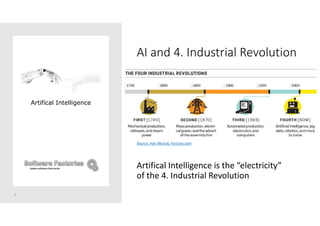
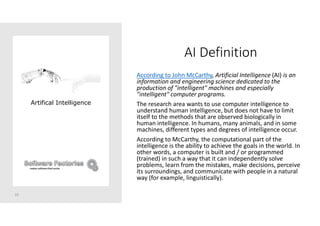
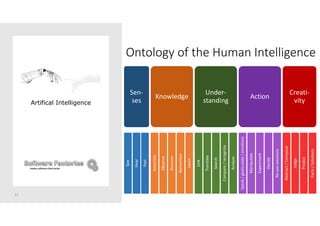
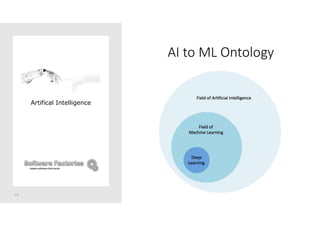
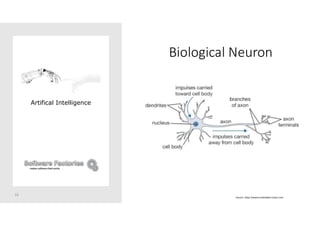
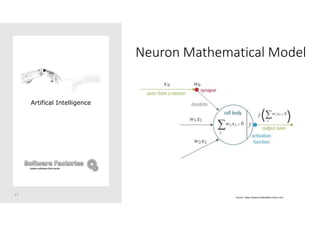
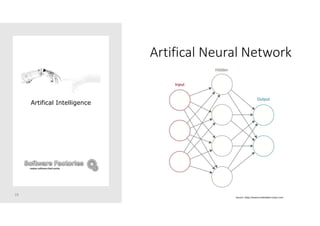
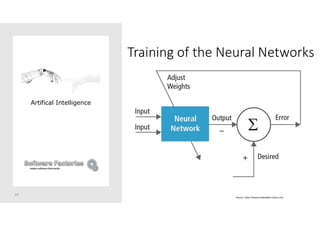
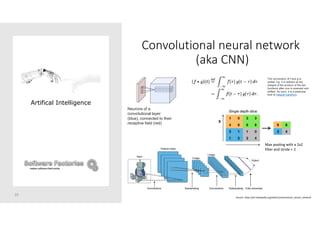
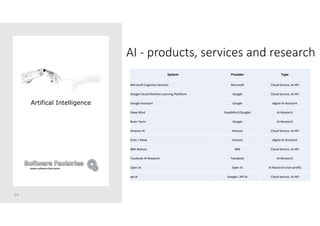
The document discusses artificial intelligence and provides an overview of key topics including:
- A brief history of AI beginning with the 1956 Dartmouth conference where the field was first proposed.
- Types of AI such as artificial weak intelligence, artificial hybrid intelligence, and artificial strong intelligence.
- Applications of AI such as computer vision, machine translation, and robotics.
- Progress in deep learning including speech recognition, computer vision, and machine translation.
- Demos of AI services including a cognitive race between AWS and Azure and using an AWS bot with Lex.