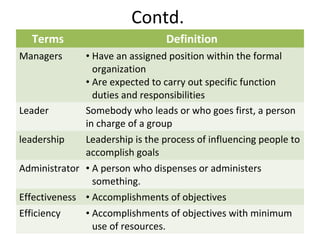
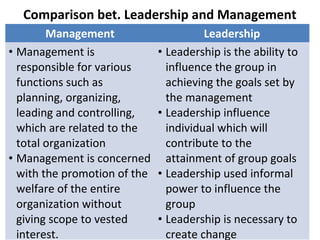
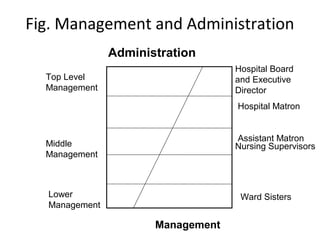
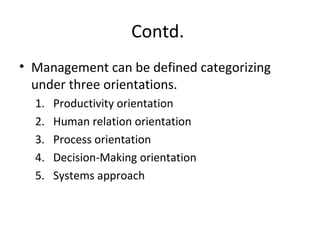
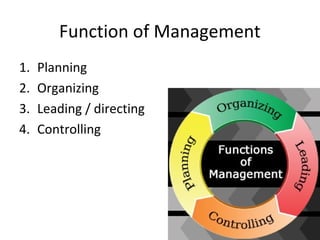
This document defines key terms related to management concepts such as organization, management, leadership, administration, and effectiveness. It compares leadership to management and administration to management. Several definitions of management are provided that focus on productivity, human relations, process orientation, and decision making. Henry Fayol's 14 principles of management are also outlined, including division of work, authority and responsibility, discipline, unity of command, and subordination of individual interests. The document provides an overview of foundational management concepts, principles, and terminology.