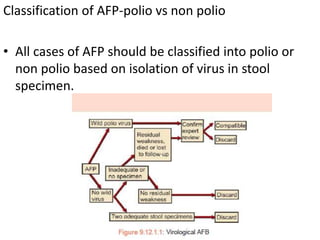
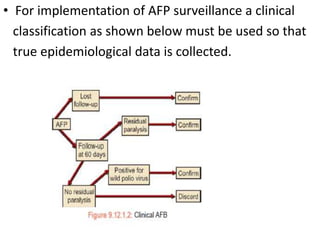
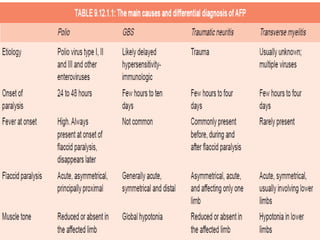
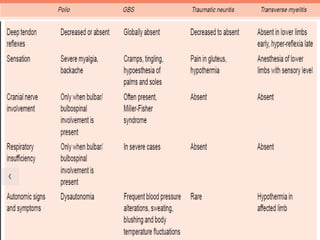
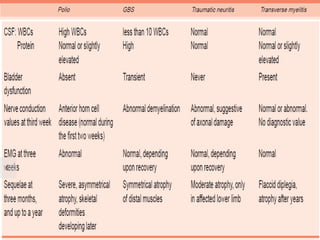
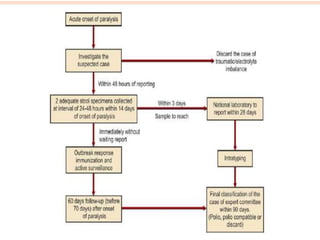
This document provides information about acute flaccid paralysis (AFP), including its definition, causes, surveillance, and clinical management. AFP is defined as paralysis of acute onset (less than 4 weeks) where the limbs are flaccid and tone is decreased. The main causes of AFP include poliomyelitis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, transverse myelitis, and traumatic neuritis. Surveillance of AFP cases is important for monitoring polio eradication efforts. All AFP cases should be reported, investigated, and have stool samples collected and tested for poliovirus. Proper clinical evaluation and management is needed to diagnose the cause and provide specific treatment.