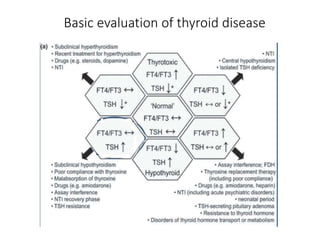
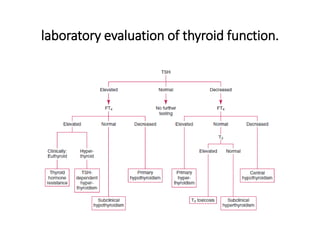
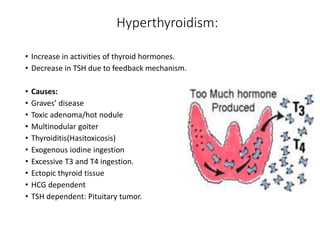
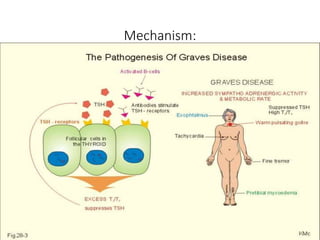
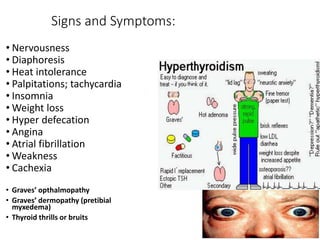
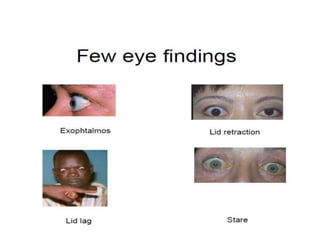
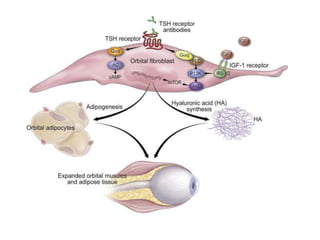
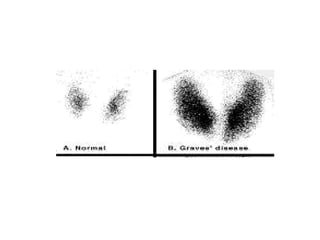
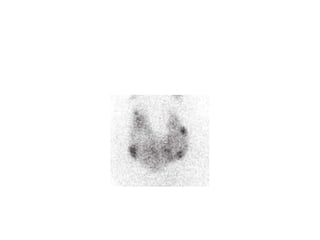
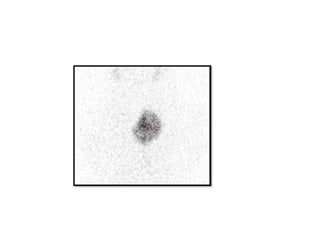
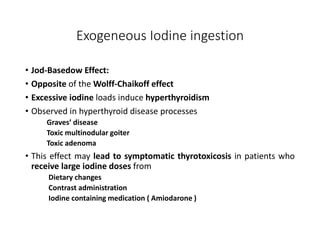
This document discusses a case of hyperthyroidism in a 39-year-old female presenting with nervousness, anxiety, palpitations, diarrhea, and weight loss. On examination, she had a heart rate of 110 bpm, tremor, increased reflexes, and an enlarged thyroid. Laboratory tests found high free T3 and T4, low TSH, and positive thyroid stimulating immunoglobulins, consistent with a diagnosis of Graves' disease. Graves' disease is an autoimmune disorder causing hyperthyroidism through thyroid stimulating antibodies. If left untreated, hyperthyroidism can progress to a thyroid storm, a life-threatening condition of severe hypermetabolism.