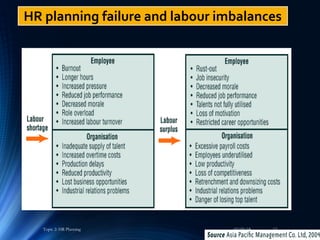
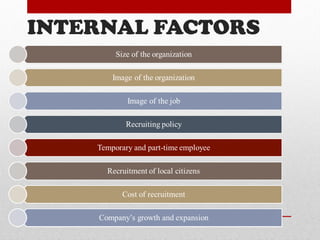
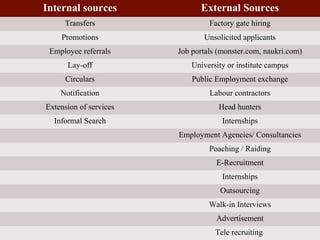
This document discusses various aspects of acquiring human resources, including human resource planning, job analysis, job design, recruitment, selection, placement and induction. It provides an overview of the key concepts and processes involved in human resource planning, such as forecasting future human resource needs and availability, identifying surpluses or deficits, and developing programs to address imbalances. The importance of human resource planning for organizations and techniques for demand and supply forecasting are also examined.