TUNDIKERI -ACUTE AND CHRONIC TONSILITIS
- 1. Dr Raju S N PG SCHOLOR DEPARTMENT OF SHALAKYA TANTRA SJGAYURVEDA COLLEGE KOPPAL TUNDIKERI, TONSILLITIS
- 2. तुण्डिके रि 1.Tundikeri is explained under the talugata rogas by sushrutha among the तालुगत िोग. 2.Acharya vagbhata explained under the कडट गत िोग 3.Acharya charaka explained under मुखिोग
- 3. Classical refferences …. १)शोफ: स्थूलस्तोद दाह प्रपाकी प्रागुक्ताभ्ाां तुण्डिके ि मता तु I सु .नि १६/४२ There will be swelling , its big in size , pricking type of pain ,burning sensation are the symptoms of tundikeri . २) तुण्डिके रि वनकापपसिक तत्पलानुकाि व््ाधिि्म ्I हनुिांध््ाधितः कां टे कापपिीफल िण्ननभः II पपण्छिलो मांदरुक् शोफः कटटणस्तुण्डिके रिका III अ.ह्रु.उ २१/४७ Due to vitiated kapha and raktha doshas it will cause big cystic swelling resembling the fruit of vanakaarpasa , and the complaints will be burning sensation ,pricking pain in the throat with suppurative cyst.
- 4. धिककत्िा िूत्र • The treatment modalities for tundikeri explained by our acharyas in ayurveda is two types • शमि चिकित्सा – shoolahara ,shotha hara , grandhi hara aushadhi will subsides the tundikeri िवल ,गन्डूष , धूम ,िस्य. • शस्र चिकित्स – • तुण्डडिे रि अध्रुषे संघाते तलुपुप्पुटे I एष एव ववचधिः िायय ववशेषिः शस्रिमयणि II su .chi २२/५७ • even though it can be cured by shasthra chikitsa but Dalhana explains the treatment for the tundikeri as bhedya sadhya vyadhi. • तुण्डडिे िी भेध्य तालुपुप्पुटिोअवप I
- 9. TONSILS • The tonsils are masses of lymphoid tissue and form an important part of our immune system located at the gateway of respiratory and digestive tract. • They act as the first line of defense against ingested or inhaled pathogens. • Four types of tonsils are arranged into a ring around the oropharynx and nasopharynx , known as Waldeyer’s ring of lymphoid tissue.
- 10. WALDEYERS RING • Heinrich Wilhelm Gottfried von Waldeyer-Hartz first described the incomplete ring of lymphoid tissue, situated in the naso-oropharynx, in 1884. The ring acts as a first line of defence against microbes that enters the body via the nasal and oral routes. Waldeyer’s ring consists of four tonsillar structures as well as small collections of lymphatic tissue disbursed throughout the mucosal lining of the pharynx.
- 11. TYPES • Tonsils are four types namely, 1. Pharyngeal 2. Tubal, 3. Palatine 4. Lingual tonsils.
- 12. 1. Pharyngeal Tonsil (Adenoids) Situated superior-posteriorly to the torus tubaris (elevation around the pharyngeal opening of the Eustachian tube, in the roof of the nasopharynx, the pharyngeal tonsil is primarily responsible for ‘screening’ the air that enters through the nostrils. The pharyngeal tonsil is lined by pseudo- stratified ciliated columnar epithelium (respiratory epithelium). Unlike the other tonsils, there are no crypts (invaginations in the surface of the tonsil) present in this tonsil.
- 14. Blood supply and venous drainage • Blood supply to the pharyngeal tonsil arise from the • ascending pharyngeal and palatine arteries. • tonsillar branch of the facial artery. • pharyngeal branch of the maxillary artery. • artery of the pterygoid canal. • basosphenoid artery. • Venous blood is returned to circulation via the pharyngeal plexus, which drains indirectly to the internal jugular veins (IJV).
- 15. TUBAL TONSIL (Gerlach’s Tonsils) • The tubal tonsils are also located in the roof of the nasopharynx. They are bilateral and posterior to the torus tubaris, in the fossa of Rosenmüller (pharyngeal recess). Due to the relative closeness of the tubal tonsils to the torus tubaris, it is sometimes referred to as “the tonsils of the torus tubaris”. The term “tubal tonsils” is also synonymous with Eustachian tonsils and Gerlach’s tonsils. • These lymphoid structures are also lined by respiratory epithelium; additionally, crypts are present and infiltrated by lymphatic tissue.
- 17. BLOOD SUPPLY AND VENOUS DRAINAGE • Gerlach’s tonsils receive arterial blood by branches of the sphenopalatine and the ascending pharyngeal arteries. Lymphatic drainage is achieved via the retropharyngeal and the deep cervical lymph nodes.
- 18. LINGUAL TONSIL • The numerous protrusions located at the posterior third of tongue are collectively known as the lingual tonsils. They are also covered by stratified non- keratinized squamous epithelium.
- 20. BLOOD SUPPLY AND VENOUS DRAINAGE • The dorsal lingual branch of the lingual artery and the lingual vein are responsible for the vascular supply and return of these lymphatic aggregates, while the glossopharyngeal nerve innervates them, along with the posterior of the tongue.
- 21. PALATINE TONSIL • The palatine tonsils have been historically referred to as “the tonsils.” They are readily visible in the oropharynx when inflamed. These bilateral lymphoid aggregates each rest within a tonsillar cleft, bordered anteriorly by the palatoglossal arch and posteriorly by the palatopharyngeal arch. Unlike the adenoids, the palatine tonsils are covered by stratified non-keratinized squamous epithelium.
- 22. • They are two in number • Each tonsil is an ovoid mass of lymphoid tissue • Tonsils are present in the lateral wall oropharynx between the anterior and posterior pillars. • Actual the size of the tonsil is bigger than the one that appears.as it extend upwards into soft pallate and downwards into the base of tongue and anteriorly into palatoglossal arch.
- 23. TONSIL PRESENTS………. • Surfaces are two 1) Medial 2)Lateral • Poles are two 1) Upper pole 2)Lower pole
- 24. MEDIAL SURFACE • Is covered by non keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium which dips into the substance of tonsil in the form of crypts. • 12-15 crypts are seen. • Crypta Maghna . • Secondary crypts arise from primary crypts. • Crypts may be filled with cheesy materials consisting of epithelial cells , bacteria , food debris.
- 26. LATERAL SURFACE • It presents well defined fibrous capsule . • There is loose areolar tissue between capsule and bed of tonsil which makes easy to dissect during the tonsillectomy. • It is also the site for the collection of pus in peritonsilar abscess.
- 27. UPPER POLE • Upper pole of the tonsil extends into the soft palate. • Its medial surface is covered by semilunar fold , extending between anterior and posterior pillars and enclosing a potential space called supratonsillar fossa.
- 28. LOWER POLE • The tonsil is attached to the tongue . • The tonsil is separated from the tongue by a sulcus called tonsillolingual sulcus.
- 29. BED OF TONSIL • Its formed by superior constrictor and styloglossus muscle. • The glossopharyngeal nerve and styloid process ,if enlarged may lie in relation to the lower part of tonsillar fossa. • Outside the superior constrictor ,tonsil is related to the facial artery ,submandibular salivary gland ,posterior belly of digastric muscle ,medialpterygoid muscle and the angle of the mandible.
- 30. BLOOD SUPPLY • Tonsil is supplied by • Tonsilar brnch of facial artery. • Ascending pharyngeal artery from external carotid. • Ascending palatine branch of facial artery. • Dorsal lingual branches of lingual artery. • Descending palatine branch of maxillary artery.
- 32. VENOUS DRAINAGE Paratonsilar vein which joins the common facial vein and pharyngeal venous plexus.
- 33. LYMPATIC DRAINAGE • Tonsils drains into the jugulodigastric lymph node ( tonsilar )(deep cervical node )
- 34. NERVE SUPPLY • lesser palatine branches of sphenopalatine ganglion • Glossopharyngeal nerve provides sensory nerve supply
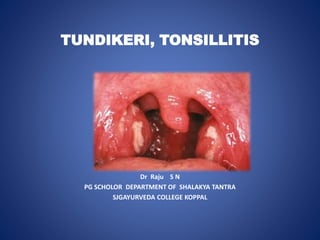
- 35. TONSILITIS • Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils,typically of rapid onset.
- 36. TYPES OF TONSILITIS Acute tonsilitis - • Acute catarrhal or superficial tonsilitis –its part of generalised pharyngitis its mostly seen in viral infections. • Acute follicullar tonsilitis –infection spreadsinto the crypts which become filled with the purulent material which present at the opening of the crypts as yellowish. • Acute parenchymatous tonsilitis –here tonsil substance is affected. Tonsil is uniformly enlarged and red. • Acute membranous tonsilitis – its later stage of acute tonsilitis where there will be exudation from the crypts will form a membrane over the tonsil.
- 38. AETIOLOGY • Usually seen in childrens but we can see in adults also. • Less in the infants and the persons above the fifty years . • The usual causative organism of tonsilitis are haemolytic streptococus is the most commonly infecting organism .other organisms are staphylococci, pneumococci or H.influenza.
- 39. SIGNS • Breath is foetid • Hyperaemia of pillars , soft pallate and uvula. • Tonsils are red swollen yellowish spots filled with purullent material. • There may be membrane over the tonsil. • Enlarged jugulodigastric lymphnodes.
- 40. SYMPTOMS • Sore throat • Fever • Ear ache • Constitutions symptoms like generalise myalgia headache , abdominalpain due to mysentric lymphedinitis , nausea,vomitting
- 41. TREATMENT • Adviced to take plenty of water . • Avoiding oily and cold beverages. • Analgesics. • Antimicrobial therapy.
- 42. COMPLICATIONS • Chronic tonsillitis • Peritonsillar abscess • Parapharyngeal abscess • Cervical abscess • Acute otitis media • Acute glomerlonephritis • Sub acute bacterial endocarditis. –due to infection from streptococcus viridans infection valvular disease patient may end up in sub acute bacterial endocarditis.
- 43. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS • Membranous tonsilitis –it occurs due to pyogenic organism. An exudate membrane will forms over the medial surface of the tonsil. • Diptheria –the membrane will be extends beyond the tonsil on to the soft palate and is dirty and grey incolour . On removal of the adhered membrane leaves bleeding surface. • c/s of throat swab will show corynebacterium diptheriae.
- 45. • Vincent angina- the membrane can be removed easily , on removal we can see irregular ulcer on tonsil. • On c/s of throat swab fusiform bacilli and spirochaets. • Infectious mononucleus- in this both tonsils are very much enlarged, congested , and covered with membrane . • Splenomegaly noted , lymphonodes are enlarged in posterior triangle of neck.
- 46. • Agranulocytosis –it presents with the ulcerative necrotic lesions over the tonsil also it may extends into the oropharynx. • Leukamia • Apthous ulcers –they may involve any part of oral cavity of oropharynx.sometimes it may involue tonsil also.. It may be small but its painfull. • Malignancy tonsil
- 54. CHRONIC TONSILITIS • It may be the complication of the acute tonsilitis. • Subclinical infection of tonsils without an acute attack. • Chronic infection in the teeth and sinuses may also be the pre disposing factor.
- 55. TYPES • CHRONIC FOLICULAR TONSILITIS –the crypts are full of infected cheesy material • CHRONIC PARANCHYMATOUS TONSILLITIS – There will hyperplasia of lymphoid tissue . Tonsils are enlarged and interfere with the speech , deglutition, and respiration. • CHRONIC FIBROID TONSILLITIS-tonsils are small but infected , with the history of repeated sore throats.
- 56. CLINICAL FEATURES • Recurrent attack of sore throat or acute tonsillitis. • Chronic irritation in throat with cough. • Foul breath , bad taste . • Thick speech , difficulty in swallowing.
- 57. ON EXAMINATION • Tonsils may show varying degree of enlargement. • Yellowish beads of pus on the medial surface of tonsil. • Enlargement of jugulodigastric lymphnodes. • Tonsils are small but pressure on the anterior pillar expressfrank pus or cheesy material.
- 58. TREATMENT • Conservative treatment • Tonsillectomy
- 59. COMPLICATION • Peritonsillar abscess • Parapharyngeal abscess • Intratonsillar abscess • Tonsilloliths • Tonsillar cyst • Rhd , glomerulonephritis, eye and skin diseases.
- 60. • TONSILLOLITHS- it is seen in chronic tonsillitis when its crypt is blocked with retention of debris. Inorganic salts of calcium and magnesium are then deposited leading to formation of stone. • INTRATONSILLAR ABSCESS- It is accumulation of pus within the substance of tonsil. There will be blocking of the crypts opening. • TONSILLAR CYST-it is due to blockage of tonsillar crypt and appears as a yellowish swelling over the tonsil. It can be easily drained.
