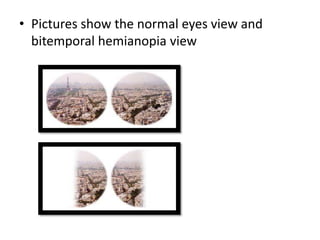
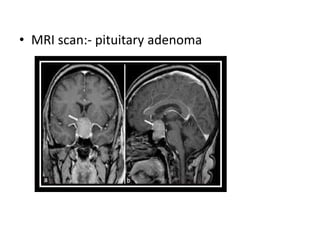
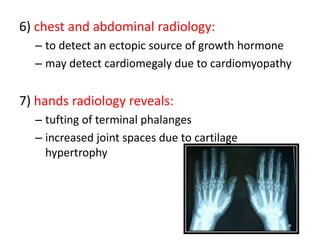
1. Investigation and management of acromegaly involves assessing GH and IGF-1 levels through tests like the glucose tolerance test and MRI of the pituitary to detect adenomas. Surgery is the first-line treatment but other options include radiotherapy, somatostatin analogues, dopamine agonists, and GH antagonists to normalize GH and IGF-1 levels.
2. Complications of acromegaly include increased risk of heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, sleep apnea, and colon polyps. The goal of management is to reduce GH levels to below 5 mU/L to minimize these risks.
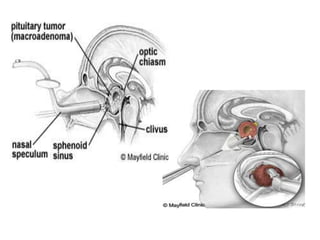
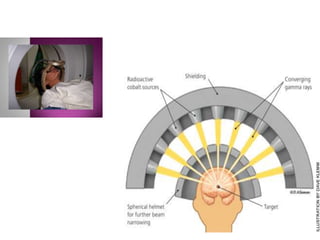
3. Treatment approaches include trans-sphenoidal pituitary surgery, followed by radiotherapy