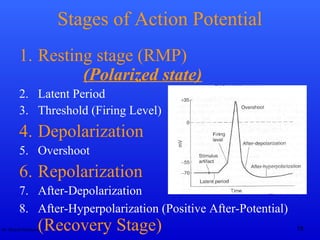
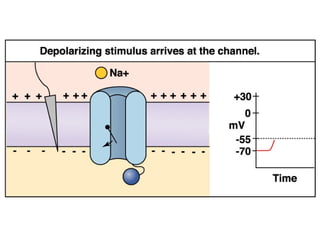
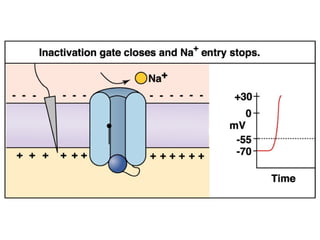
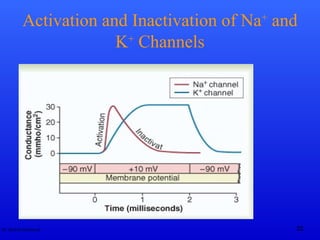
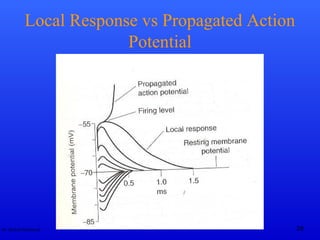
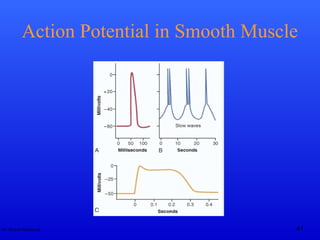
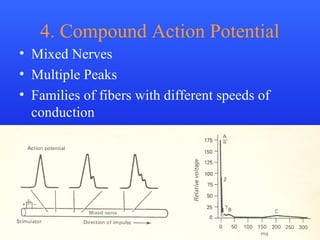
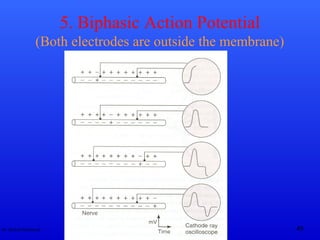
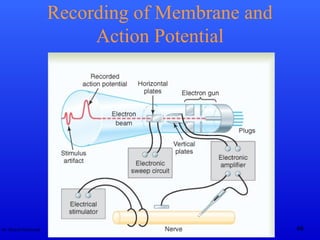
The document discusses action potentials and their propagation in excitable tissues. It begins by stating the objectives of understanding the mechanisms of action potential production and propagation. It then lists the main contents that will be covered, including the definition of action potential, the stages of a typical action potential, and the types of ion channels involved. It goes on to describe key aspects of action potentials in more detail, such as the stages of an action potential, how they propagate through saltatory conduction, and different types of action potentials that can occur. It emphasizes that action potentials are rapid changes in membrane potential that involve the coordinated opening and closing of sodium and potassium ion channels.