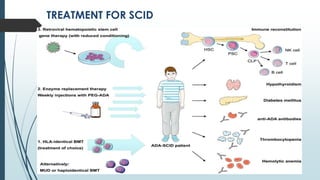
Severe combined immunodeficiency syndrome (SCID) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the absence of both T cells and B cells. This leaves the body unable to fight infections and affected infants often develop severe, life-threatening infections within the first year of life if untreated. There are 13 known genetic causes of SCID. The main treatment is a bone marrow transplant from a matched donor, which can cure the condition if performed early in life. Gene therapy is also being explored as a potential treatment.