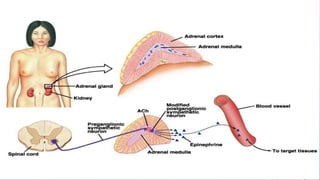
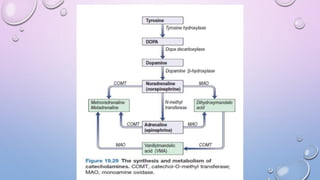
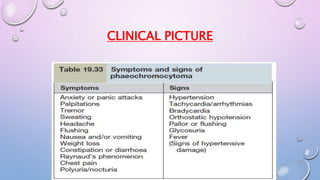
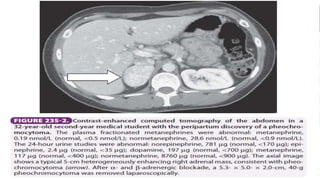
A 35-year-old man presented with increasing headaches, palpitations, anxiety, and panic attacks over the past six months. His history and examination were consistent with possible conditions including anxiety disorders, hyperthyroidism, and pheochromocytoma. Pheochromocytoma was considered the most likely diagnosis given the classic signs and symptoms. Pheochromocytomas are rare catecholamine-secreting tumors that typically arise from the adrenal medulla or sympathetic ganglia. Diagnostic testing revealed elevated levels of catecholamines and metanephrines confirming the diagnosis of a pheochromocytoma. The patient was started on alpha- and beta-blockers in preparation for surgical removal of the tumor.