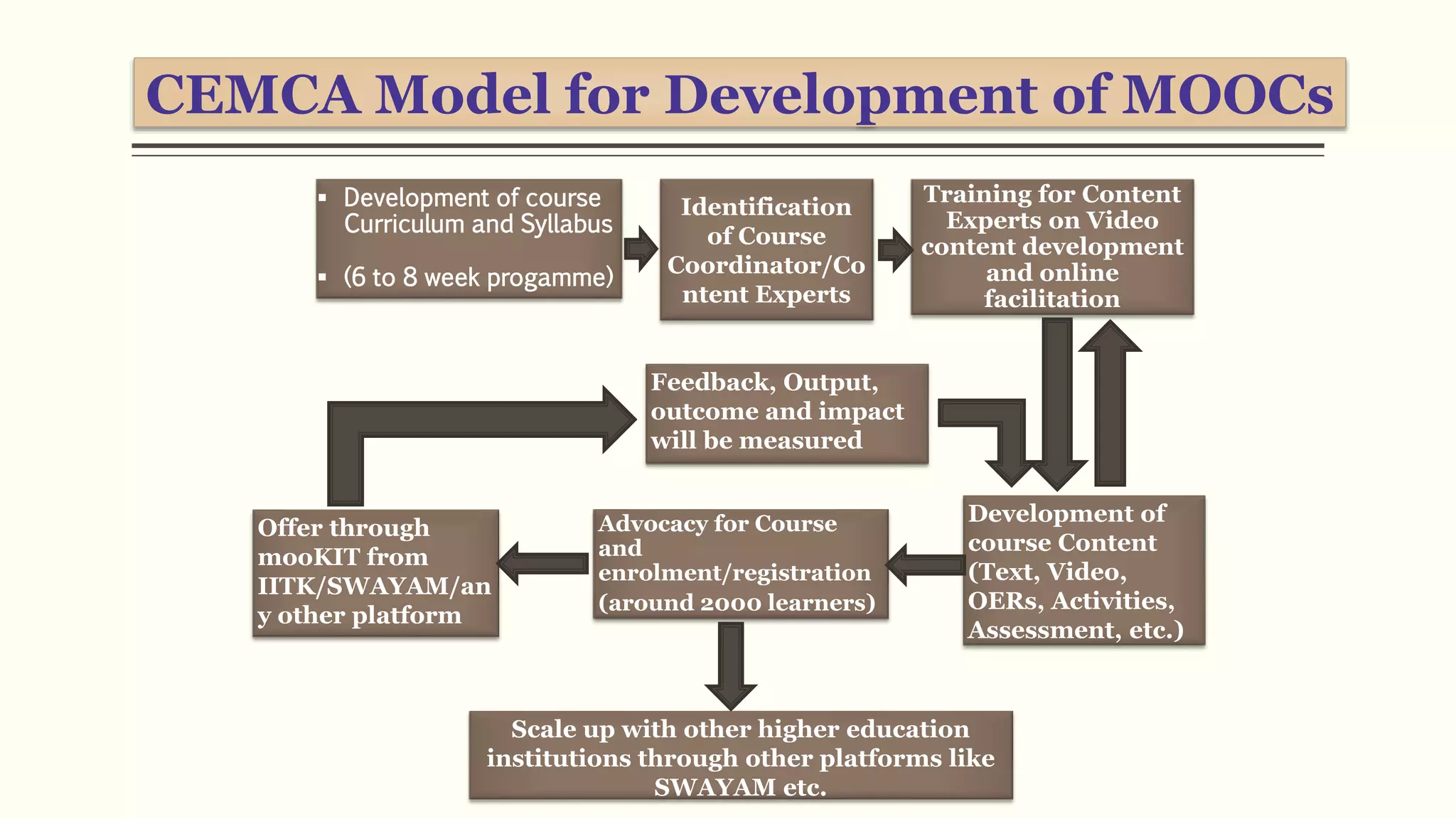
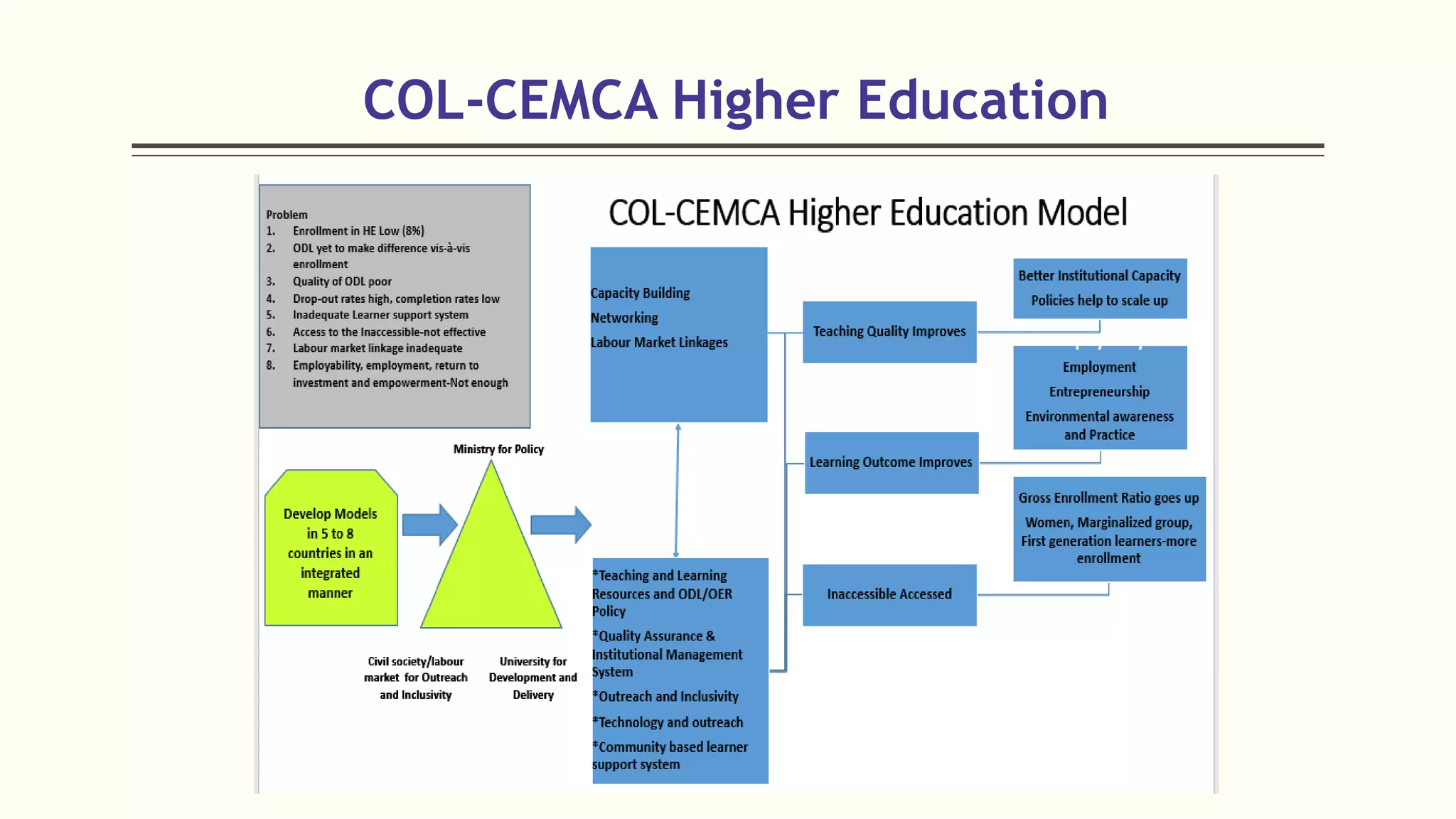
4) Initiatives like MOOCs, SWAYAM, and programs by CEMCA aim to leverage digital tools and open educational resources to make quality education accessible for all.