This document discusses the concepts of administration and management in public health. It defines administration as the process of efficiently completing activities through other people, while management involves implementing plans and policies set by administration. Some key points:
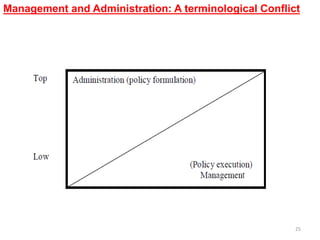
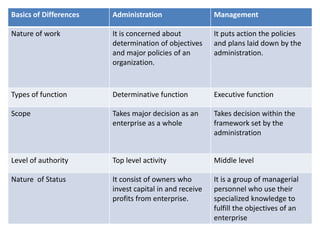
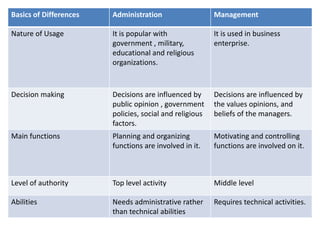
- Administration determines objectives and policies at the top level, while management executes decisions at middle levels within the policy framework.
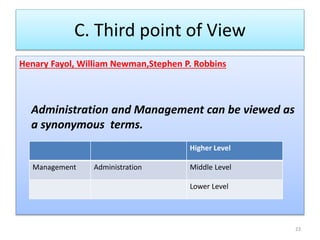
- Administration is viewed as policymaking, rules, and finance, while management is implementation and operations. However, others see administration and management as synonymous terms.
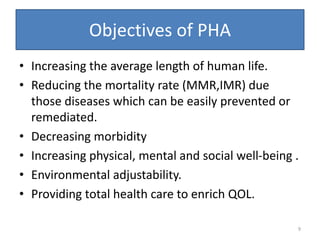
- Public health administration deals with promoting health, preventive services, medical care, resources for health, and more, while applying principles of management. The major aspects are organizational structure, health workforce development, and health planning