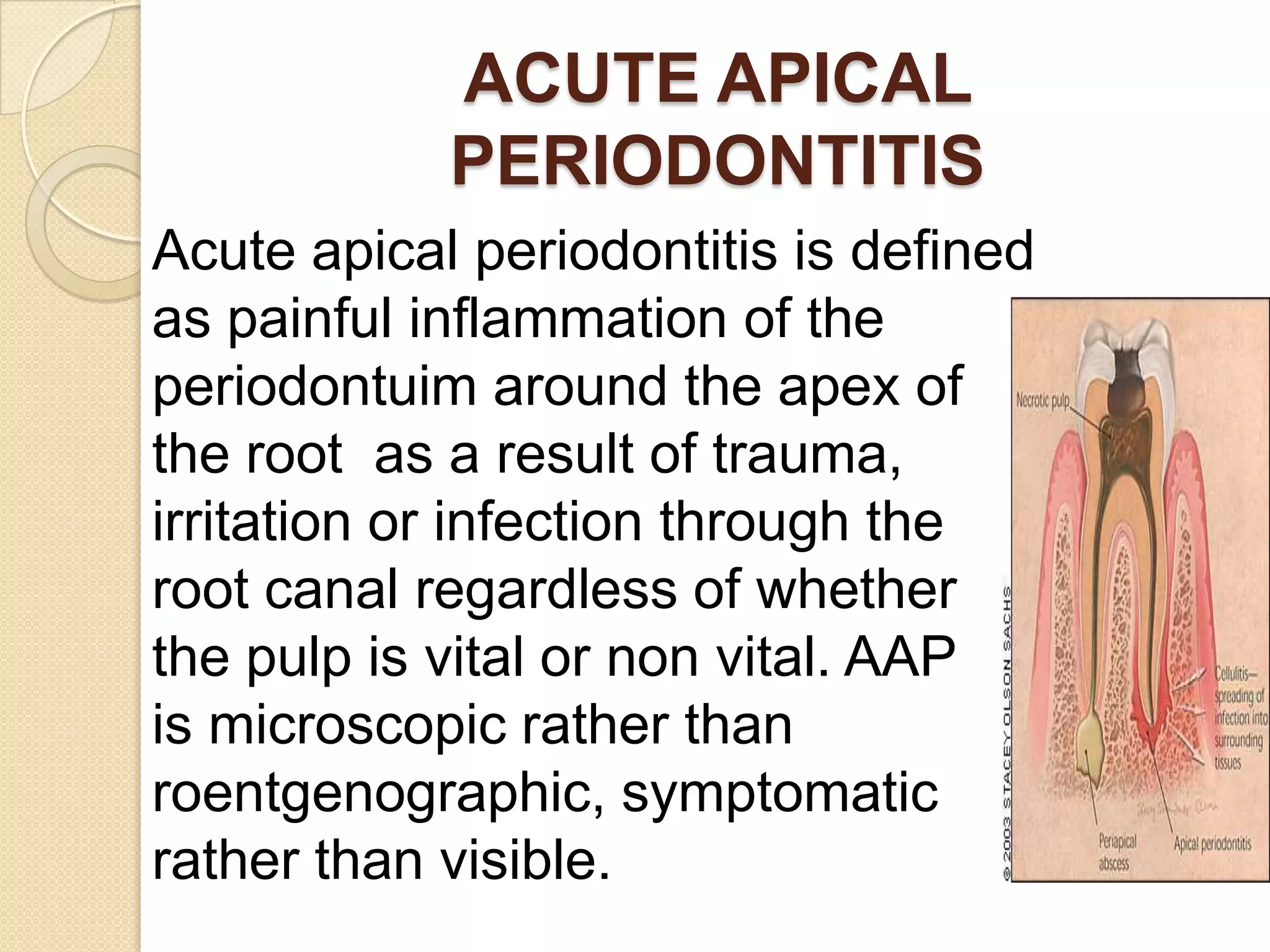
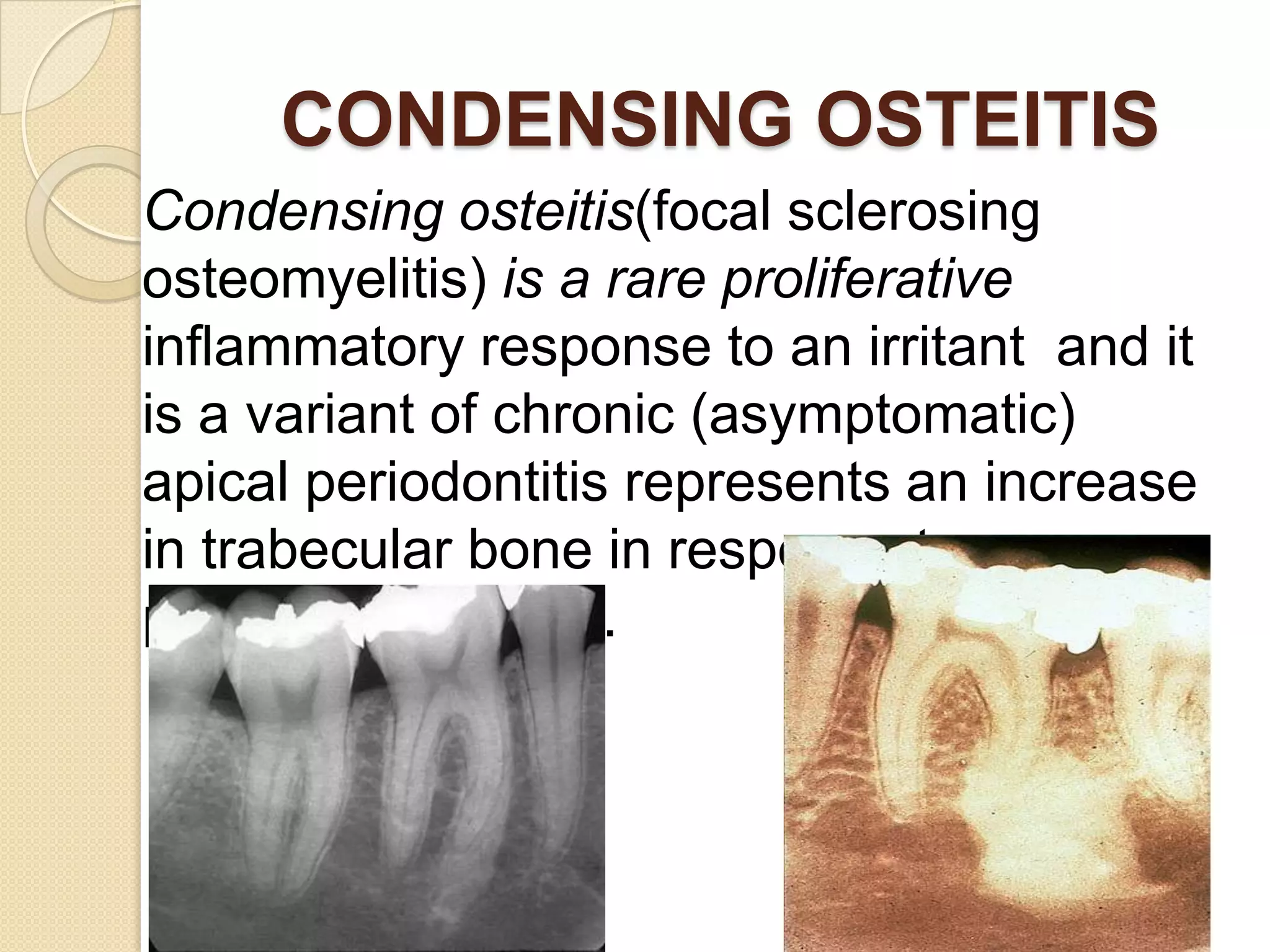
1) The periradicular tissue contains apical root cementum, periodontal ligaments, and alveolar bone. Untreated pulpal infection can lead to total pulp necrosis and periapical pathologies as irritants leak into the periradicular region.
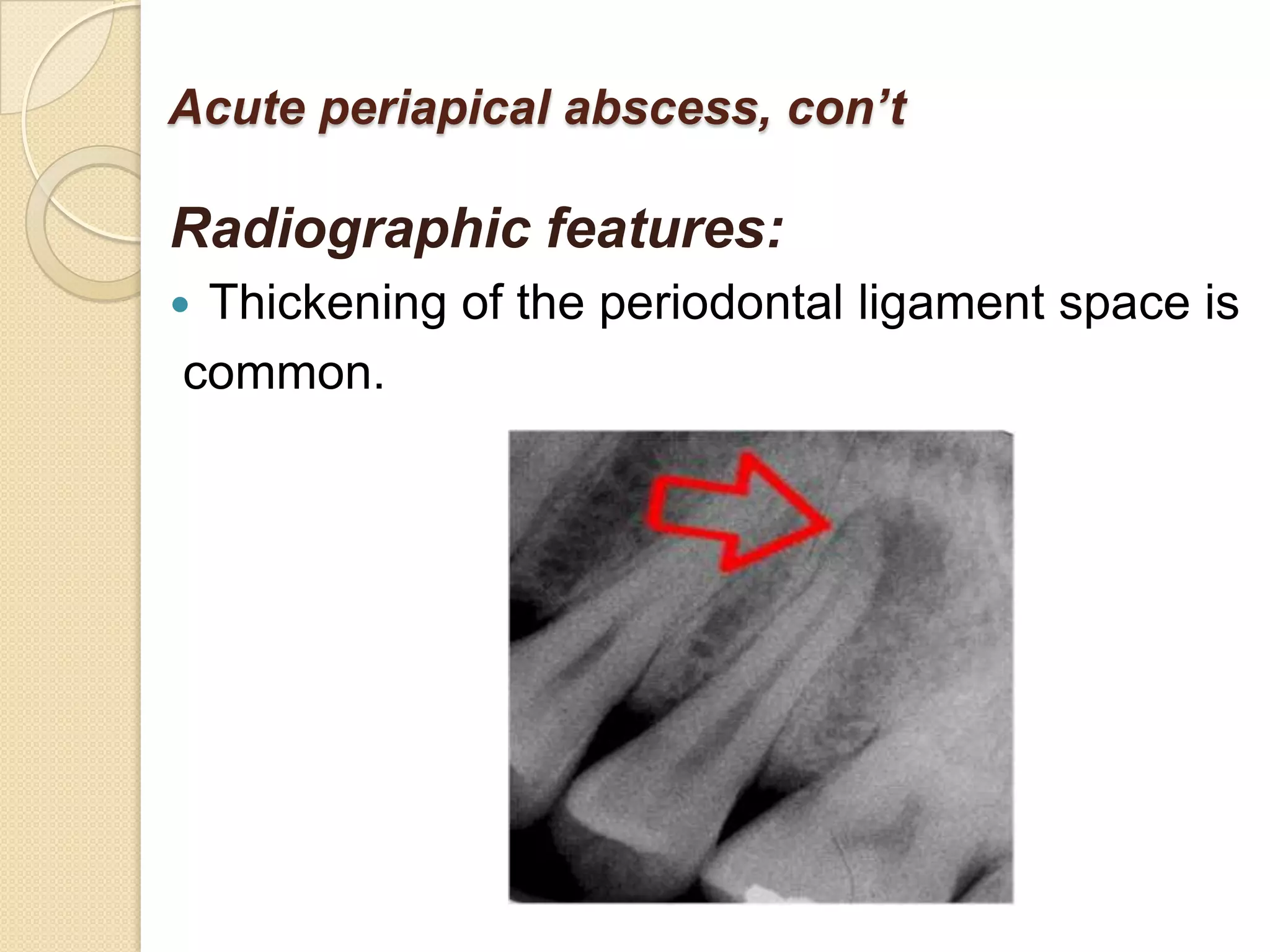
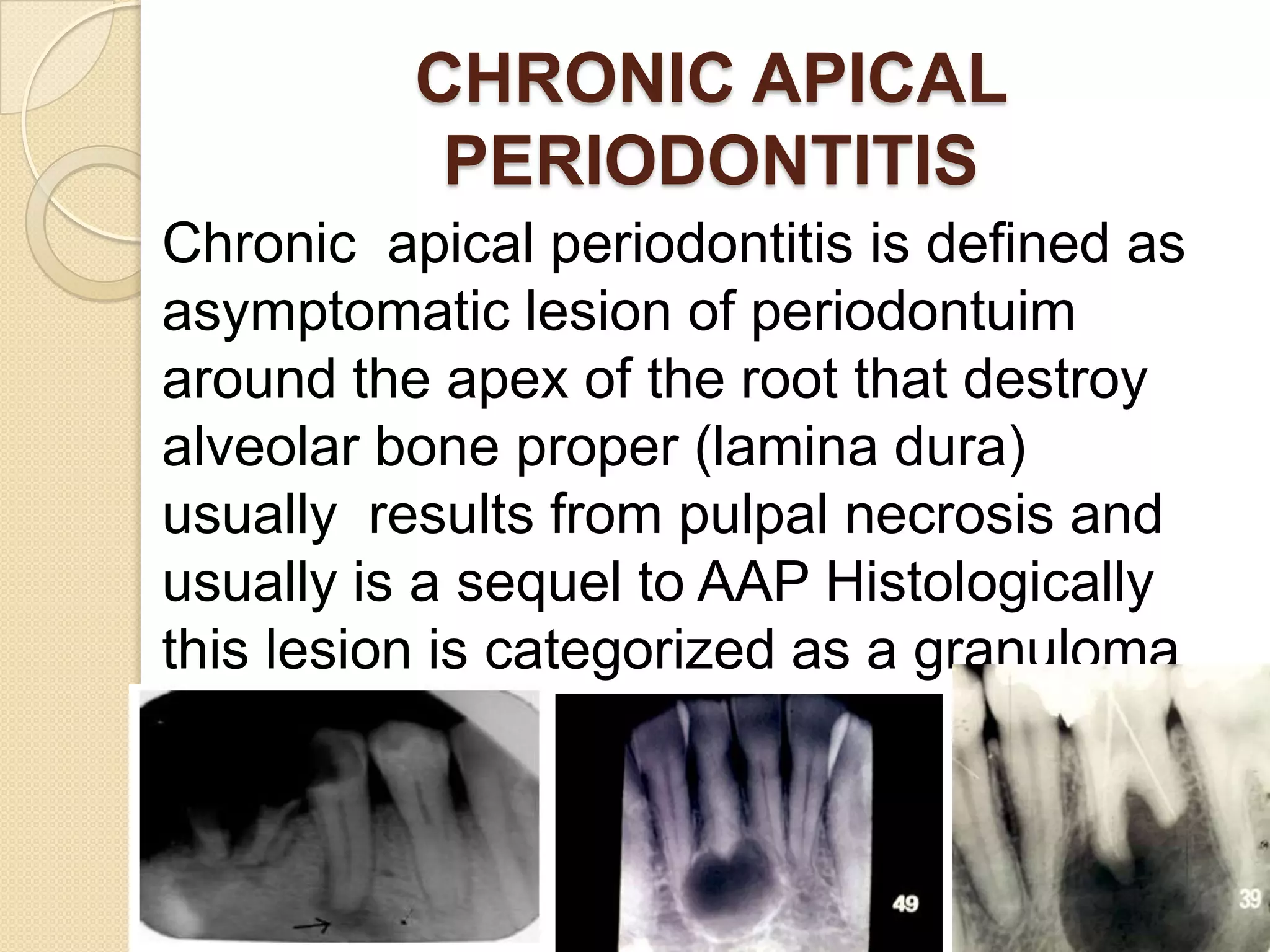
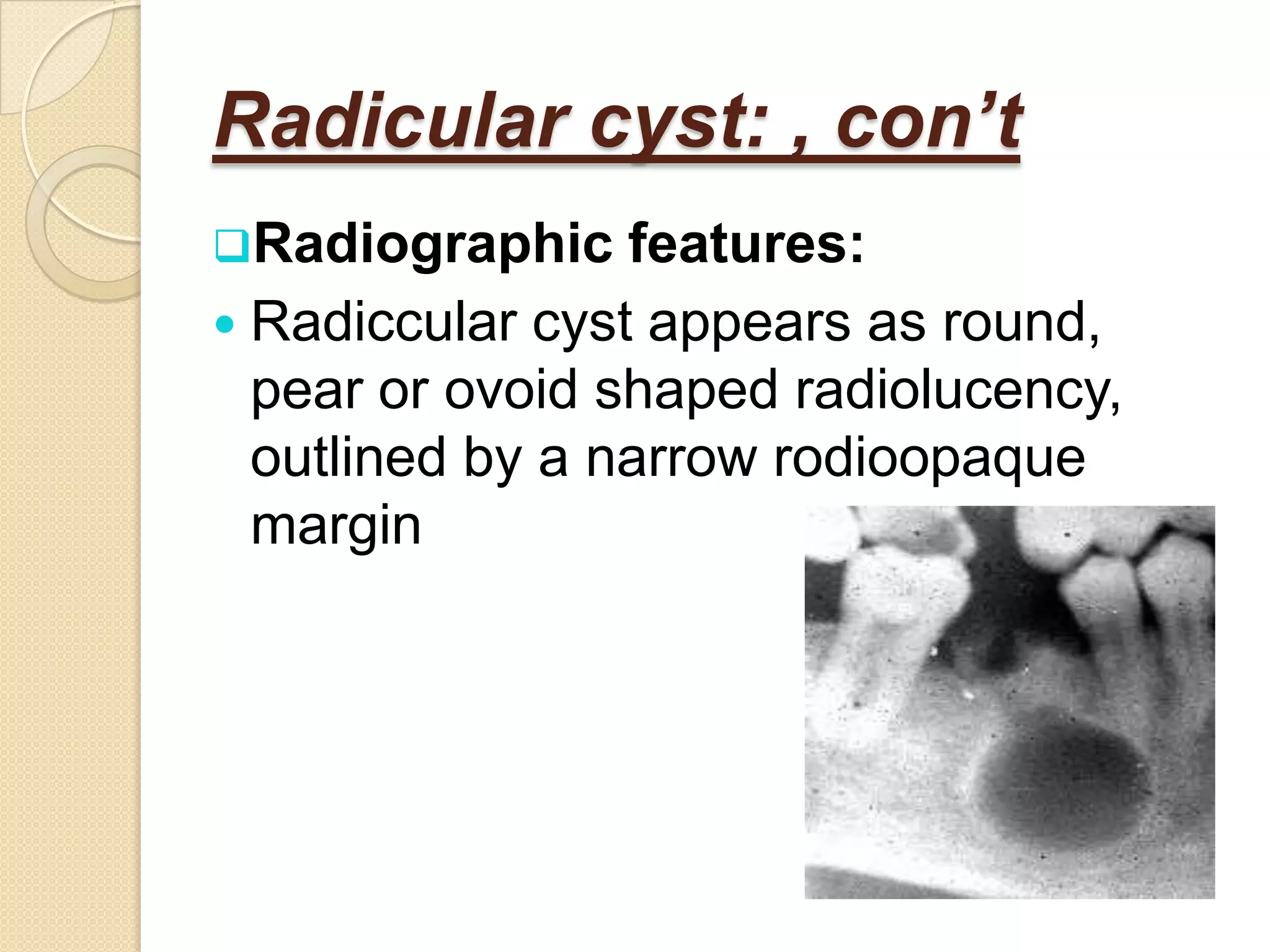
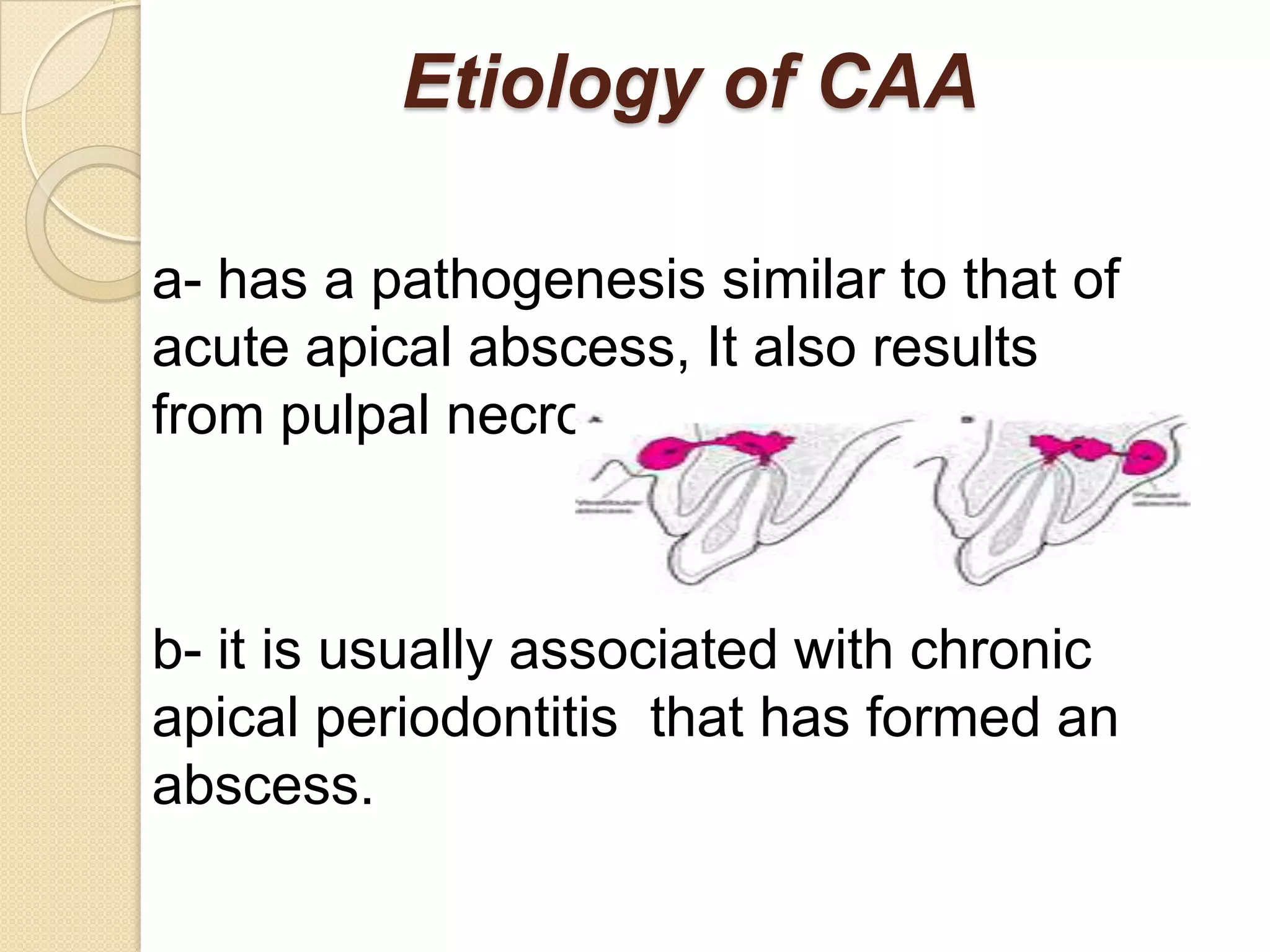
2) Periradicular pathologies include acute and chronic apical periodontitis, acute and chronic apical abscesses, granulomas, cysts, and condensing ostitis. Signs and symptoms vary but generally include pain, swelling, and radiographic evidence of bone loss.
3) Treatment involves removing the source of irritation through root canal treatment or extraction and surgically addressing any associated periradicular lesion if present.