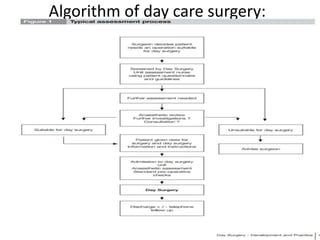
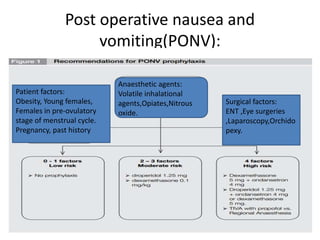
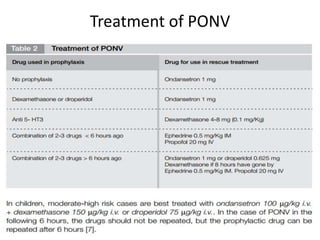
This document provides an overview of day care or ambulatory surgery. It discusses the history and development of day care surgery. Key points include that day care surgery aims to have patients discharged on the same day of surgery. Patient selection involves assessing medical, social and surgical factors to identify appropriate candidates. The document also outlines common procedures performed in day care settings and considerations for anesthesia, analgesia, and post-operative recovery and discharge criteria. The overall goal of day care surgery is to provide surgical care without an overnight hospital stay when possible.