This document discusses types of network addresses and internet address classes. It contains the following key points:
- There are 32-bit global internet addresses that include network and host identifiers in dotted decimal notation like 192.228.17.57.
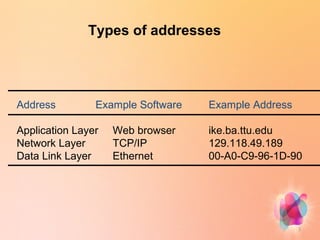
- Internet addresses have application, network, and data link layers with examples provided.
- InterNIC is responsible for network layer IP addresses and application layer domain names.
- There are five classes of internet addresses - Classes A, B, and C are available to organizations, while Classes D and E are reserved for special purposes.
- Class A addresses start with 1-126 and allow for 16 million addresses. Class B starts with 128-191 allowing 65