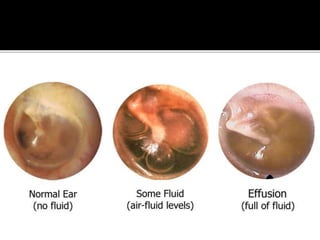
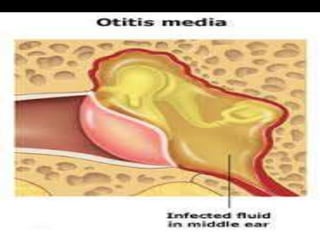
The document summarizes acute otitis media (middle ear infection). It notes that it is caused by pyogenic (pus-forming) organisms and is more common in children, especially of lower socioeconomic status. It can spread to the middle ear through the eustachian tube, external ear, or bloodstream. Risk factors include recurrent colds and other respiratory infections. Common bacteria include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis. The infection progresses through stages of occlusion, presuppuration, suppuration, resolution, and potential complications if not treated. Symptoms include earache, fever, and deafness. Signs include a red, bulging e