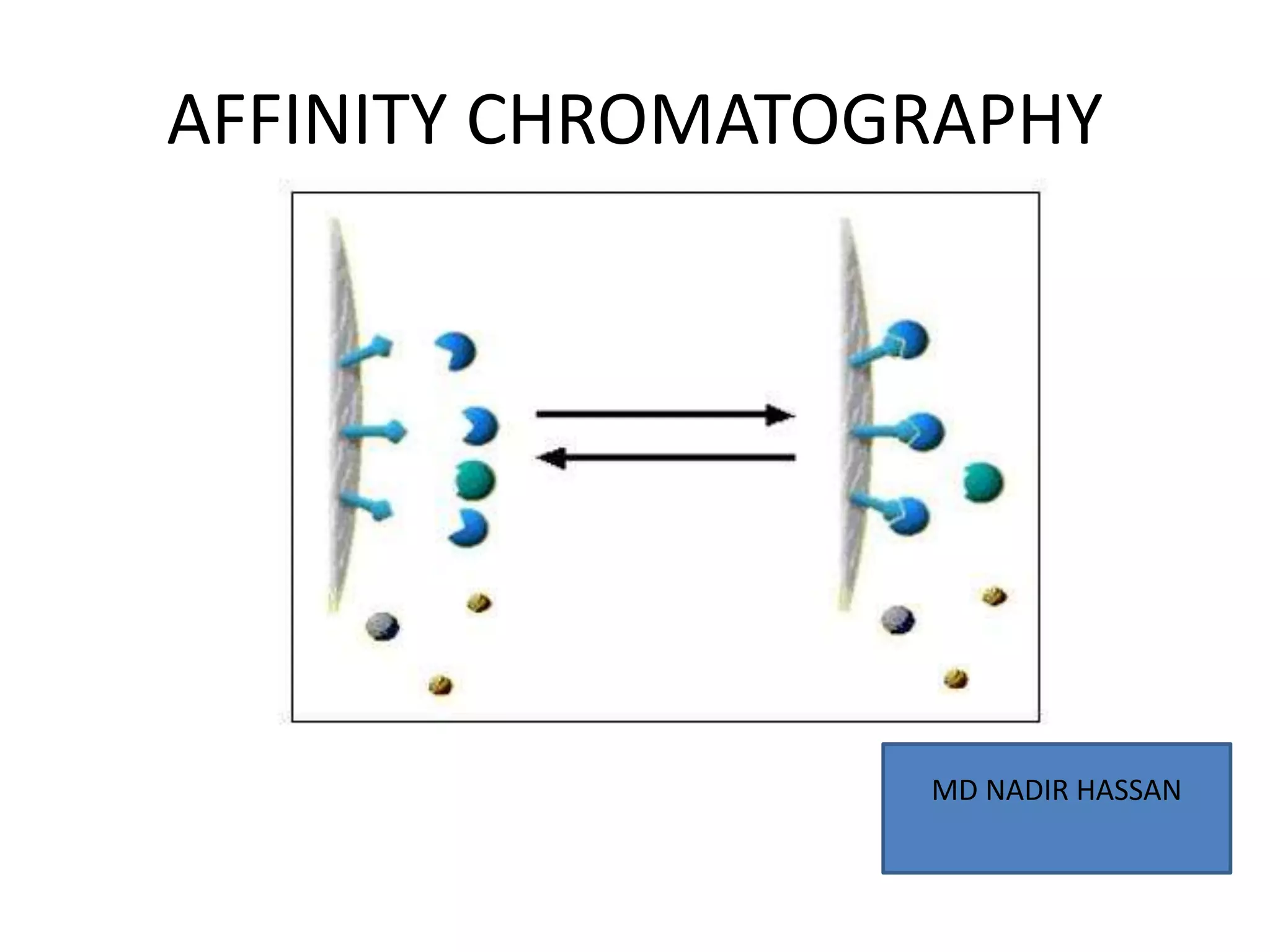
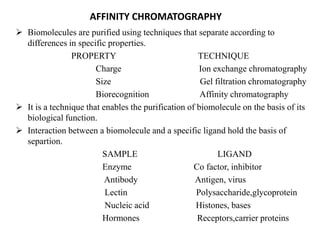
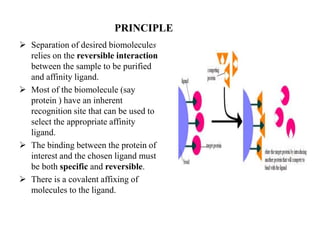
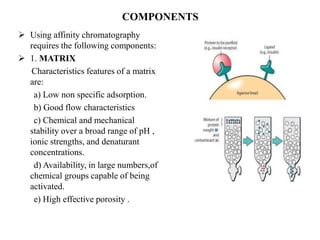
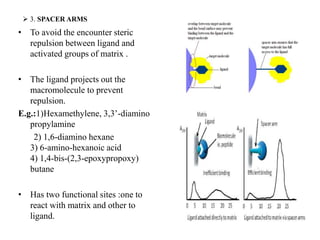
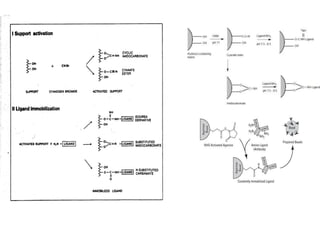
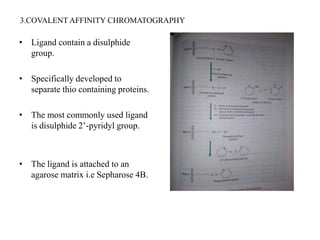
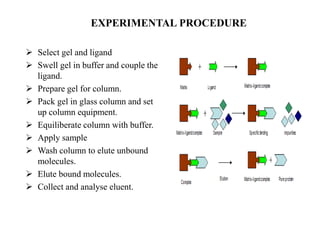
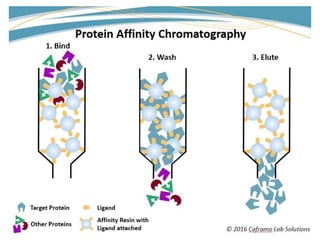
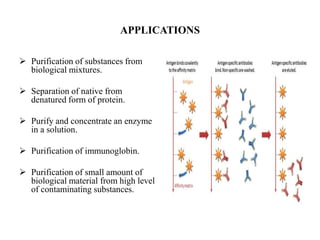
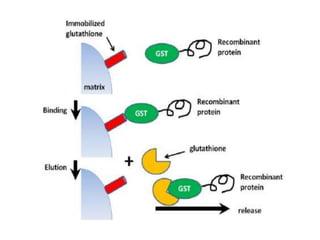
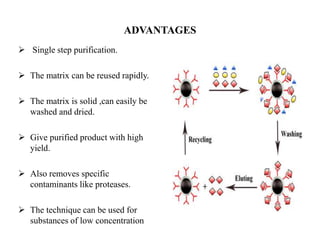
Affinity chromatography is a technique that separates biomolecules based on a biological interaction between the target biomolecule and an immobilized ligand. It involves coupling a specific ligand to a solid support matrix, then allowing the target biomolecule from a sample to bind reversibly to the ligand. Unbound molecules are washed away, while the bound target can then be eluted. Affinity chromatography is useful for purifying enzymes, antibodies, nucleic acids, and other biomolecules due to its high selectivity and ability to isolate molecules from complex mixtures in a single step.