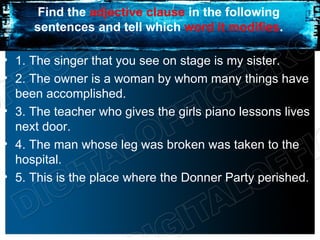
This document discusses adjective clauses. It defines an adjective clause as a dependent clause that is used to modify a noun or pronoun. Adjective clauses begin with a relative pronoun like who, whose, whom, which, or that, or a subordinate conjunction like when, where, or since. Examples are provided to illustrate how adjective clauses modify specific nouns or pronouns in sentences. The document also discusses combining sentences using adjective clauses and properly placing adjective clauses near the words they modify.