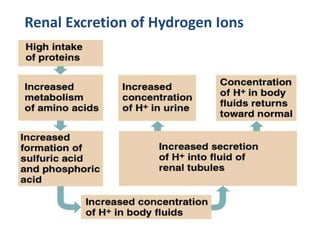
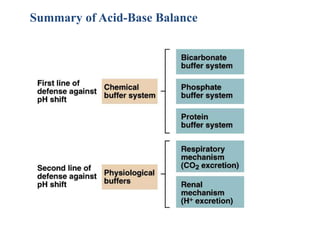
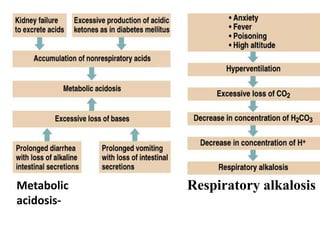
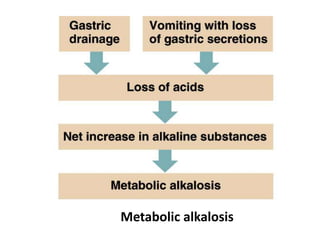
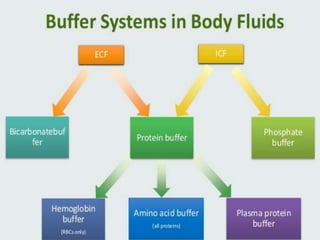
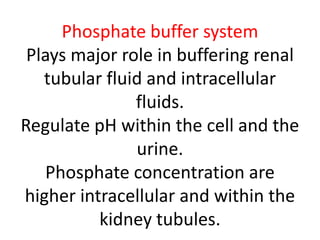
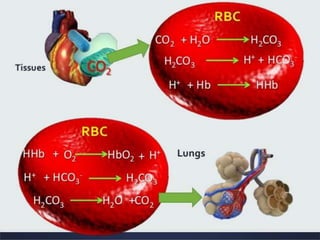
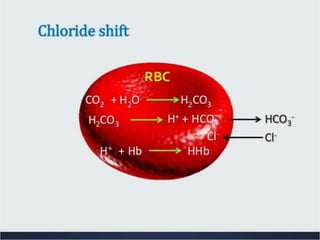
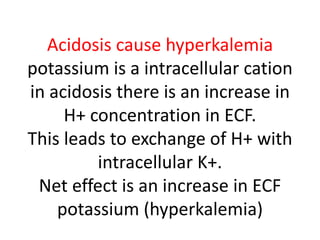
The document discusses acid-base balance and the mechanisms that regulate pH levels in the human body. There are three primary systems that regulate hydrogen ion levels to maintain blood pH between 7.35-7.45: 1) the buffer system acts rapidly to prevent excessive changes in pH by combining with acids or bases, 2) the respiratory system regulates carbon dioxide levels in the blood through breathing, and 3) the renal system permanently eliminates hydrogen ions through urine and maintains bicarbonate levels. Disruptions to acid-base balance can cause conditions like acidosis or alkalosis with neurological symptoms and the body aims to compensate for underlying issues.



























![Acid-base balance
Maintenance of homeostasis depends on controlling
the conc. of acids [H+] & bases [H+] in the body fluid
Solutions turn into acids when concentration of
hydrogen ions rises and turns to a base when it falls.
pH of Extracellular fluid ranges from pH 7.35 – 7.46
Does not apply to whole body : there are more
extreme/variable pH ranges elsewhere
Digestive tract
Gastric Juice 1.0-3.0
Pancreatic Juice 8.0-8.3
Intercellular organelles
Lysosomal pH 4-5
Digestive and lysosomal enzymes function optimally
at these pH ranges](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbasebalance-210309150324/85/Acid-base-balance-36-320.jpg)