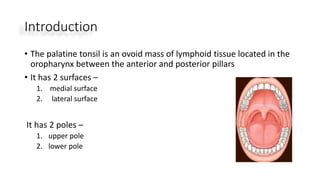
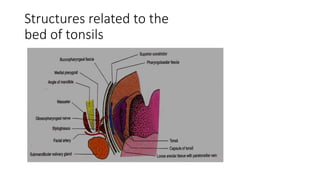
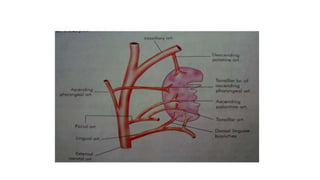
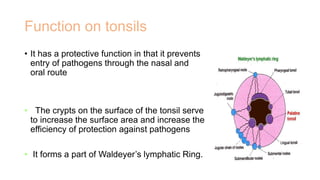
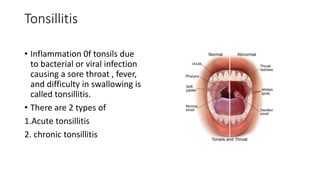
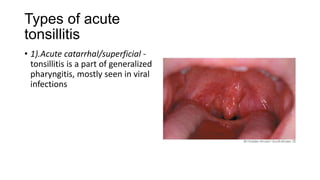
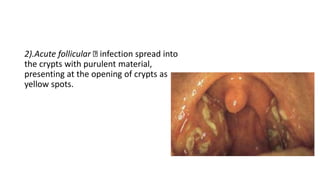
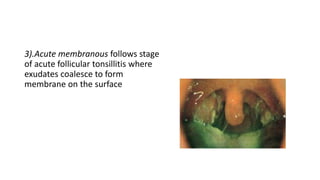
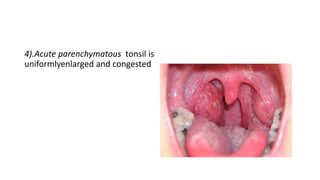
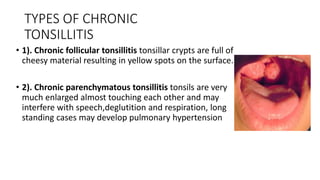
The document discusses the anatomy, functions, and types of acute and chronic tonsillitis. It describes the location and structures of the palatine tonsils. Acute tonsillitis is usually caused by bacterial or viral infections and causes sore throat, fever, and difficulty swallowing. It can be superficial, follicular, membranous, or parenchymatous. Chronic tonsillitis is a complication of repeated acute infections and can be follicular, parenchymatous, or fibroid. Symptoms include recurrent sore throats and tonsil enlargement may require tonsillectomy.