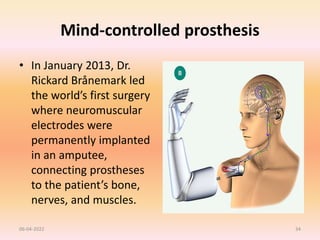
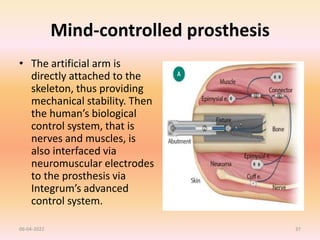
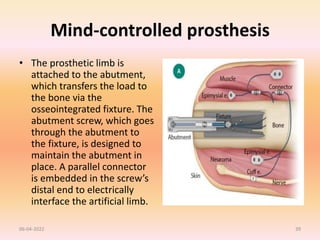
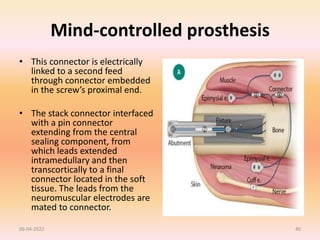
The document discusses advancements in upper extremity prosthetics, emphasizing custom design and fabrication techniques to improve comfort and functionality for amputees. Key innovations include myoelectric systems, which enhance control through muscle signals, and 3D printing technologies that streamline the fitting process. It also outlines the benefits and challenges of technologies such as osteo-integration and mind-controlled prostheses, highlighting a future where prosthetics can closely mimic natural limb performance.