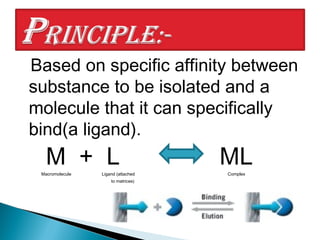
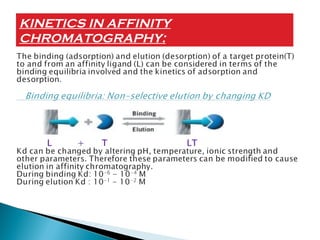
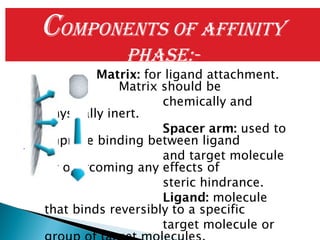
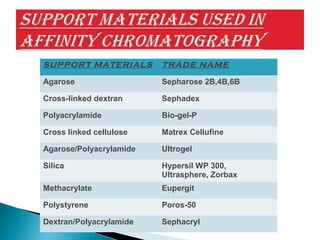
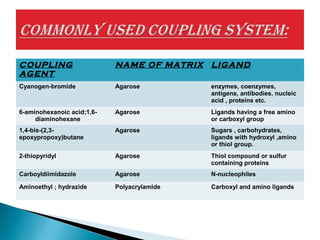
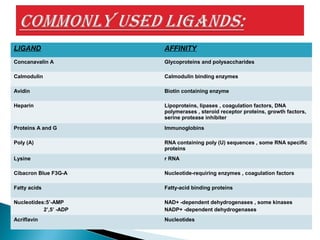
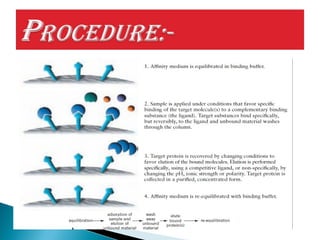
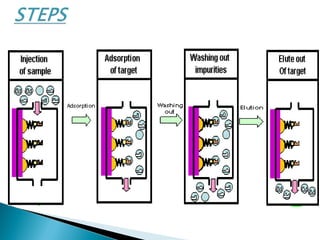
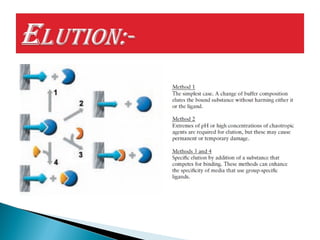
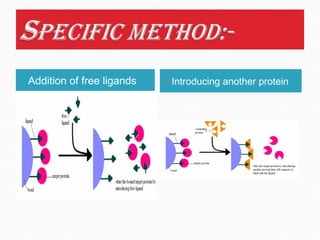
This document discusses affinity chromatography. It begins by explaining that affinity chromatography uses a specific affinity between a substance to be isolated and a molecule (ligand) that it can bind to. The ligand is attached to an inert matrix. Various matrices, ligands, and coupling agents are discussed. Applications include purifying enzymes, antibodies, and glycoproteins. While single step and high yielding, limitations include non-specific binding and ligand availability/cost. Overall, affinity chromatography provides high selectivity and resolution for target molecule purification.