This document discusses acute apical abscess, which is a severe localized inflammatory condition characterized by the formation of pus around the apex of a tooth. The most common cause is bacterial invasion of the dental pulp from tooth decay. Clinically, it presents as acute pain that is worsened by pressure, percussion or palpation. Diagnosis involves a dental examination and x-rays. Emergency management involves establishing drainage to relieve pain, either through root canals or surgical drainage. After drainage is achieved, root canal treatment should be performed to thoroughly clean and disinfect the canals and remove the source of infection. Antibiotics may be prescribed in some cases but are generally not needed if adequate drainage is established.
![ACUTE APICAL ABSCESS [AAA]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acuteapicalabscess-dranirudhchauhan-150401081257-conversion-gate01/75/Acute-apical-abscess-dr-anirudh-singh-chauhan-1-2048.jpg)




![ACUTE APICAL ABSCESS [AAA]
• A severe localized Inflammatory condition
characterized by formation of purulent exudates(
PUS) involving the dental pulp or pulpal remnants
and the tissues surrounding the apex of a tooth.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acuteapicalabscess-dranirudhchauhan-150401081257-conversion-gate01/75/Acute-apical-abscess-dr-anirudh-singh-chauhan-6-2048.jpg)









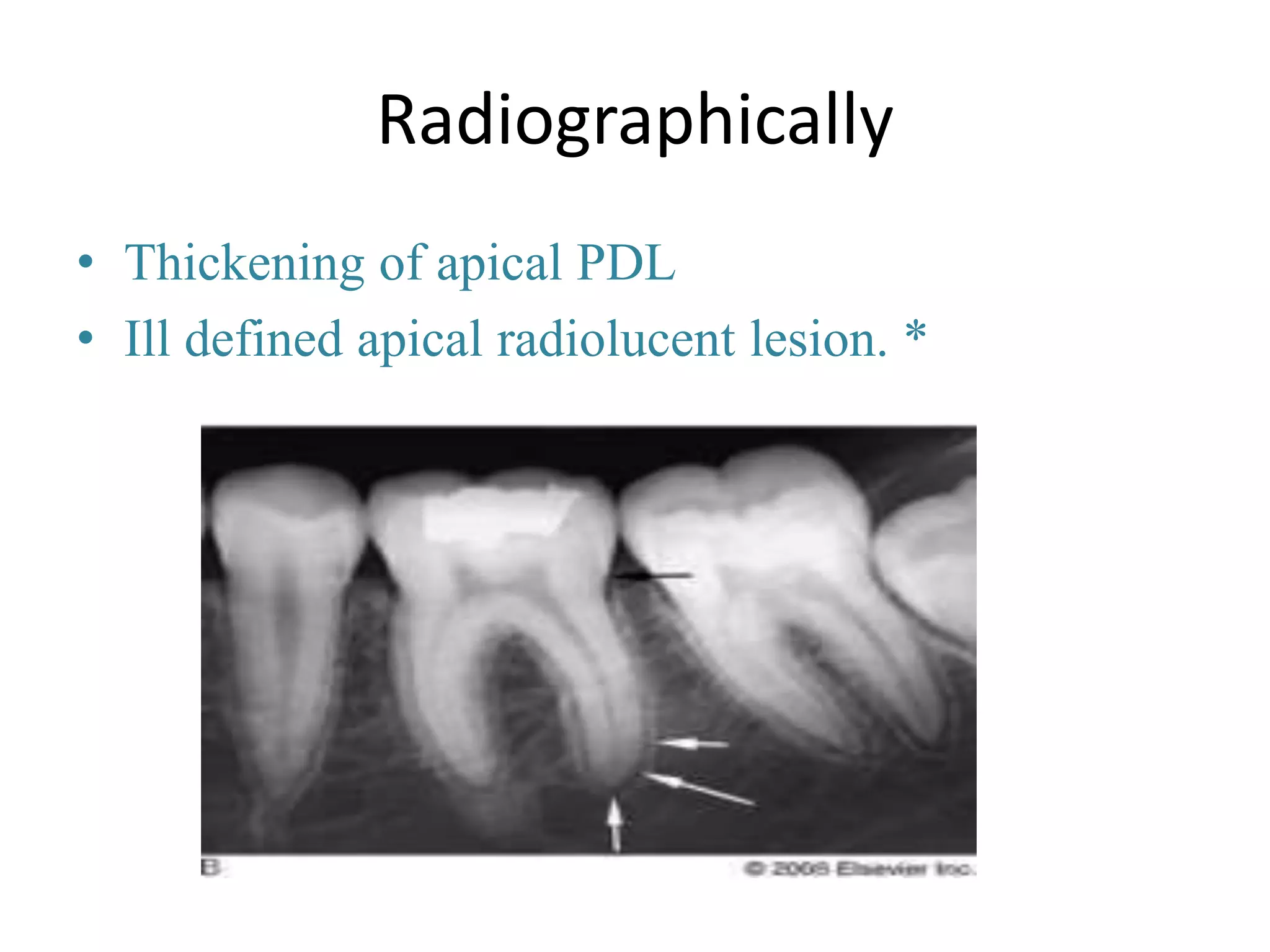






![• DRAINAGE ACHIEVED BY :-
– Surgical Drainage
• Immediate relieve from Pain
– Access Opening and Drainage
first visit accomplishes two things
• Relief from pain and pressure
• Removal of potent irritants [pus]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acuteapicalabscess-dranirudhchauhan-150401081257-conversion-gate01/75/Acute-apical-abscess-dr-anirudh-singh-chauhan-23-2048.jpg)






















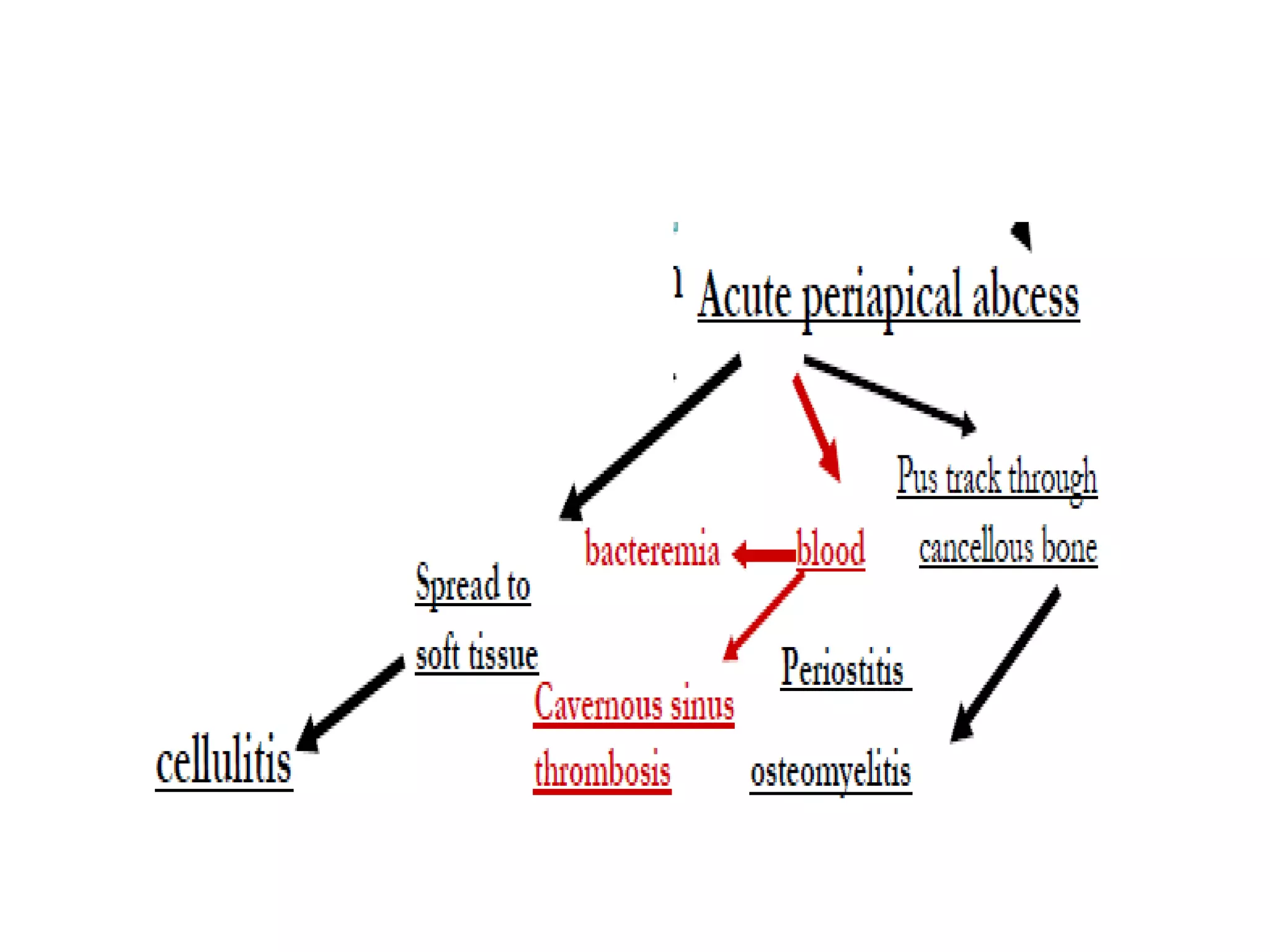






![• Fortunately these rarely occurs
• Rapidly progressive , painful . Severe discomfort
• Swelling not localized
• Regional lymphadenopathy with tenderness [ sub-
mandibular – cervical ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acuteapicalabscess-dranirudhchauhan-150401081257-conversion-gate01/75/Acute-apical-abscess-dr-anirudh-singh-chauhan-53-2048.jpg)






