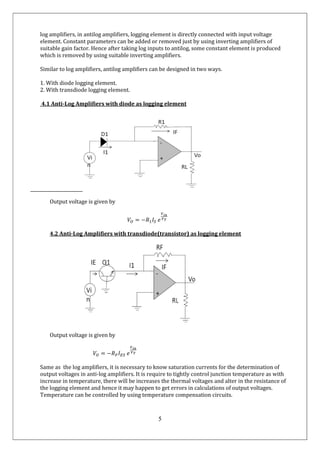
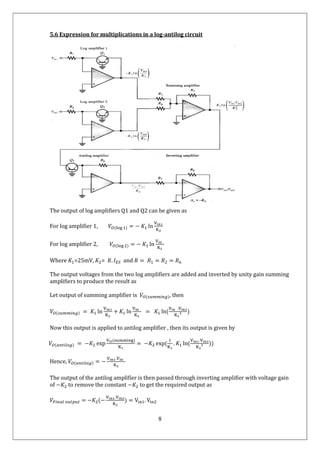
1) The document describes the theoretical operation of log-antilog single quadrant multipliers. Log amplifiers produce an output proportional to the logarithm of the input voltage, while antilog amplifiers produce an output proportional to the exponential of the input.
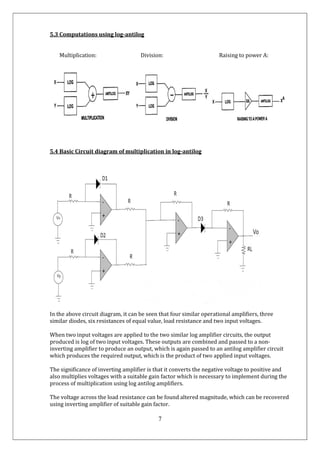
2) By passing the sum of the outputs of two log amplifiers into an antilog amplifier, the circuit can produce an output equal to the product of the two original input voltages, thus performing multiplication.
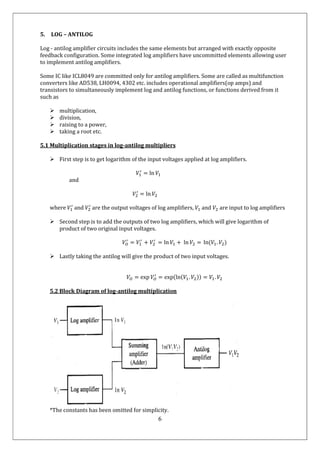
3) The key stages are taking the logarithm of each input, adding the results, then taking the exponential to obtain the final product. This allows multiplication to be performed using simpler addition and exponential operations.




![10
10. REFERENCES
[1] Microelectronics Circuits by Sedra and Smith.pdf
[2] Donald A. Neamen Microelectronic Circuits Analysis and Design.pdf
[3] Op Amps: Design, application, and Troubleshooting by David L. Terrel.pdf
[4] https://www.slideshare.net
[5] https://www.analog.com
[6] https://www.electronicshub.org
[7] https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Electronics/Analog_multipliers
[8] https://en.wikipedia.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1814110projectreportanalogictecnology-210510125032/85/Log-antilog-amplifiers-by-ransher-10-320.jpg)