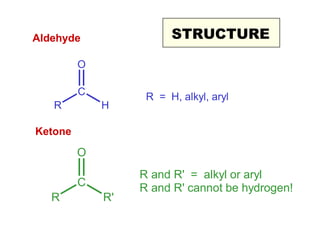
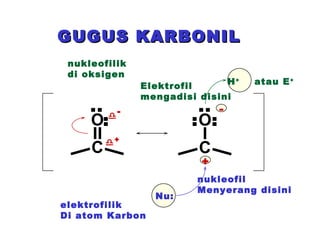
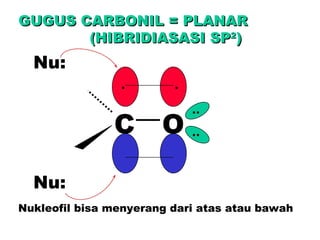
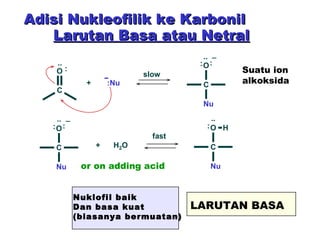
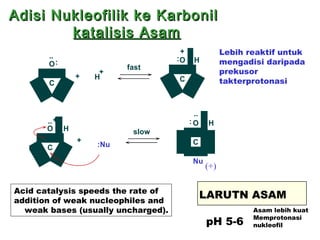
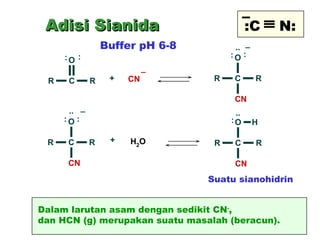
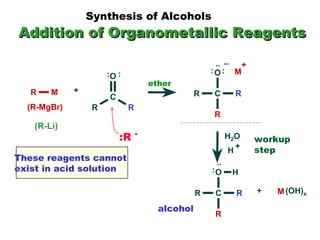
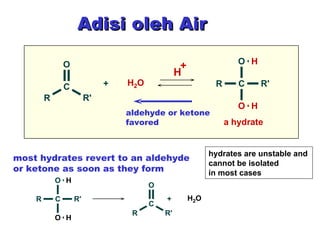
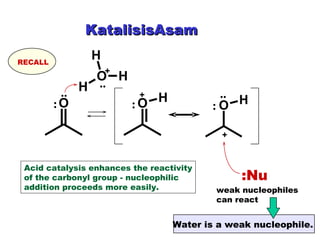
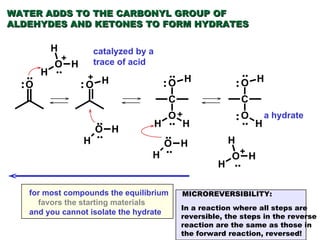
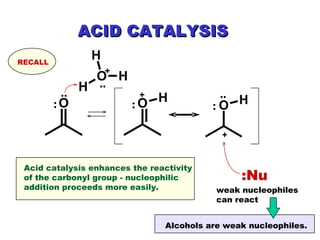
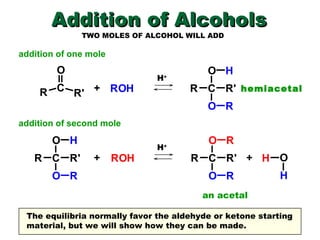
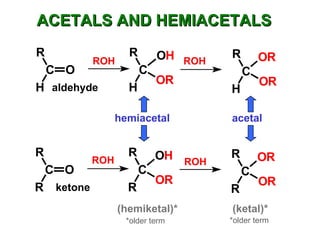
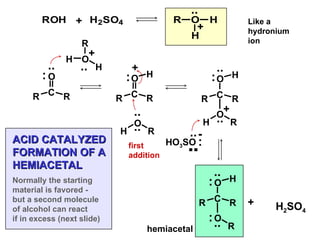
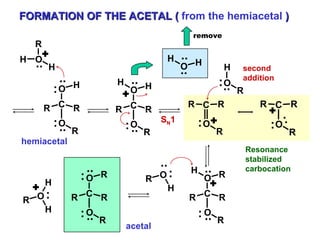
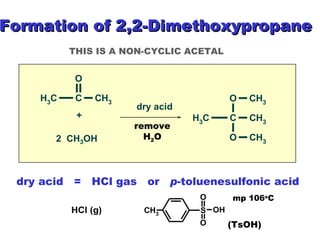
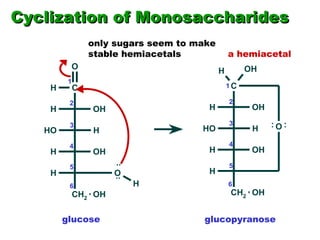
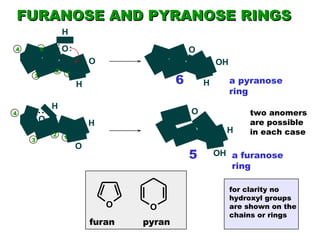
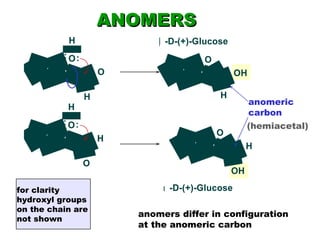
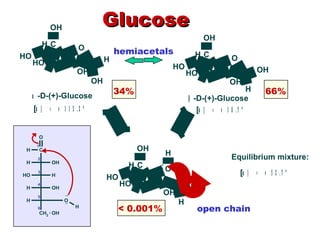
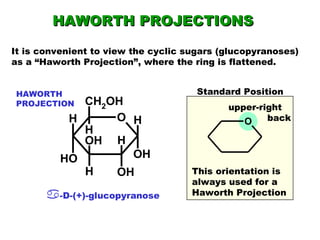
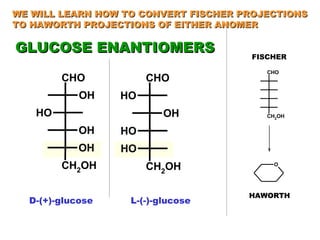
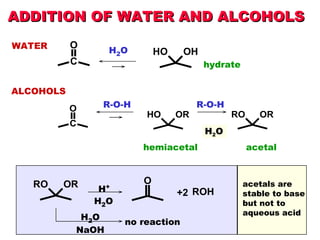
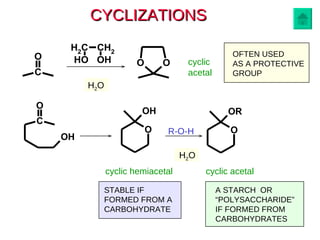
This document discusses nucleophilic addition reactions to carbonyl groups such as aldehydes and ketones. It explains that the carbonyl carbon is electrophilic and susceptible to attack by nucleophiles such as water, alcohols, cyanide, and organometallic reagents. The addition reactions can proceed through acid or base catalysis. Products like hydrates, hemiacetals, and acetals can form depending on the nucleophile and conditions. Carbohydrates exist as cyclic hemiacetals called pyranoses and furanoses, which have alpha and beta anomers.