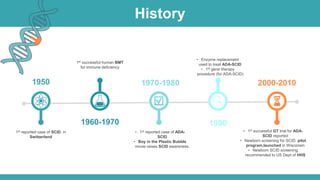
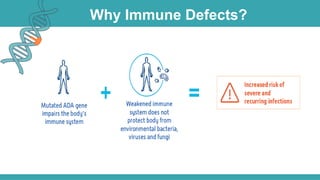
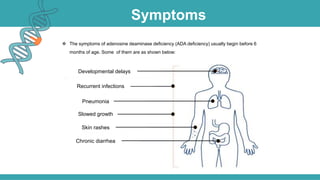
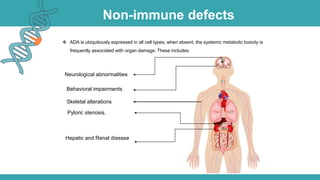
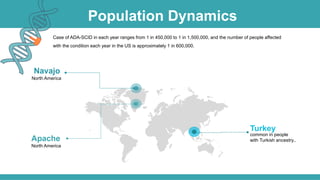
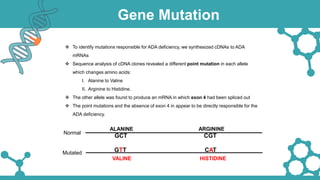
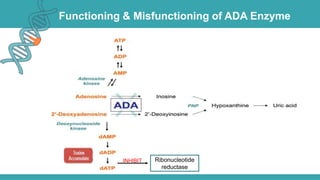
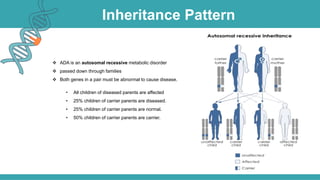
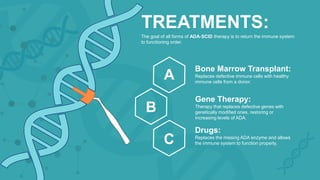
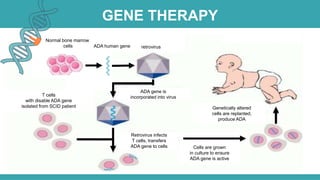
Adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency is a rare, autosomal recessive immunodeficiency disorder first identified in 1972, characterized by a lack of the ADA enzyme crucial for immune system function. Symptoms typically emerge before six months of age, including developmental delays and recurrent infections, with diagnosis facilitated through genetic testing and newborn screening. Treatment options include bone marrow transplantation and gene therapy, with high success rates in restoring immune function.