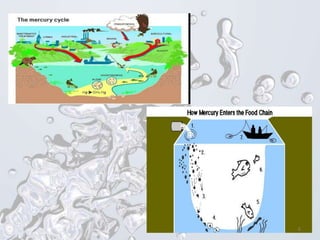
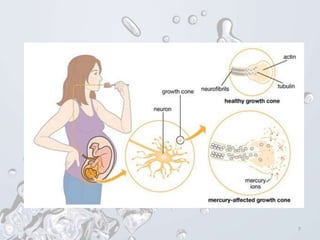
The document provides a history of mercury use and discusses the Minamata Convention. It describes how mercury has been used as a pigment and medicine for thousands of years. It then summarizes the Minamata Bay mercury poisoning incident in Japan in the 1950s-60s caused by industrial pollution. The rest of the document outlines the key points of the Minamata Convention, including banning mercury in various products and processes by certain dates, with exceptions for some traditional uses. It also notes industry opposition in Japan to restrictions on mercury trade.