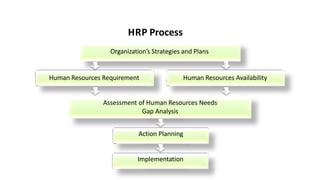
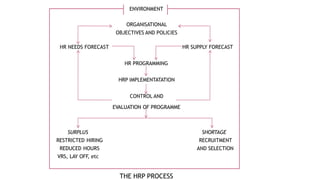
Human Resource Planning (HRP) involves forecasting an organization's future demand for and supply of employees. It ensures the organization will have the right number and types of qualified people in the right places and times to achieve organizational objectives. HRP is a continuous process that is part of corporate planning and involves forecasting personnel needs, analyzing current staffing levels, and developing recruitment, training, and other programs to close any gaps between demand and supply. The goal of HRP is to link human resources with organizational strategy and ensure optimal staffing that benefits both the organization and employees.