This document summarizes key concepts regarding oncogenes:
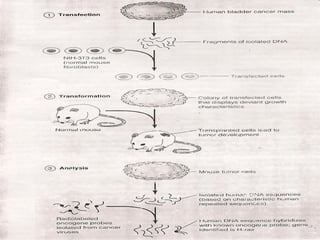
1. Oncogenes are genes that can trigger cancer development through viral insertion or mutation of normal cellular genes.
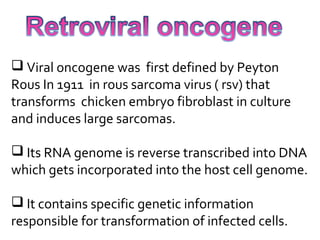
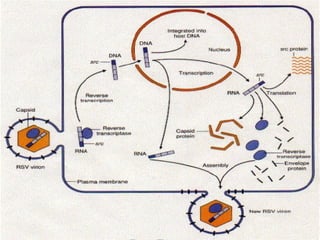
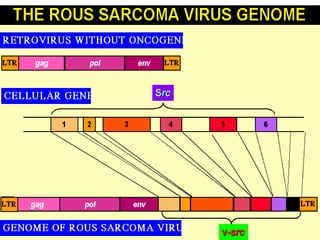
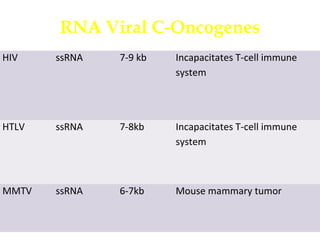
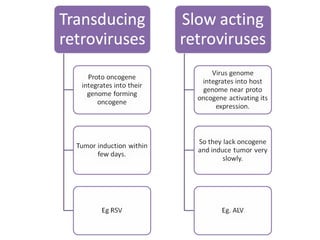
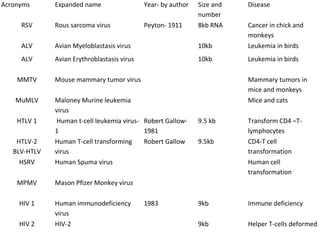
2. Early retroviruses like RSV were found to contain viral oncogenes like v-src that caused cancer upon infection.
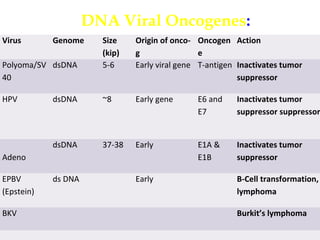
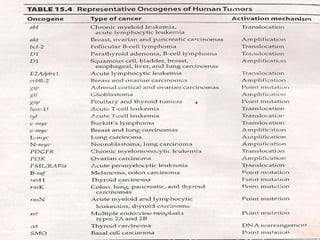
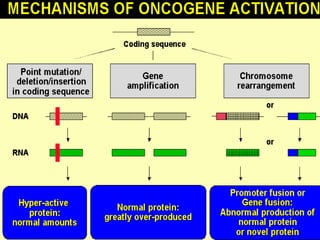
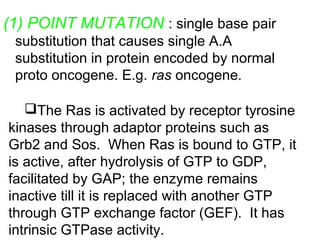
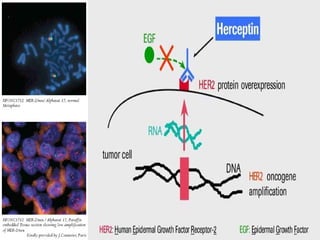
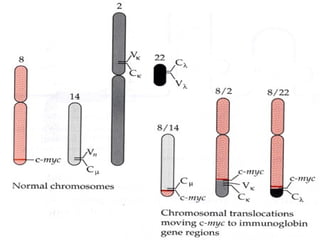
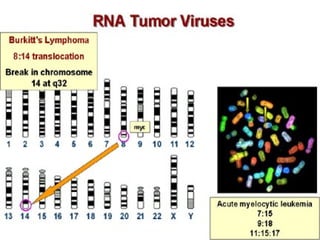
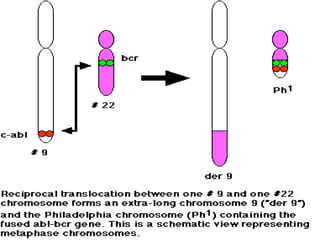
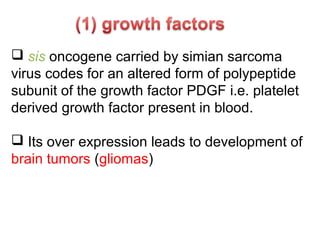
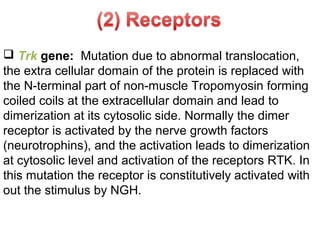
3. Normal cellular genes called proto-oncogenes were later discovered that are homologous to viral oncogenes and can become activated by mutations to drive cancer. Common mutations include point mutations, gene amplifications, and chromosomal translocations.