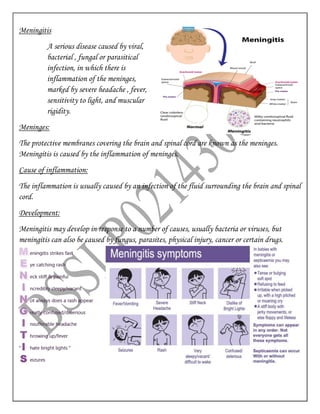
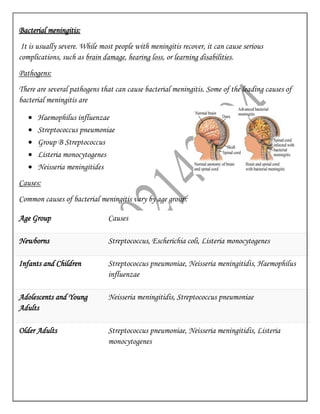
Meningitis is an inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, that is usually caused by a viral or bacterial infection. Common symptoms include severe headache, fever, sensitivity to light, and muscle stiffness. Bacterial meningitis requires immediate antibiotic treatment while most cases of viral meningitis resolve on their own. Vaccines exist for some common causes of bacterial meningitis. Meningitis can also be caused by fungi, parasites, physical injury, cancer or certain drugs.