Embed presentation
Downloaded 174 times






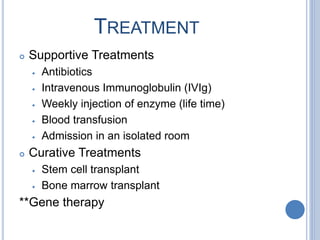

Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), also known as "Bubble Boy Disease", is a primary immunodeficiency caused by mutations in several genes resulting in the lack of T-cells and sometimes B-cells and NK cells as well. It was widely known due to David Vetter who lived in a germ-free plastic bubble for 12 years. SCID is diagnosed through newborn screening, blood tests, and showing a lack of white blood cells in newborns. Treatments include supportive therapies like antibiotics and immunoglobulin injections as well as curative therapies such as stem cell transplant or gene therapy.







