Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) are essential glycoproteins that facilitate cell interactions and tissue formation in the body. They play crucial roles in various biological processes, including inflammation, cancer metastasis, and wound healing, with different types categorized into families such as cadherin, integrin, selectin, and the immunoglobulin superfamily. Abnormal functioning of these molecules can lead to diseases like breast cancer, leukocyte adhesion deficiency, and other epithelial cancers.



![CLASSIFICATION
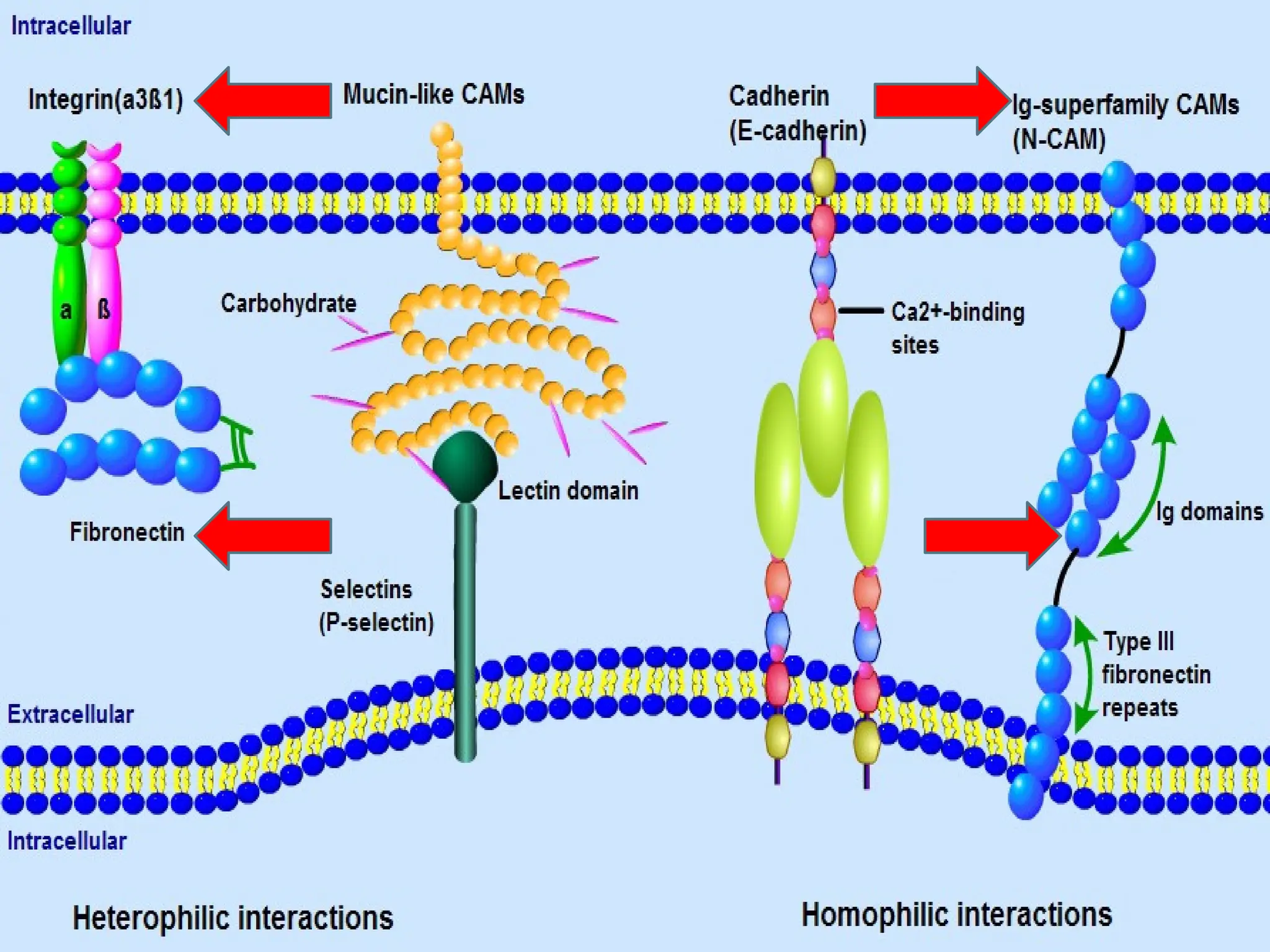
Most of CAM belong to four protein family:
Cadherin
Integrin
Selectin
Ig Super Family [IgS]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/celladhesionmolecules-1-241023133333-36774b1f/75/CELL-ADHESION-MOLECULES-1-pptx-5-2048.jpg)






![Ig Super Family [IgS]
They are calcium independent CAM.
They exhibit both homophilic and heterophilic
adhesion.
Involved in recognition, binding, adhesion process.
They possess an extracellular region known as
immunoglobulin domain.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/celladhesionmolecules-1-241023133333-36774b1f/75/CELL-ADHESION-MOLECULES-1-pptx-12-2048.jpg)







![SELECTIN
They are divalent cation dependent CAM
They are carbohydrate binding proteins.
Eg: E – selectin [endothelial].
L – selectin [leukocyte].
P – selectin [platelet].
Play major role in many host defense mechanism.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/celladhesionmolecules-1-241023133333-36774b1f/75/CELL-ADHESION-MOLECULES-1-pptx-20-2048.jpg)








![ Integrin - cytoskeleton complex function as
activated receptors and trigger number of signal
transduction pathway including MAP kinase, PKC,
PI3K pathway which are also activated by growth
factors.
Integrin and growth factor receptor ineract [cross –
talk] to transmit environmental signals to the cell
that regulate proliferation, apoptosis,
differentiation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/celladhesionmolecules-1-241023133333-36774b1f/75/CELL-ADHESION-MOLECULES-1-pptx-29-2048.jpg)

![ Clustering of integrin on the cell surface also
increases the likelihood of effective binding and
plays a role in leukocyte migration.
Lack of this role of integrin leads to LEUKOCYTE
ADHESION DEFICIENCY [LAD type 1] AR.
Characterized by recurrent bacterial infection and
impaired wound healing.
Similar deficiency with impaired expression of
selection is termed as [LAD type 2].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/celladhesionmolecules-1-241023133333-36774b1f/75/CELL-ADHESION-MOLECULES-1-pptx-31-2048.jpg)
![DISEASES RELATED TO INTEGRIN DEFICIENCY
There are three inherited autosomal recessive
disorders associated with integrin.
1.mutation in alpha 2 b and beta 3 subunit =
GLANZMANN’S THROMBASTHENIA [ platelet
dysfunction and bleeding disorder]
2.point mutation and gene deletion in beta 2 =
LAD.
3.mutation in alpha 6 and beta 4 = JUNCTIONAL
EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA skin blistering.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/celladhesionmolecules-1-241023133333-36774b1f/75/CELL-ADHESION-MOLECULES-1-pptx-32-2048.jpg)

















