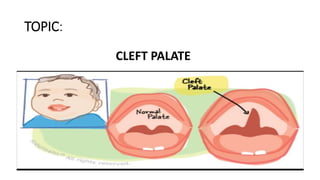
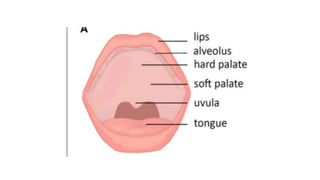
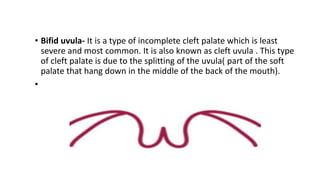
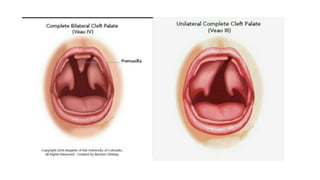
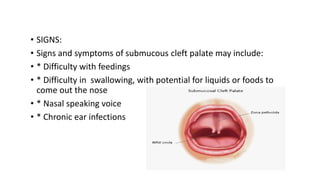
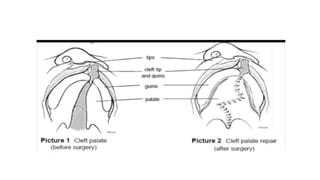
This document provides information about cleft palate, including its definition, symptoms, types, causes, risk factors, complications, treatment, and prevention. Cleft palate occurs when the tissues that form the roof of the mouth do not fuse completely during development in the womb. It can range from a small split in the soft palate to a complete opening involving both the soft and hard palates. The main treatment is surgery called palatoplasty to close the opening between the mouth and nose. Preventive measures include prenatal vitamins, avoiding tobacco and alcohol during pregnancy, and genetic counseling for families with a history of cleft palate.