The document discusses CEMCA and its work promoting community media and lifelong learning in Asia. Some key points:
- CEMCA was established in 1987 as a regional office of the Commonwealth of Learning based in New Delhi to deliver educational media and opportunities for lifelong learning.
- It works in 8 Asian Commonwealth countries, focusing on areas like open educational resources, community learning programs, and skills development.
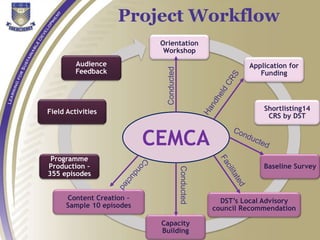
- CEMCA supports community radio through advocacy, facilitating new community radio stations, capacity building, and mentoring for content creation. It has helped establish over 70 new community radio stations.
- Examples of CEMCA projects include a science for women's health and nutrition project delivered through community radio stations in partnership with India