Embed presentation
Downloaded 433 times















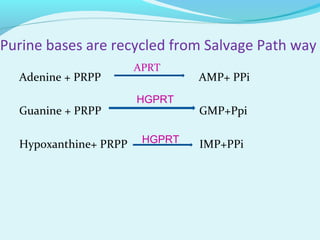











This document discusses the metabolism of purine nucleotides. It describes how purine bases are recycled through the salvage pathway using phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) and enzymes like adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT) and hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT). Primary gout is caused by enzyme defects while secondary gout results from overproduction or decreased excretion of uric acid. Symptoms of gout include arthritis in the big toe joint and treatment involves a low purine diet, allopurinol to inhibit xanthine oxidase, and probenecid or colchicine. Lesch-Ny


























