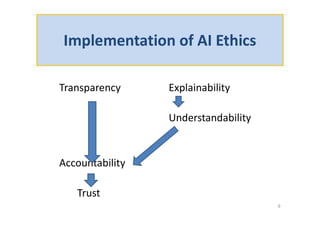
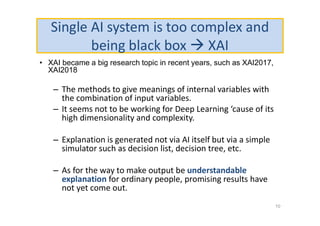
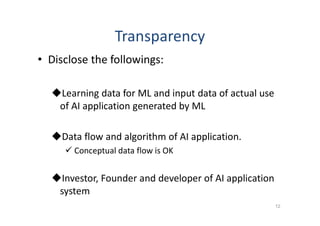
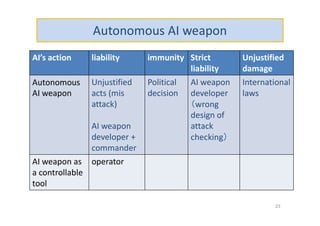
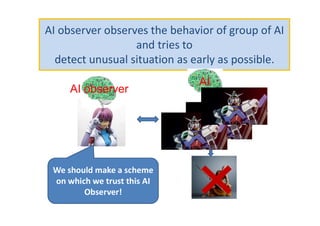
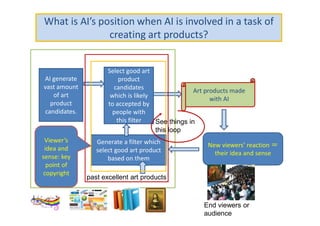
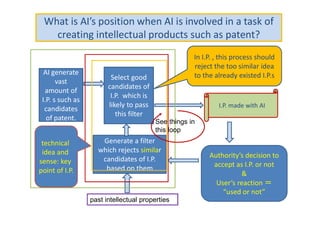
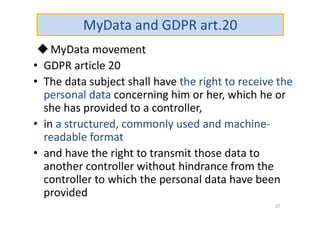
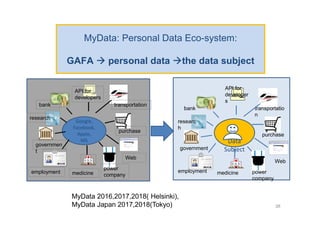
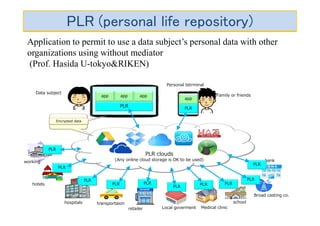
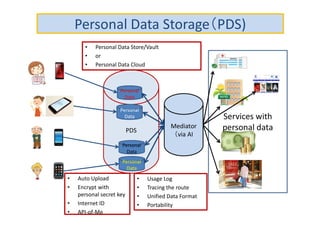
The document discusses ethical guidelines for the development and use of artificial intelligence, highlighting principles such as accountability, transparency, and trust. It emphasizes the need for responsible AI systems that respect human rights, promote well-being, and allow individuals control over their personal data. The text also examines the implications of AI misuse, the importance of explainability, and legal considerations surrounding AI accountability and intellectual property.