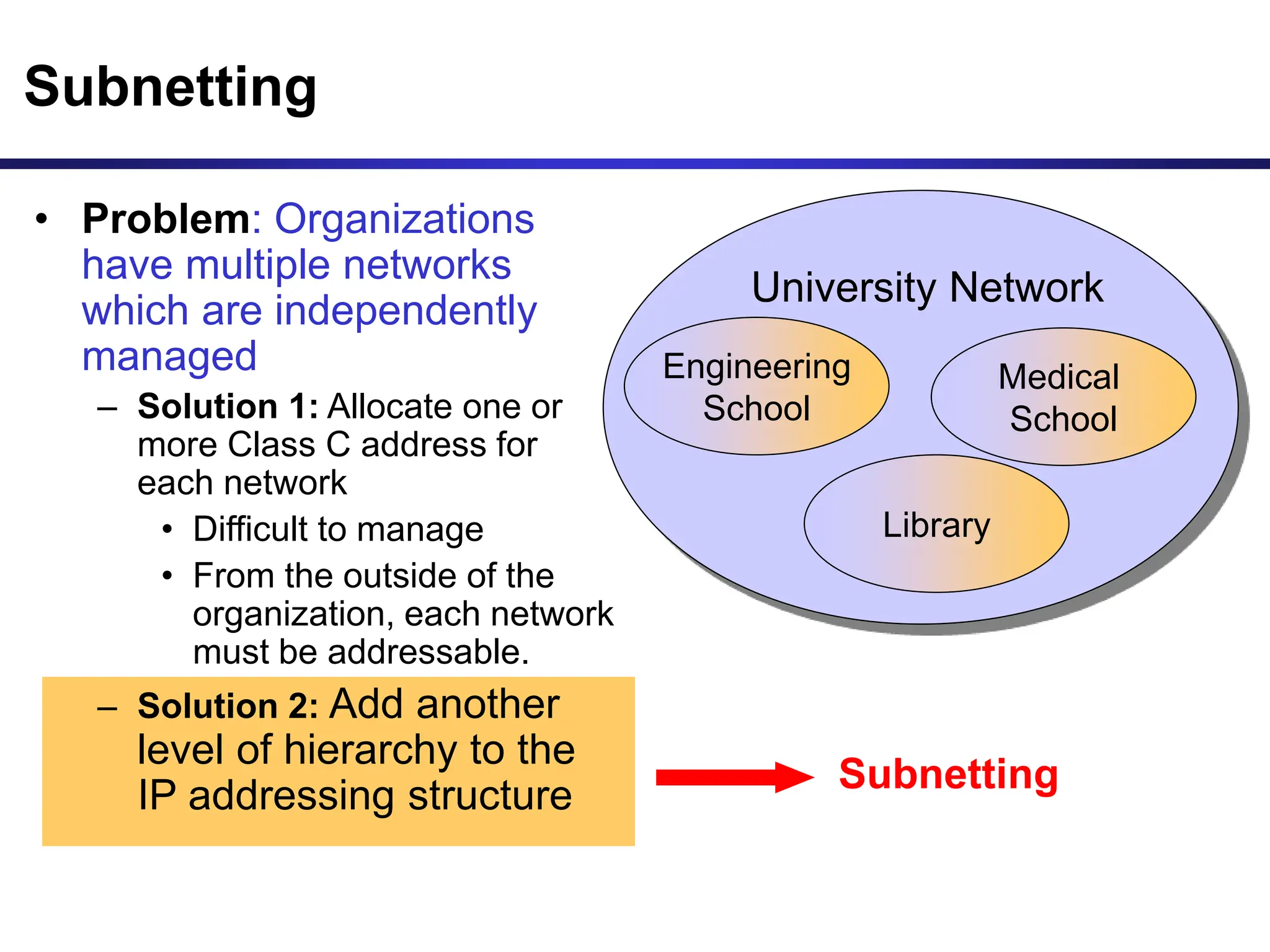
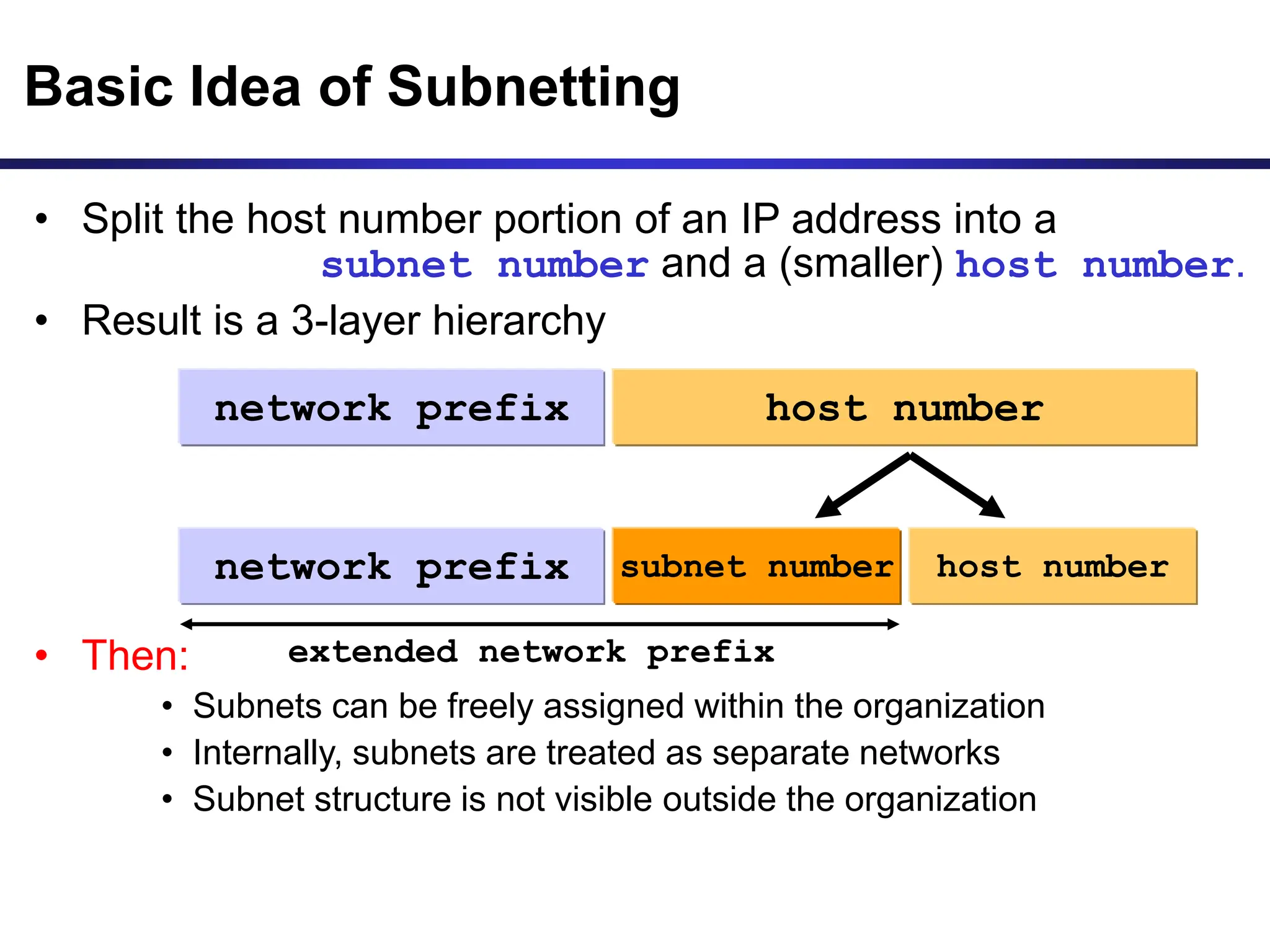
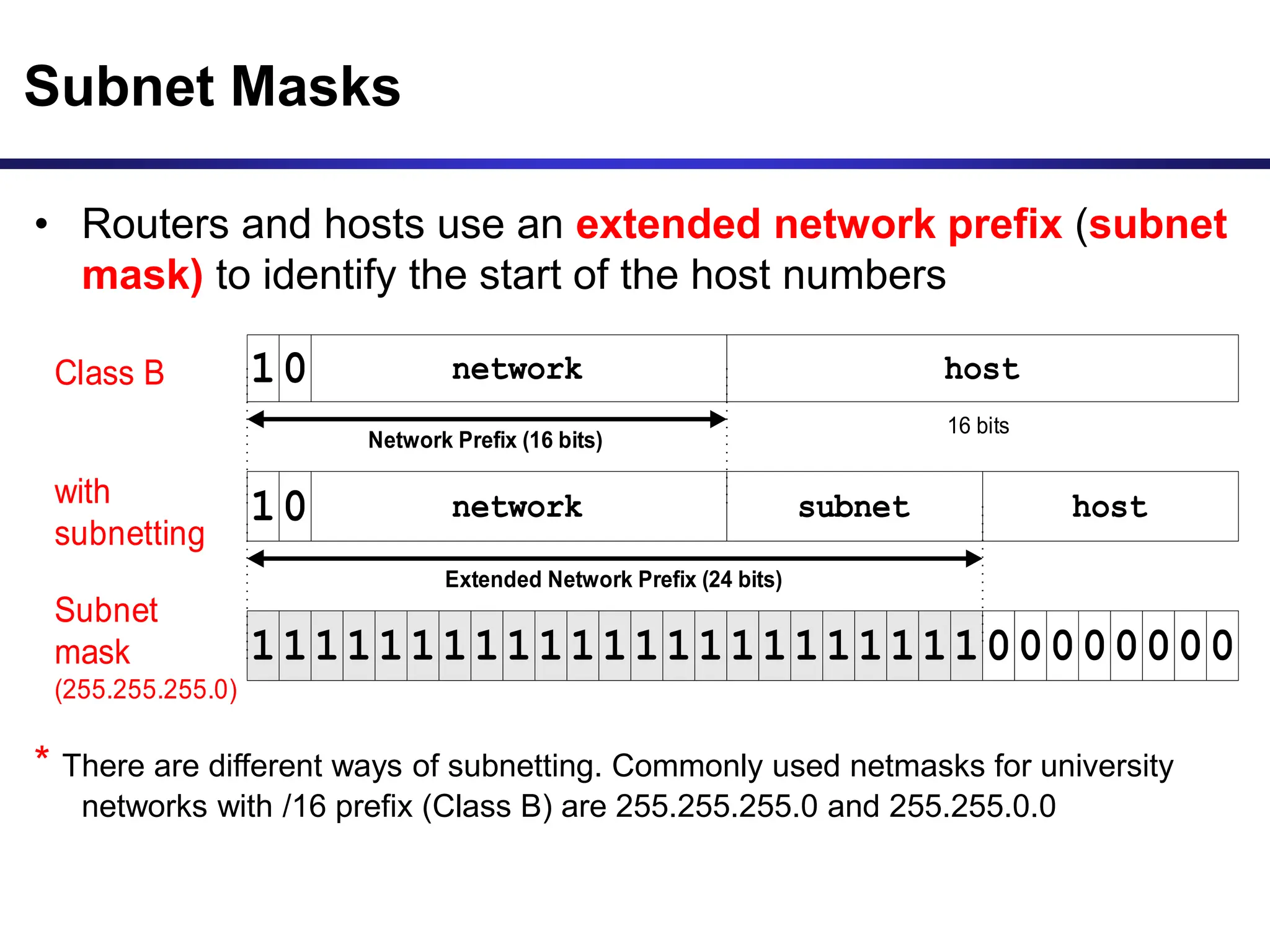
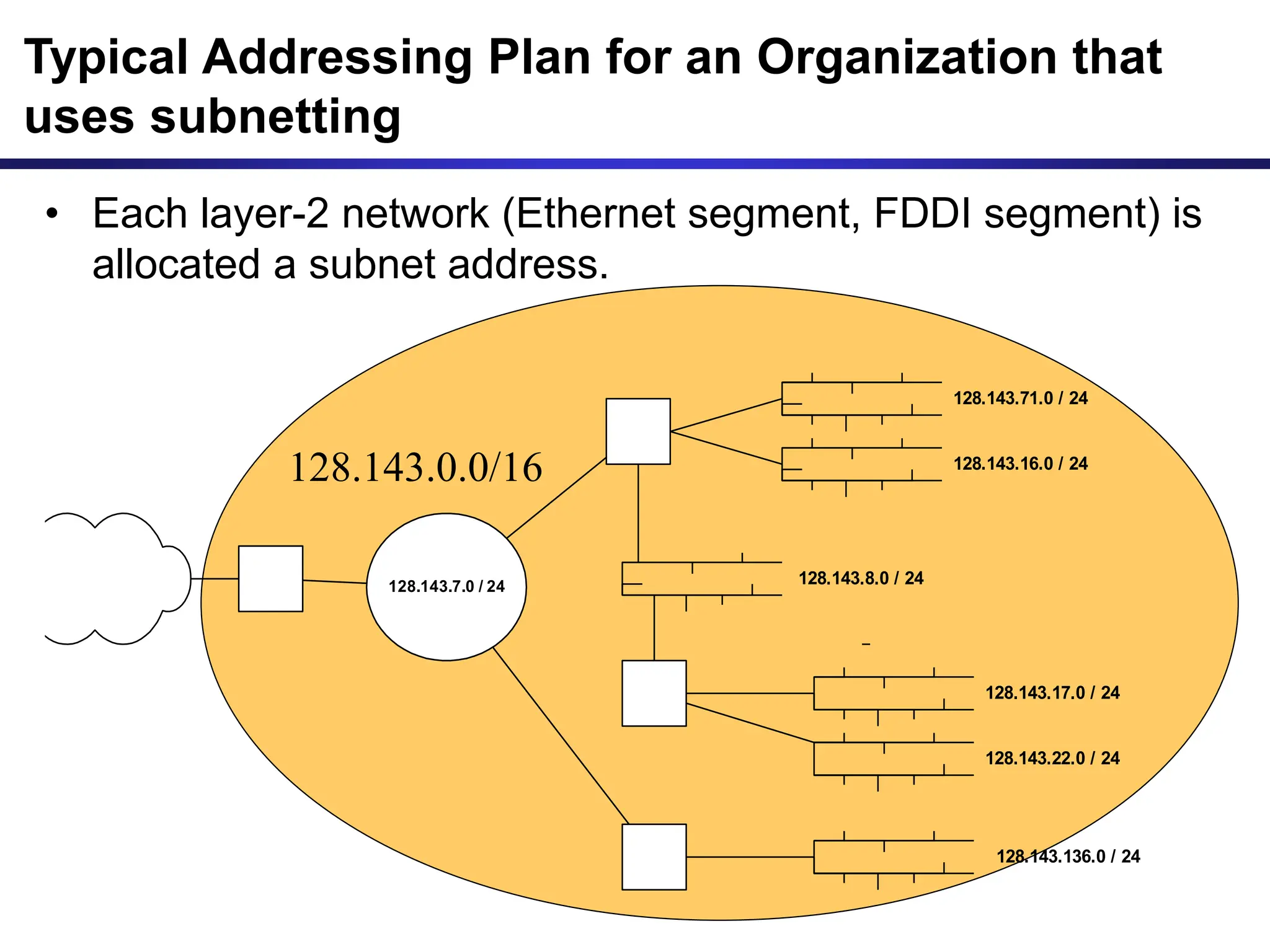
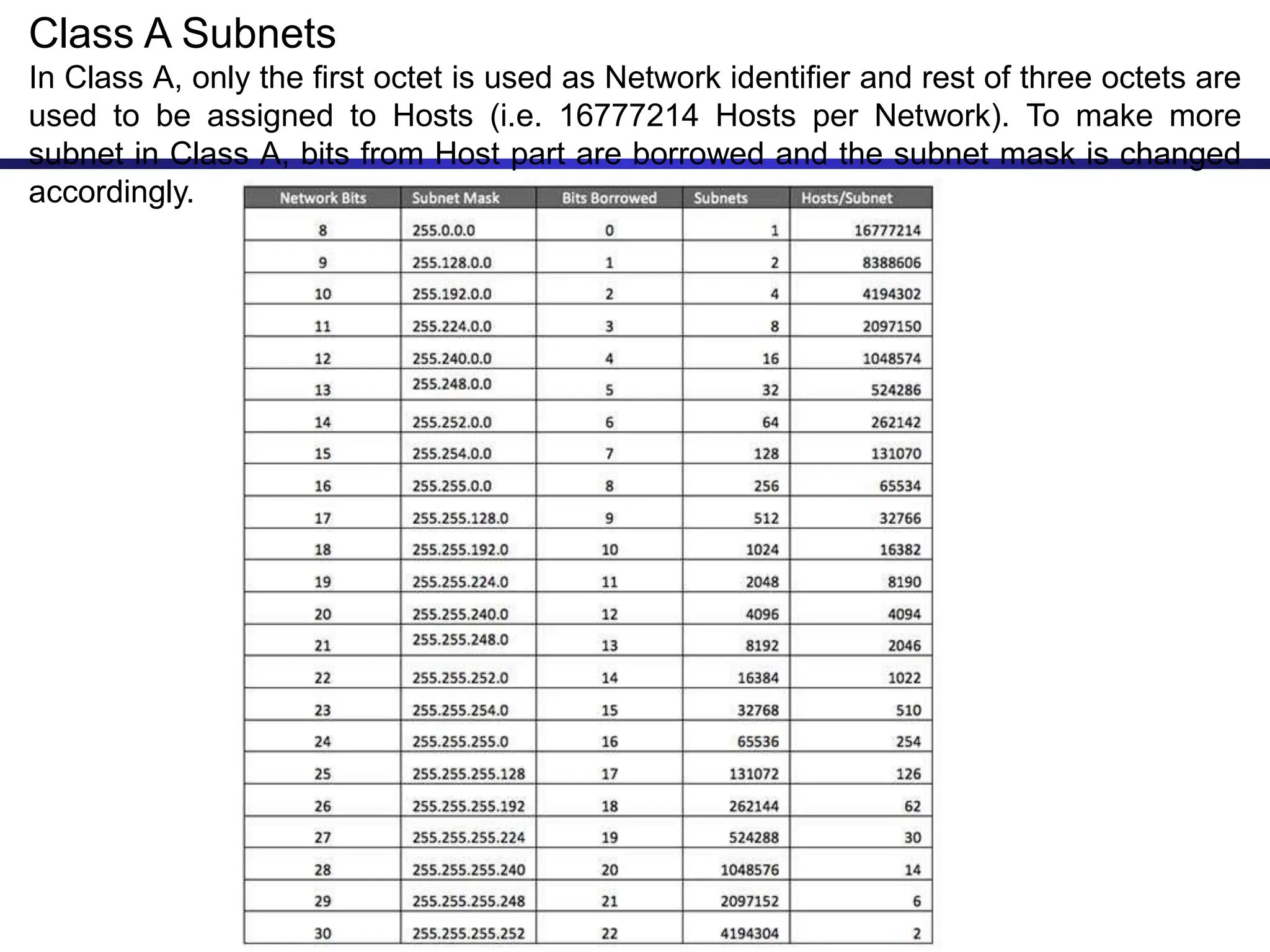
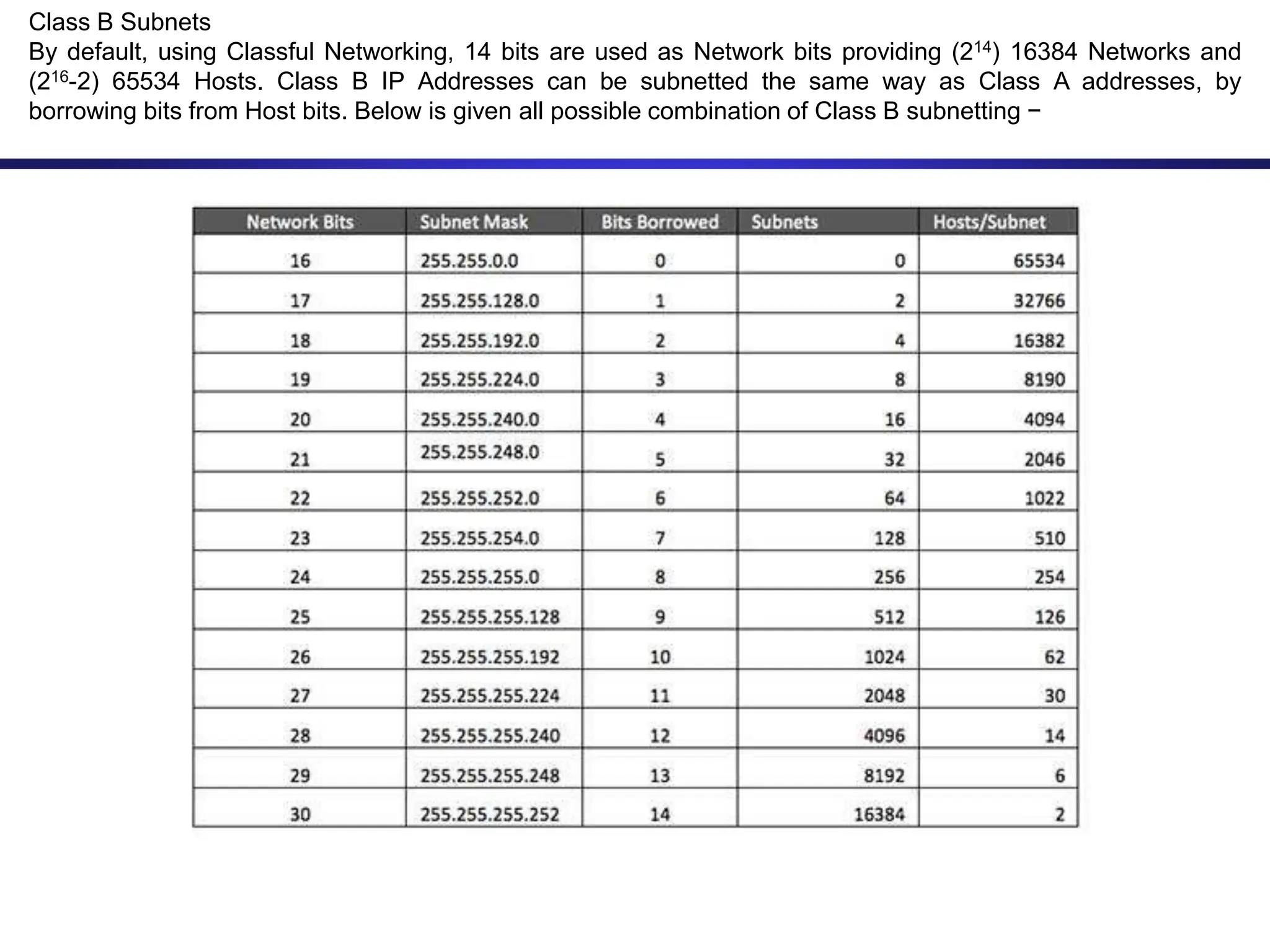
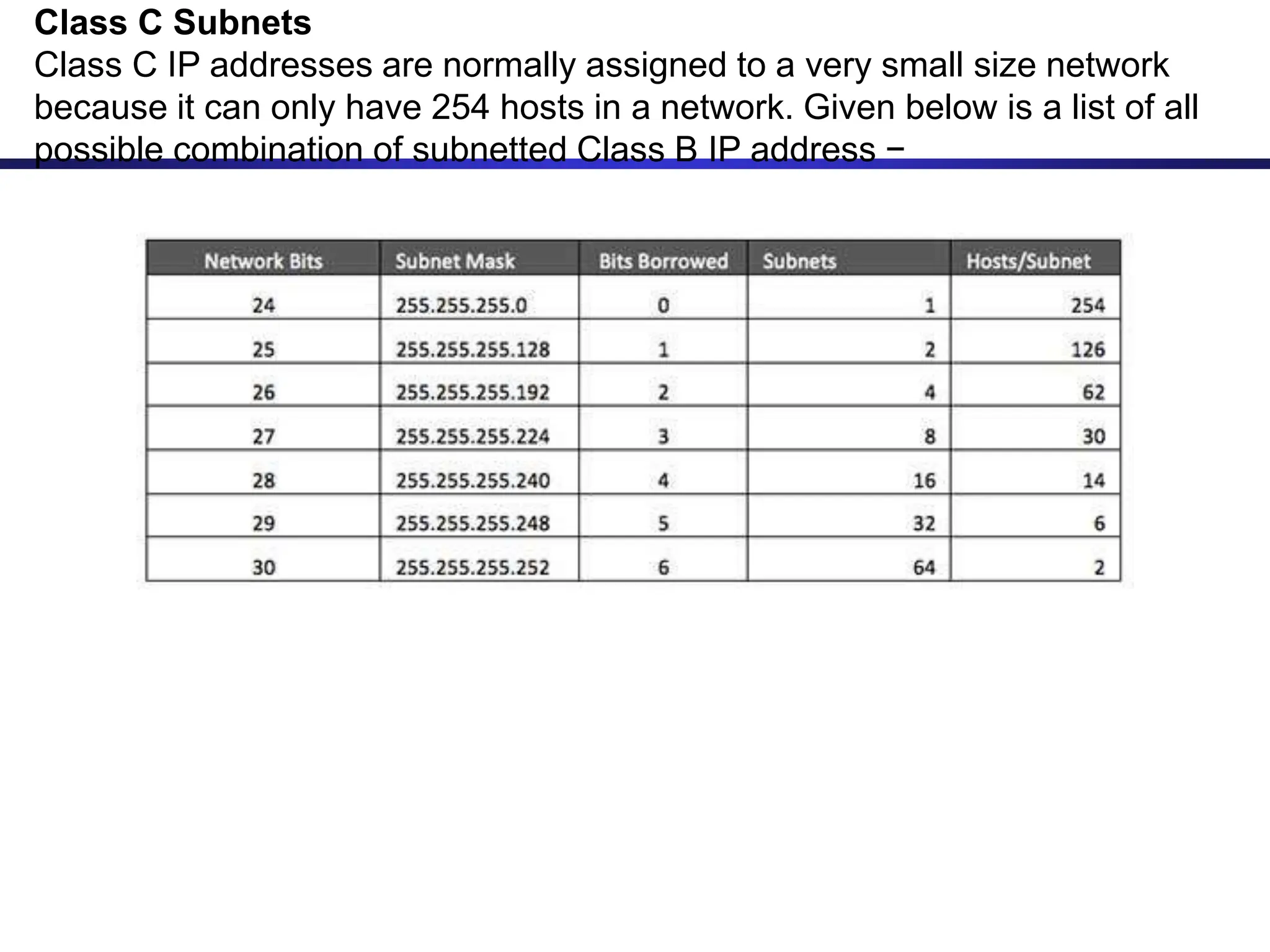
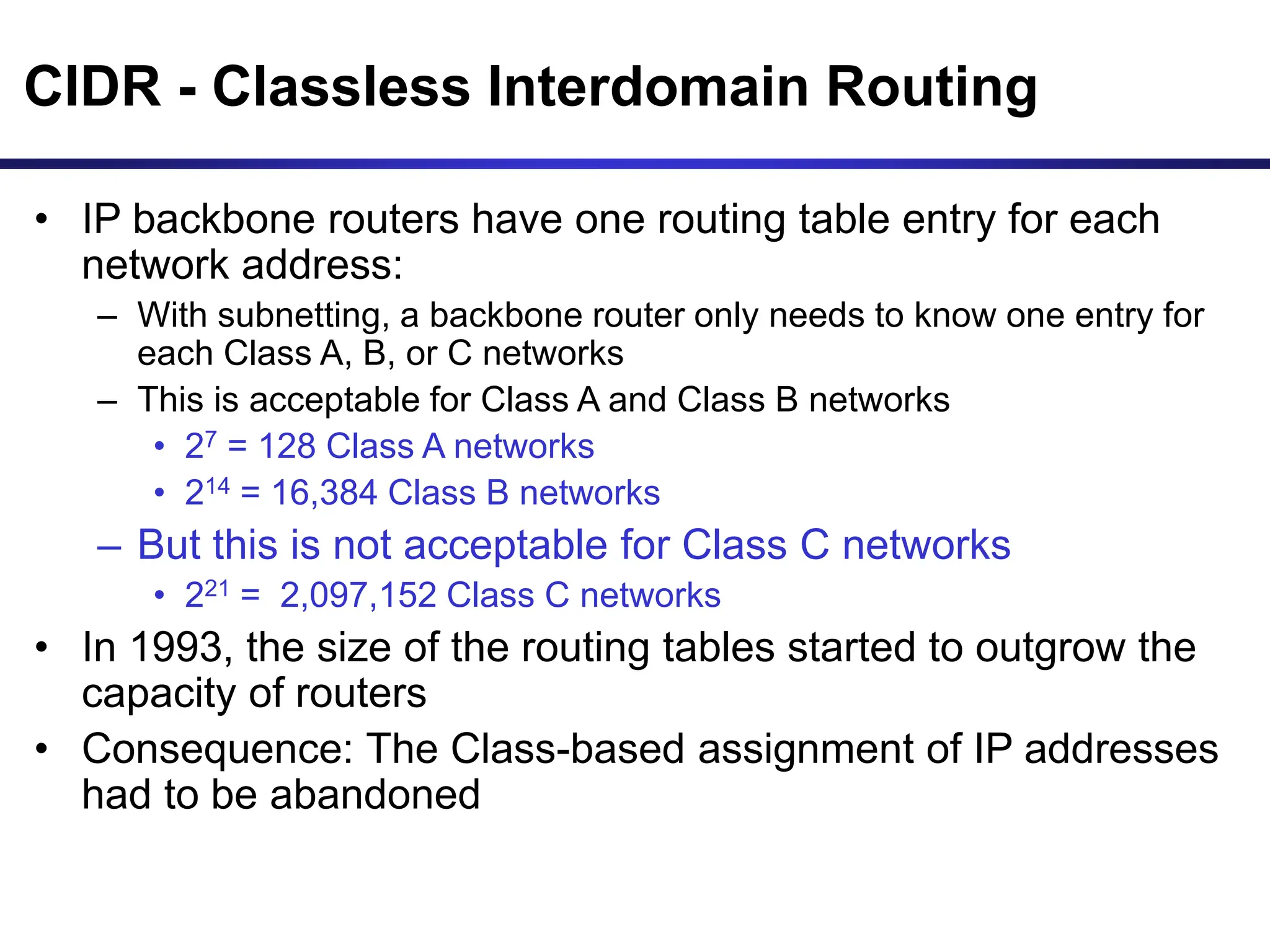
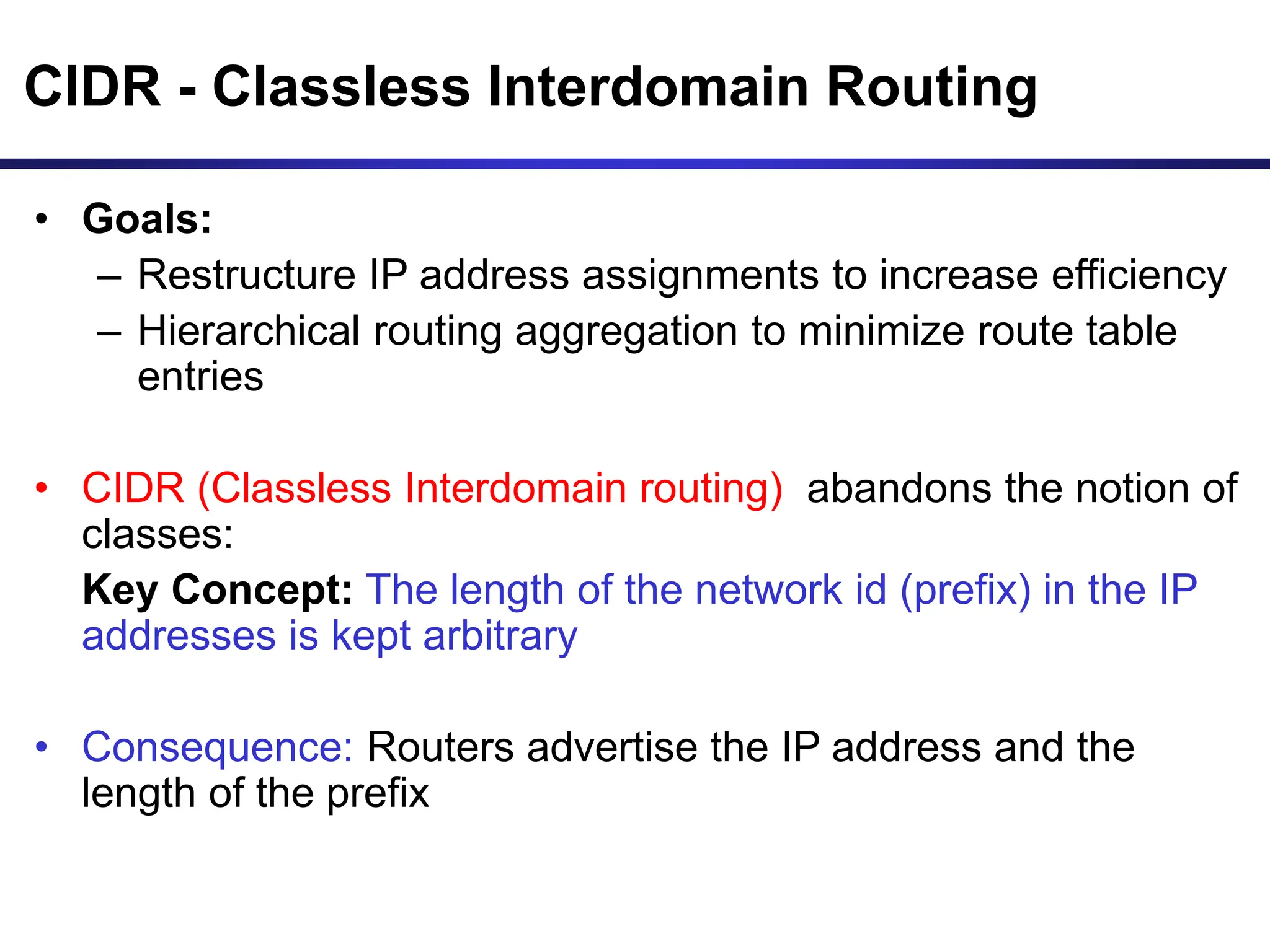
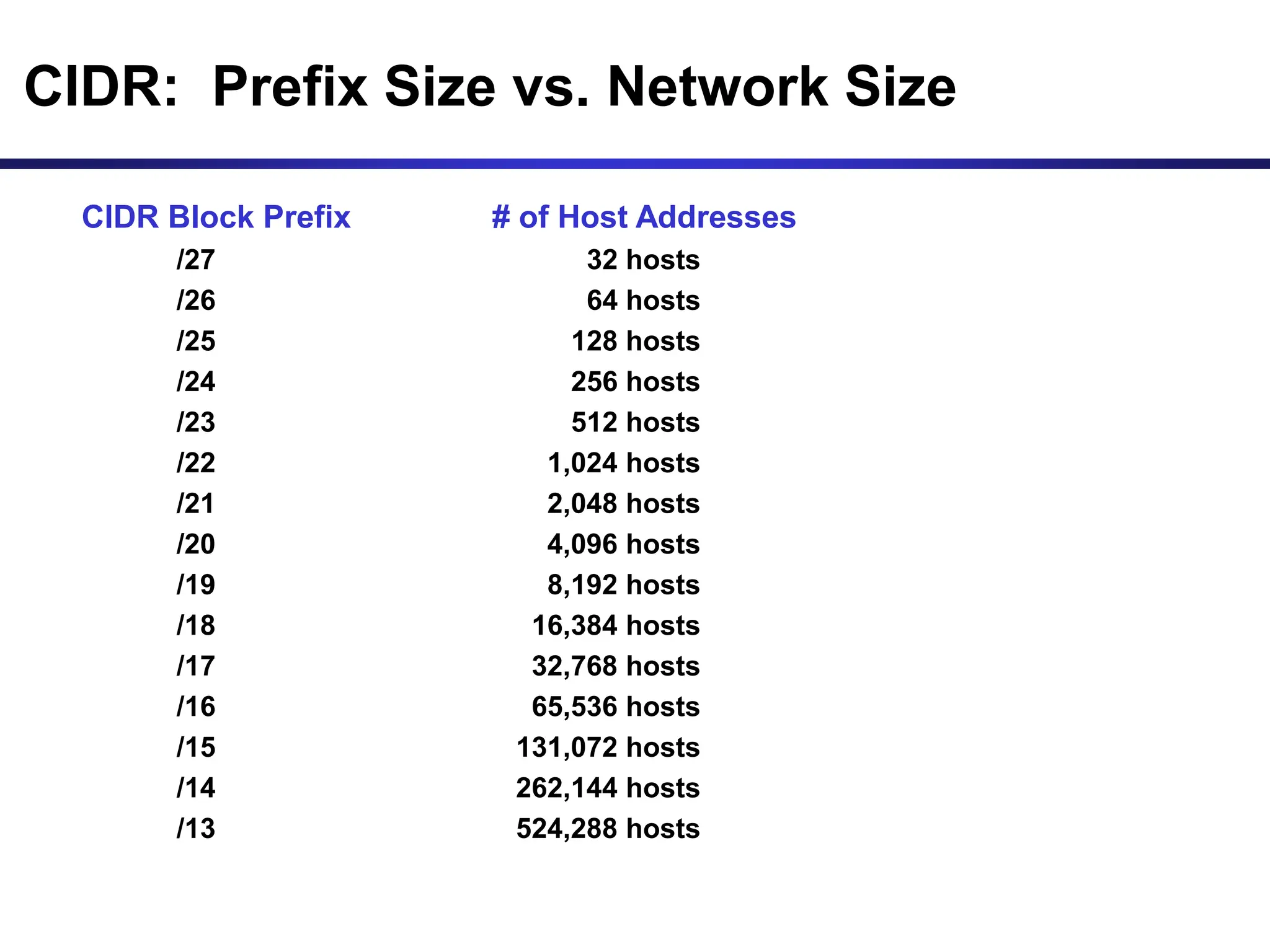
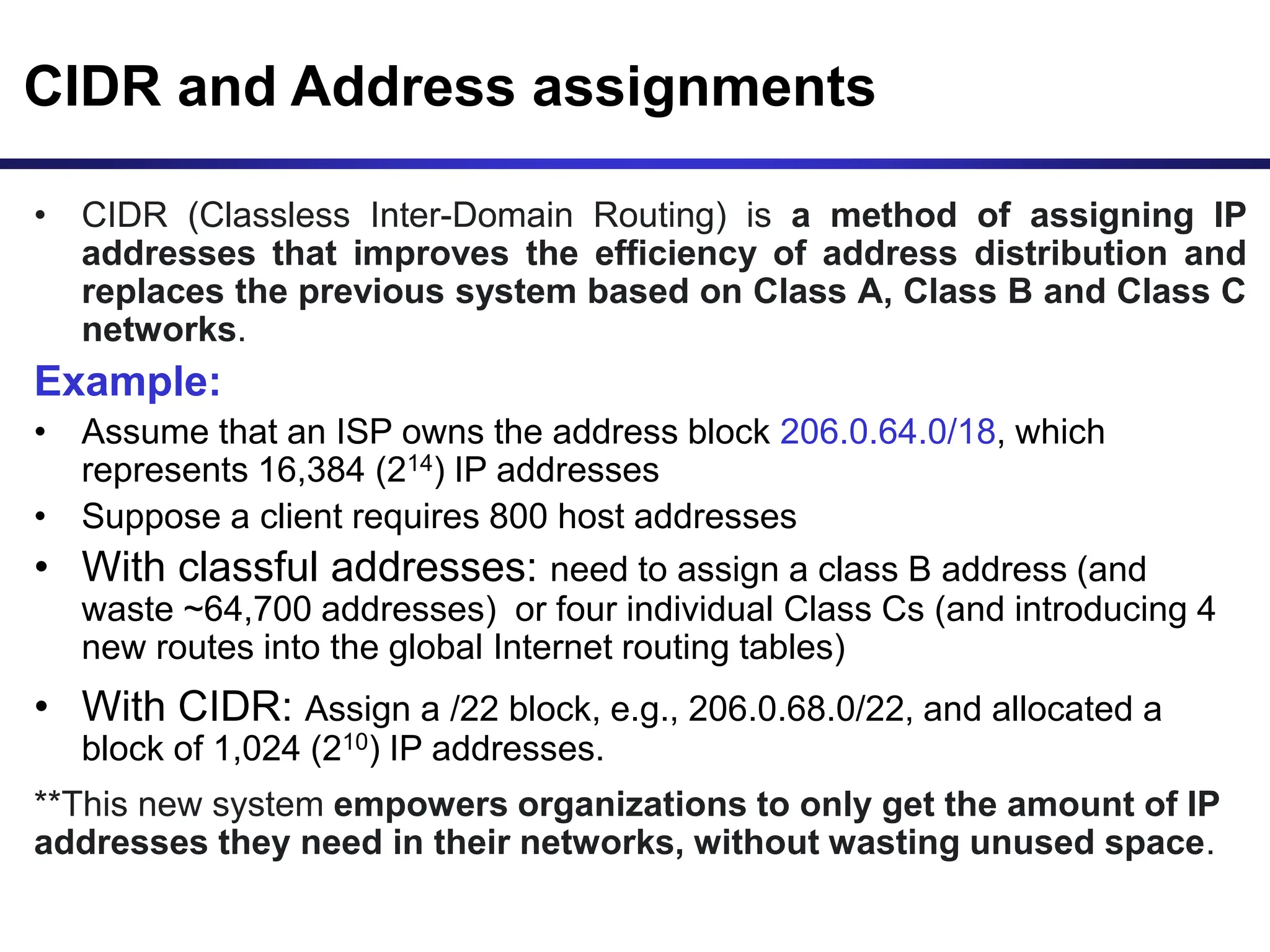
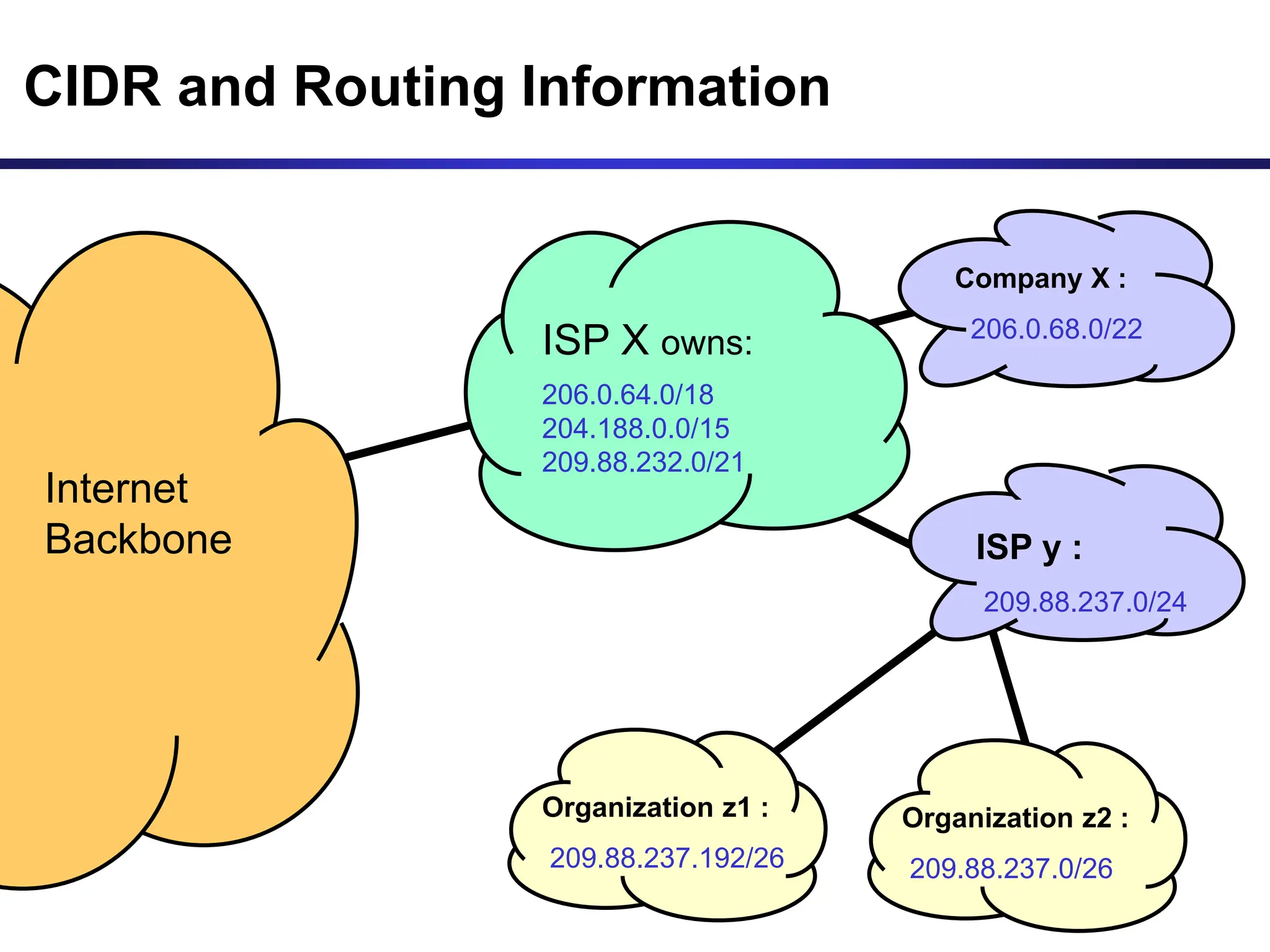
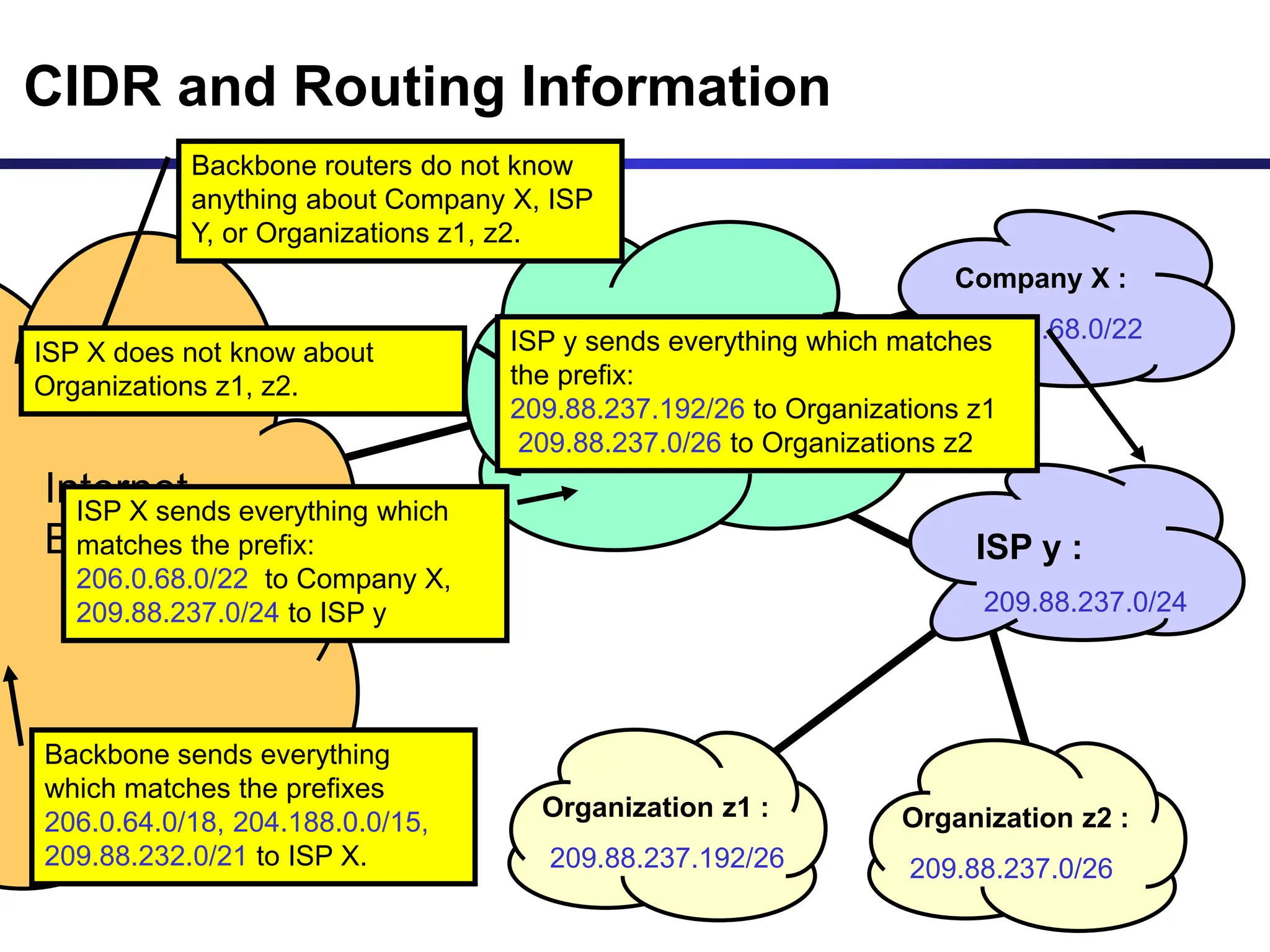
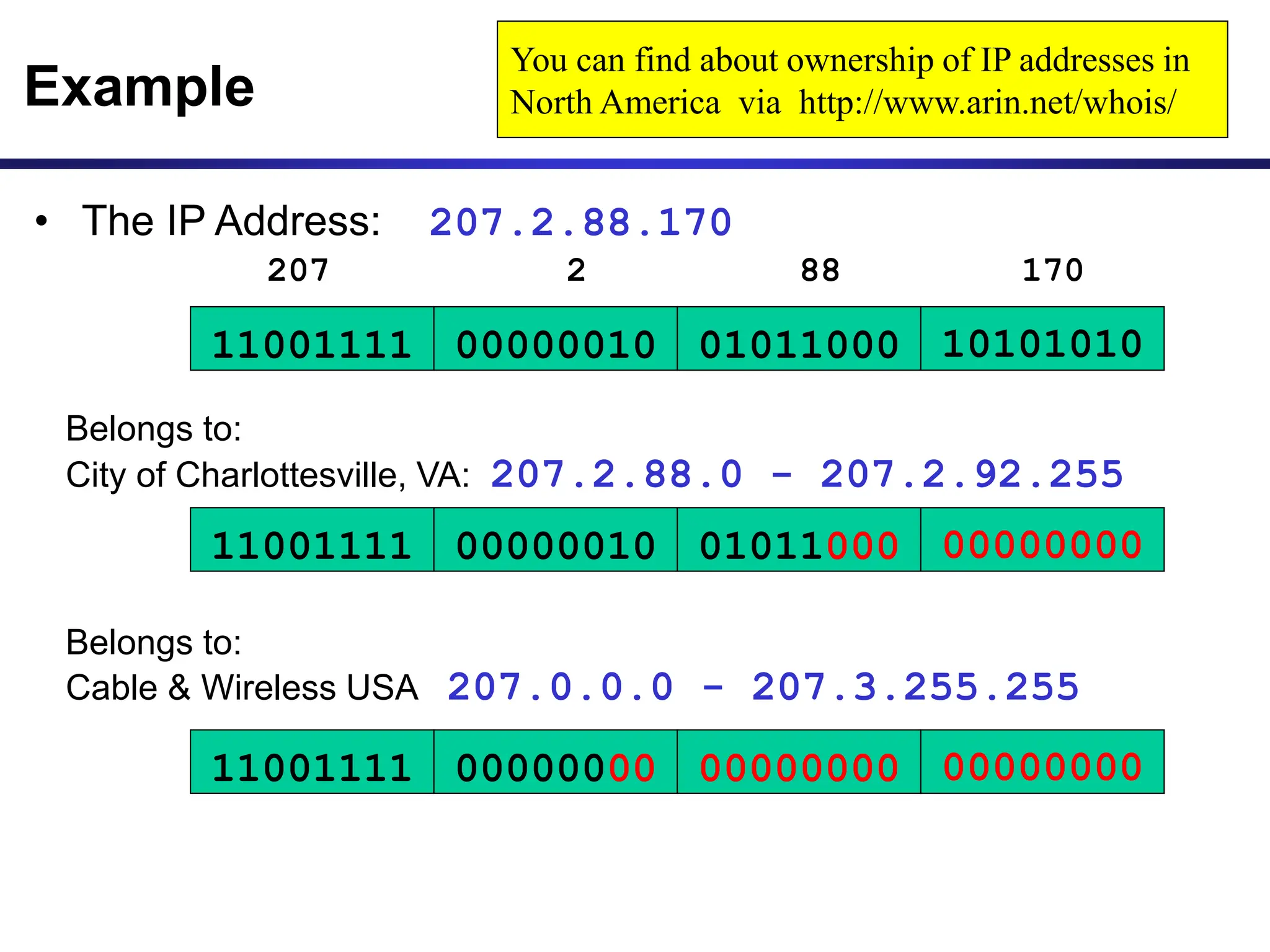
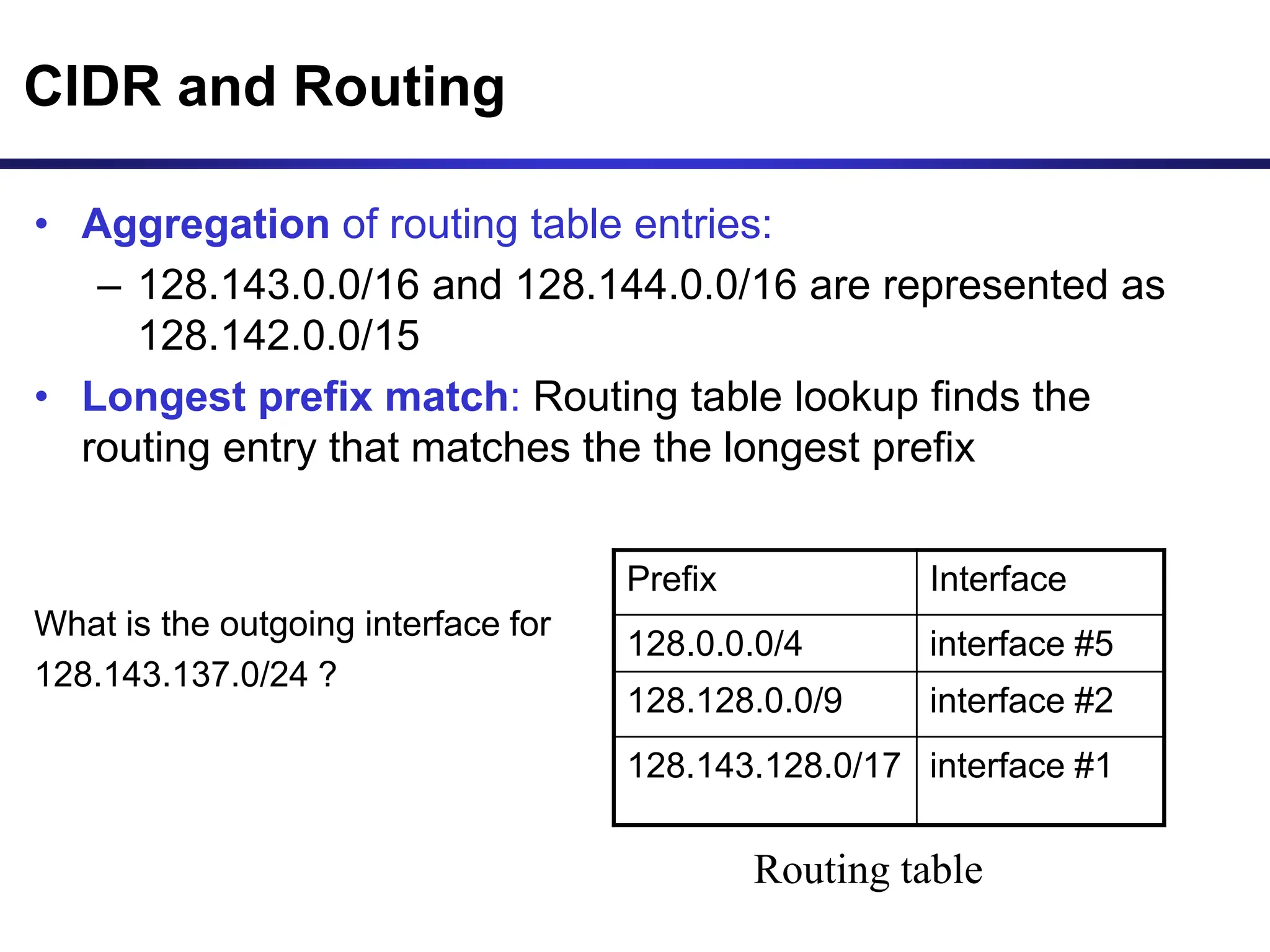
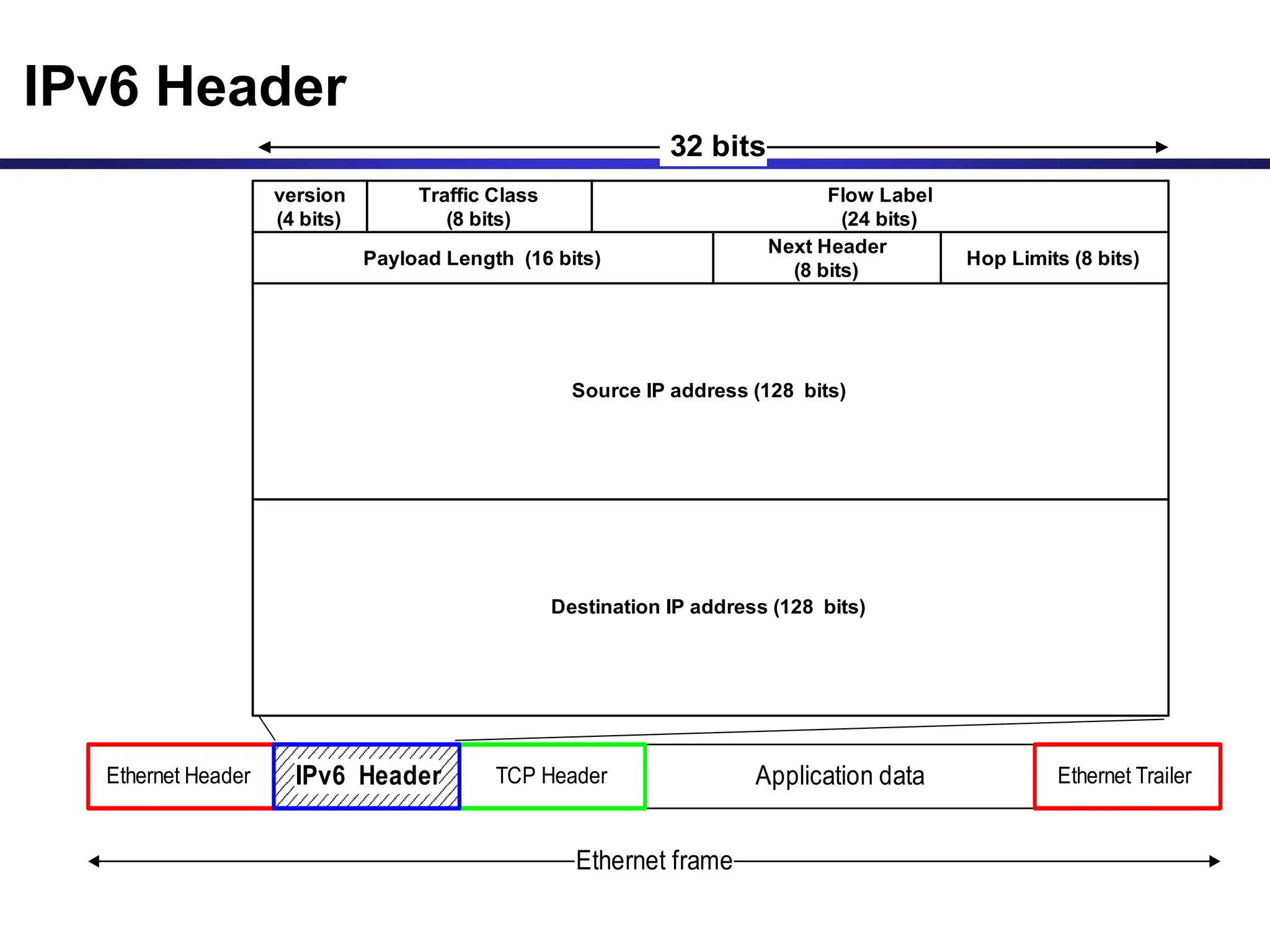
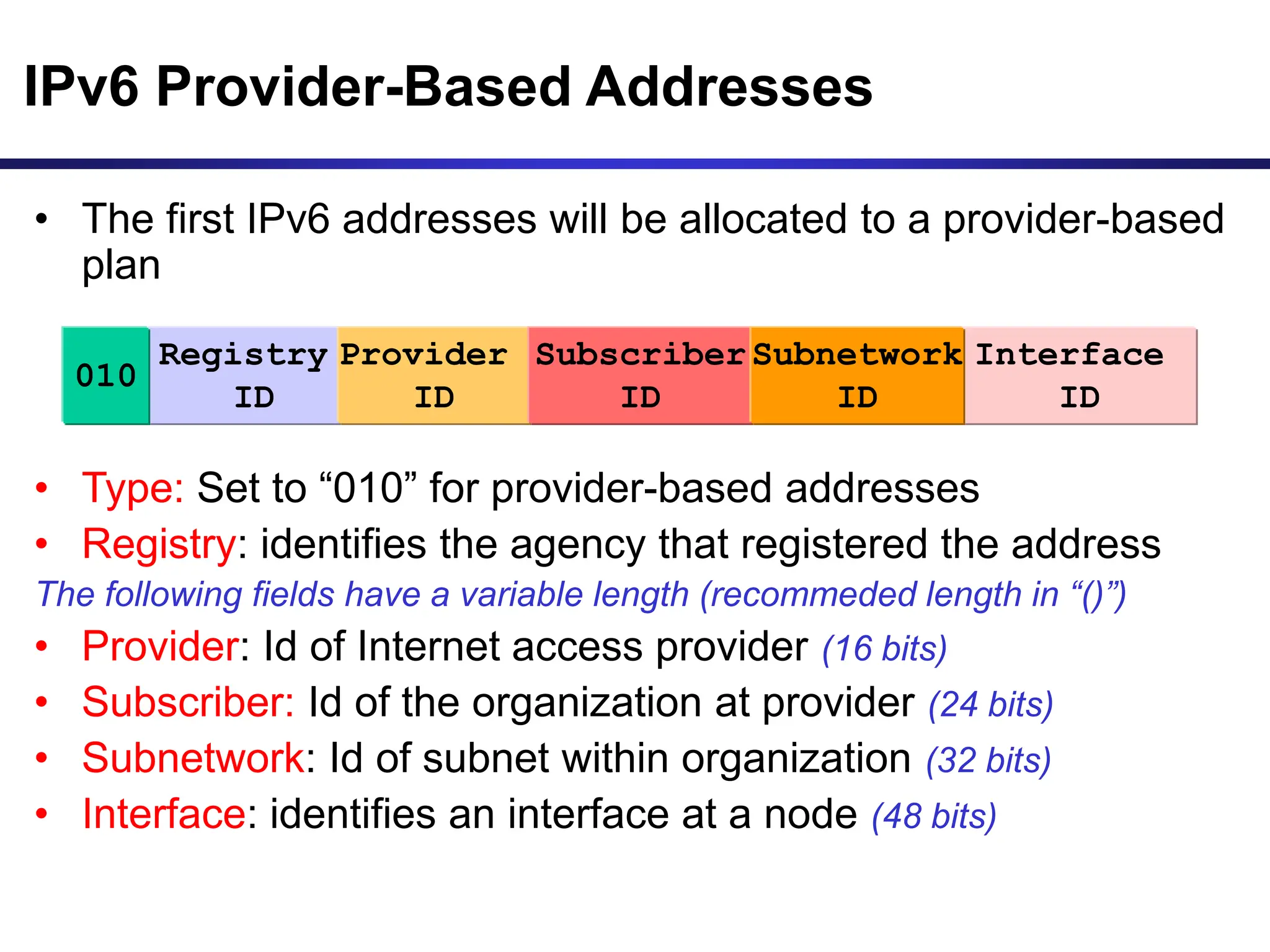
The document discusses IP addressing and related concepts. It covers the structure of IP addresses, classful IP addresses and their limitations, subnetting to add hierarchy and flexibility, and CIDR which abandons classes and allows arbitrary prefix lengths to improve efficiency and reduce routing tables. It also mentions IPv6 which was developed to replace IPv4 due to its limited 32-bit address space.


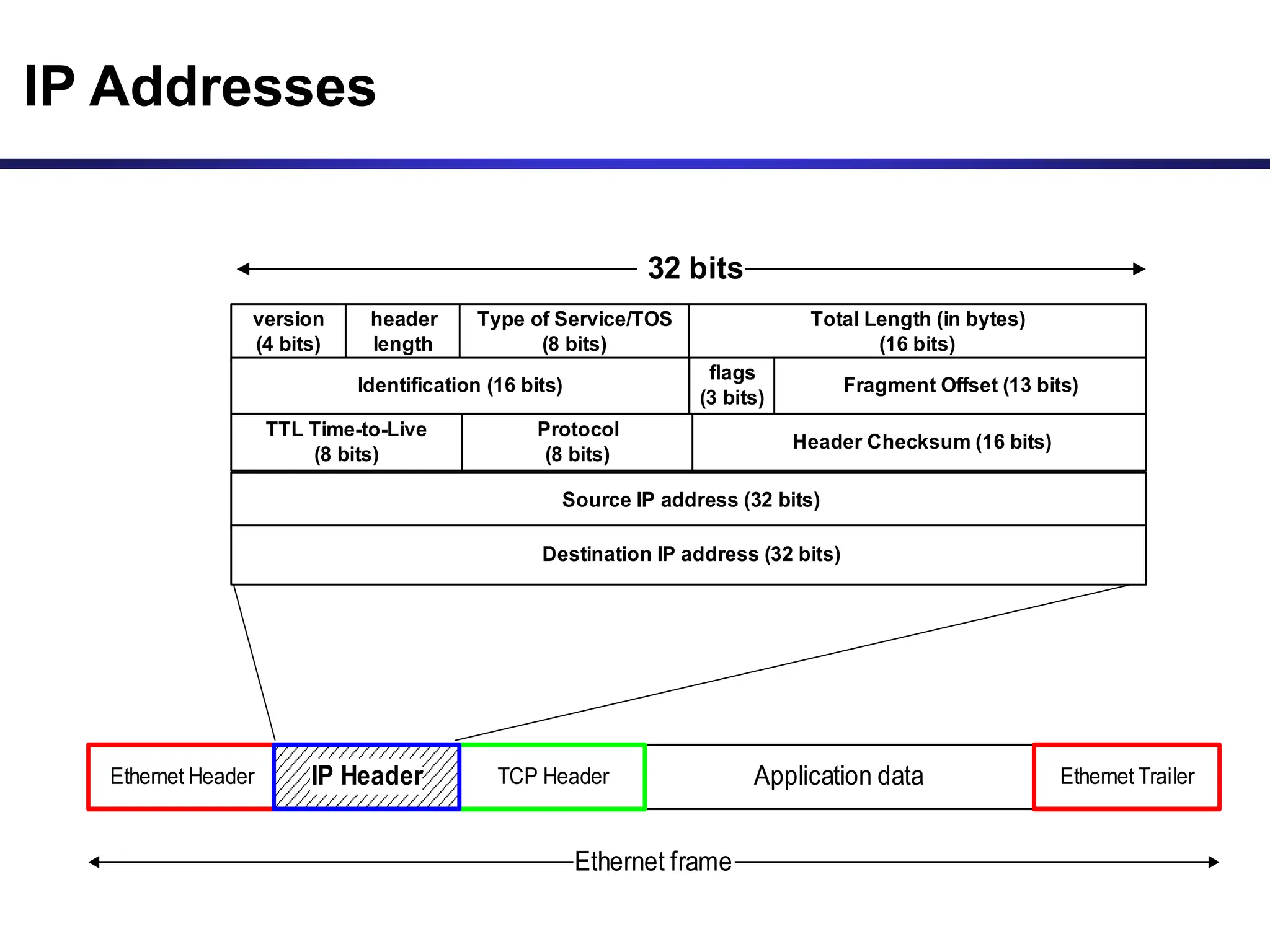
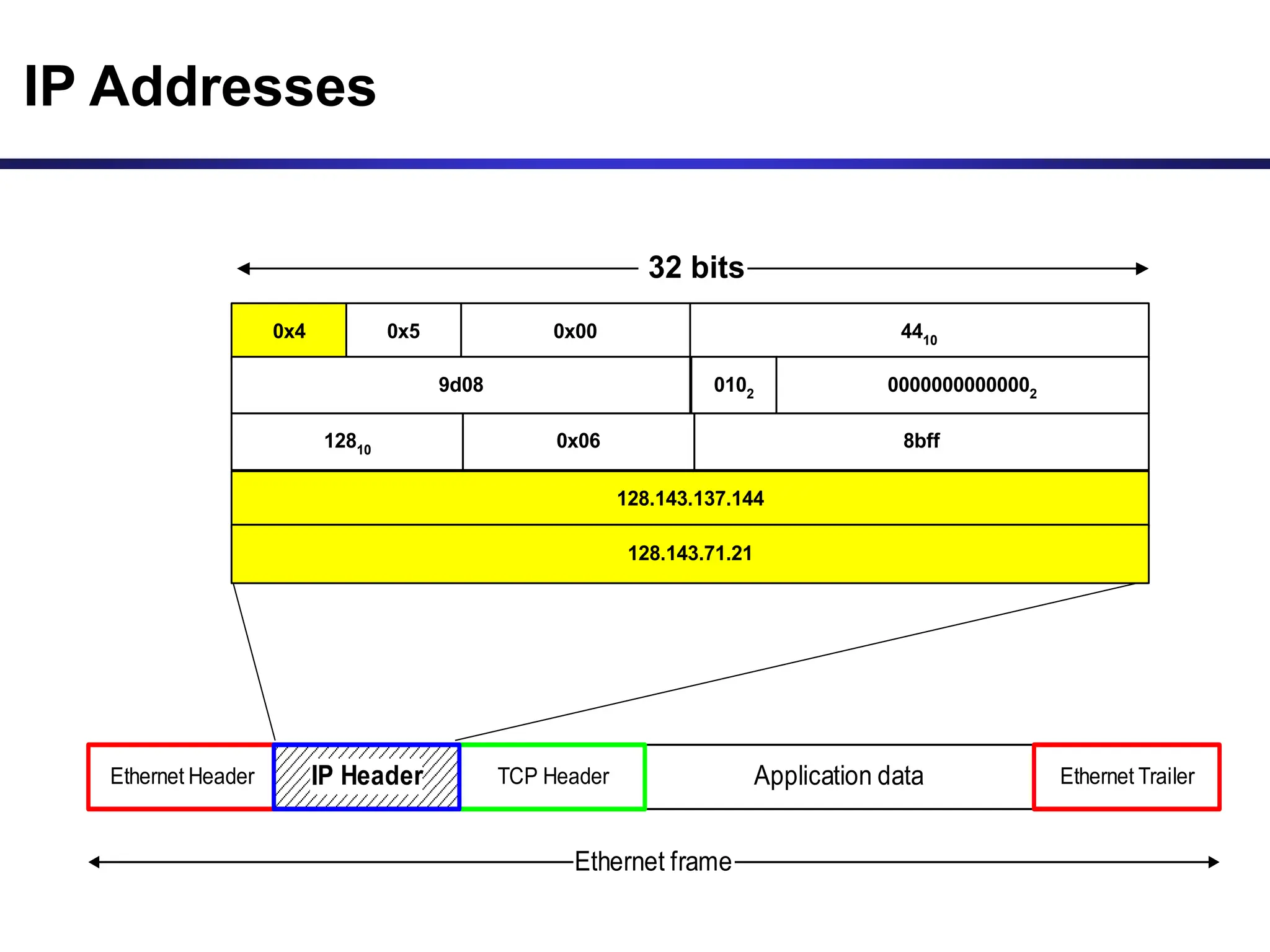

![Dotted Decimal Notation
• IP addresses are written in a so-called dotted decimal
notation
• Each byte is identified by a decimal number in the range
[0..255]:
• Example:
10001111
10000000 10001001 10010000
1st Byte
= 128
2nd Byte
= 143
3rd Byte
= 137
4th Byte
= 144
128.143.137.144](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ipandcidrbasics-240306132618-c9b78603/75/this-is-a-presentationon-ip-and-cidr-ppt-6-2048.jpg)