Embed presentation
Downloaded 100 times

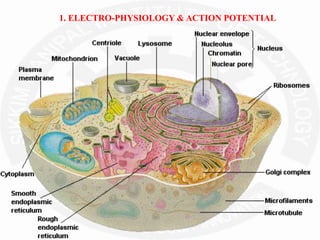
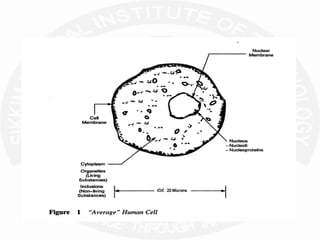
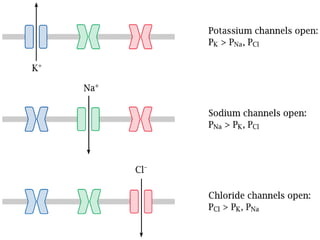
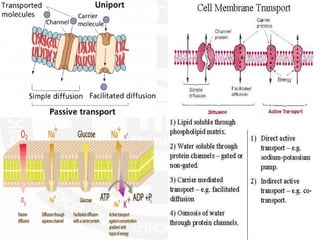
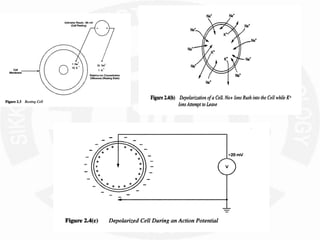
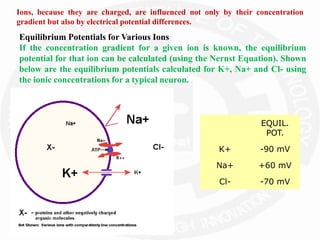

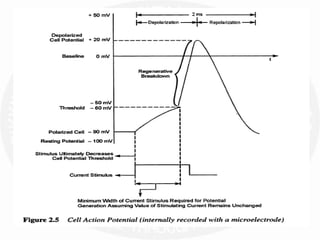
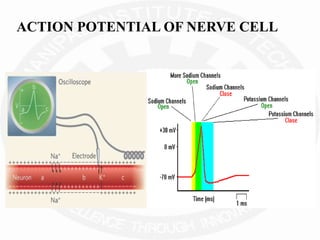
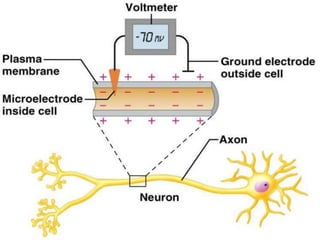
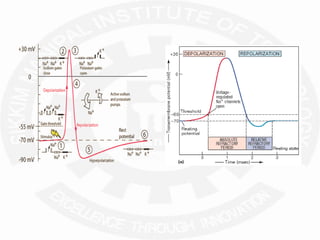
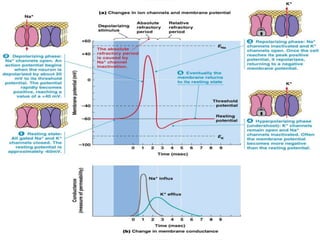
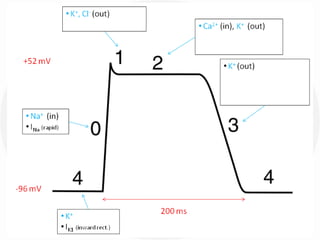

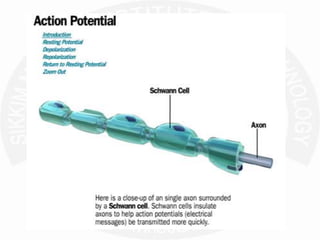

The document discusses action potentials and resting potentials in neurons. It first defines the equilibrium potentials for potassium (K+), sodium (Na+), and chloride (Cl-) ions based on their concentrations inside and outside the neuron cell membrane. The equilibrium potential for K+ is -90 mV, Na+ is +60 mV, and Cl- is -70 mV. It then introduces the topic of action potentials in nerve cells, which will be further detailed.





















