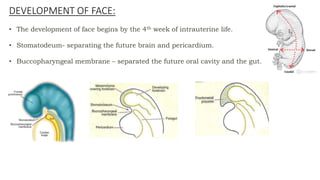
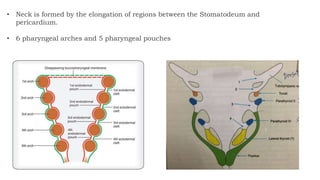
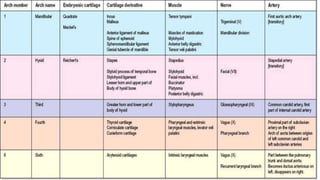
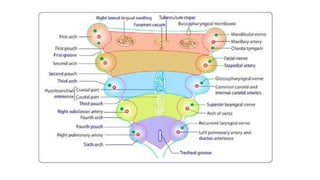
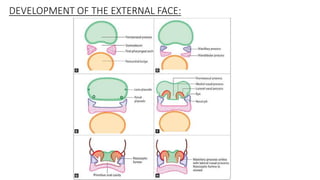
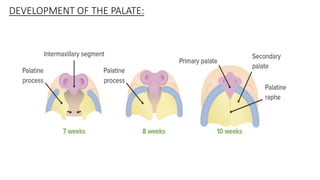
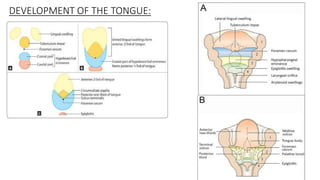
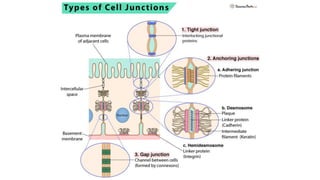
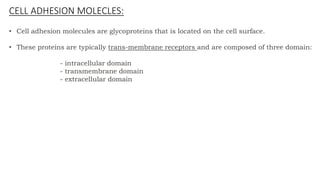
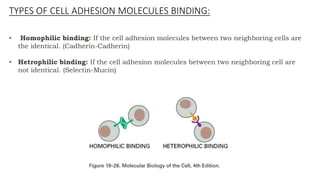
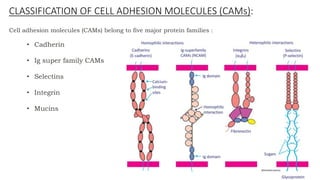
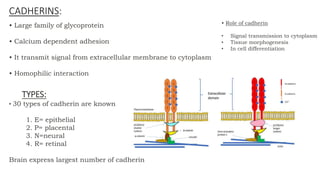
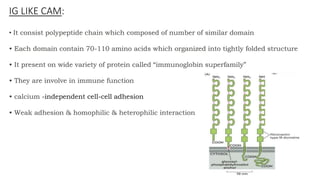
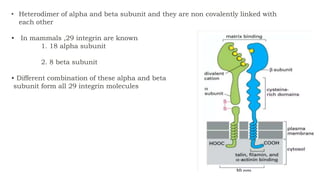
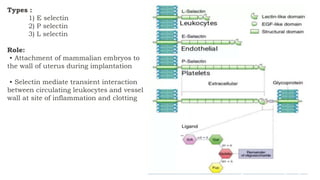
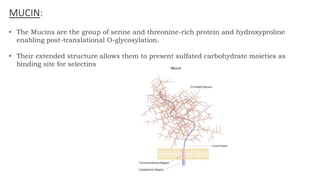
The document discusses cell adhesion molecules which are glycoproteins located on cell surfaces that mediate cell-cell binding. There are five major classes of cell adhesion molecules: cadherins, immunoglobulin superfamily CAMs, selectins, integrins, and mucins. Cadherins are calcium-dependent and mediate homophilic binding between identical cells through intracellular signal transmission. Integrins are heterodimers that bind cells to the extracellular matrix and transmit outside-in and inside-out signals. Selectins mediate transient interactions between cells through calcium-dependent binding of their extracellular domains to sugar moieties on other cells.