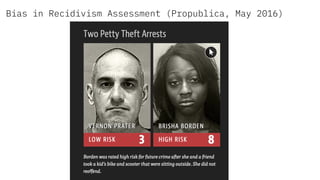
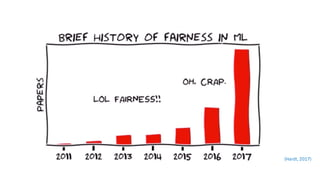
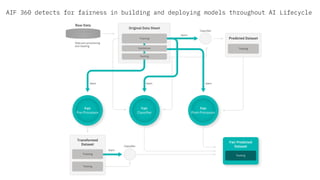
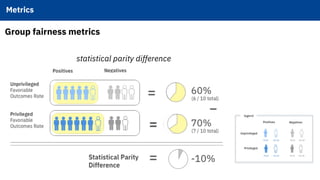
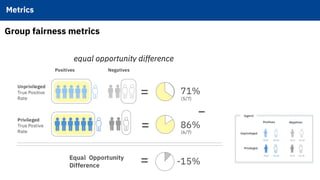
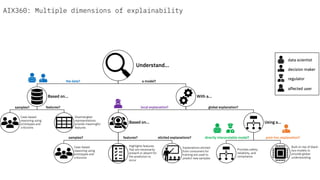
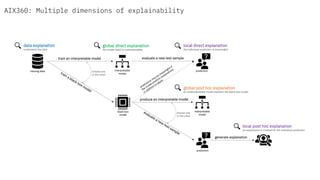
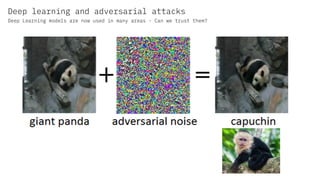
The document discusses IBM's efforts to bring trust and transparency to AI through open source. It outlines IBM's work on several open source projects focused on different aspects of trusted AI, including robustness (Adversarial Robustness Toolbox), fairness (AI Fairness 360), and explainability (AI Explainability 360). It provides examples of how bias can arise in AI systems and the importance of detecting and mitigating bias. The overall goal is to leverage open source to help ensure AI systems are fair, robust, and understandable through contributions to tools that can evaluate and improve trusted AI.










![https://bigcheck.mybluemix.net
[Weng et al., 2018. Evaluating the Robustness of Neural Networks: An Extreme Value
Theory Approach. ICLR 2018]
How does it impact us?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lfai-trusted-ai-190821020211/85/Trusted-Transparent-and-Fair-AI-using-Open-Source-13-320.jpg)