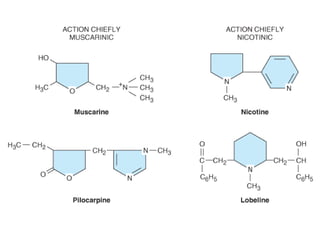
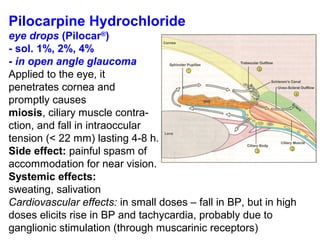
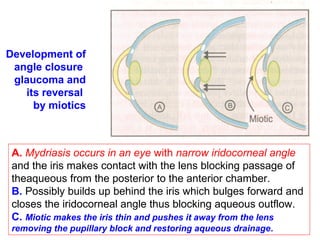
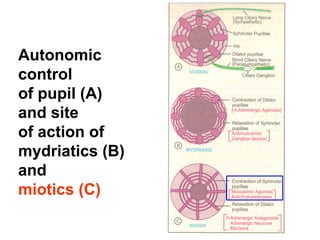
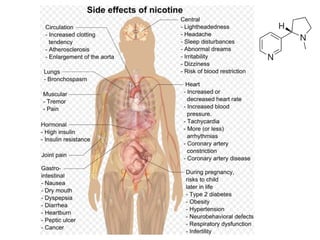
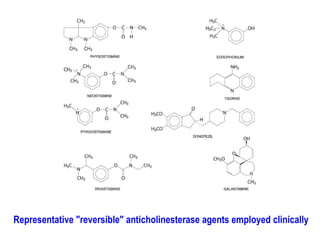
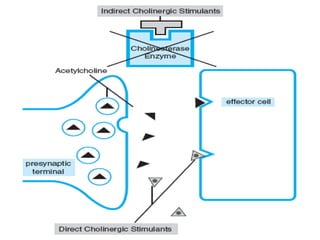
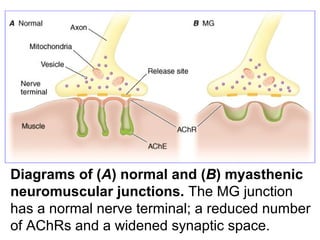
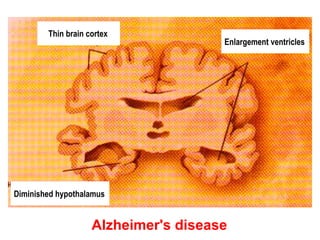
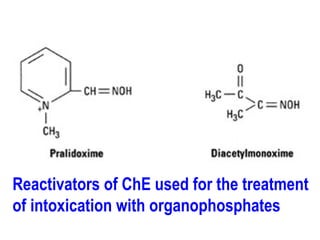
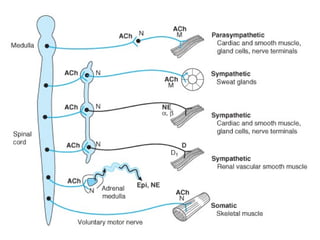
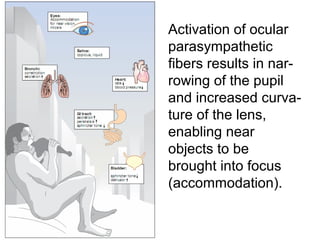
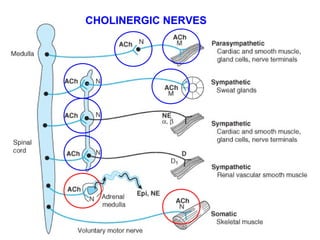
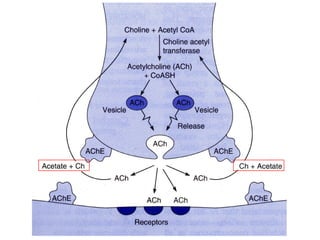
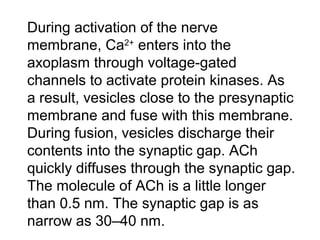
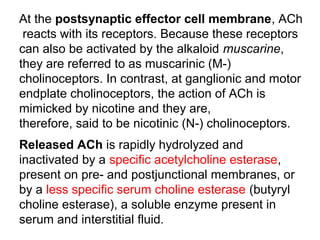
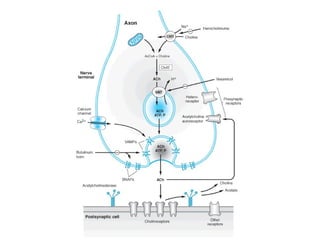
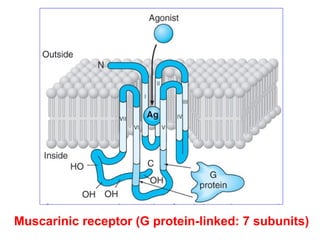
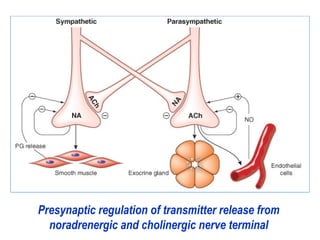
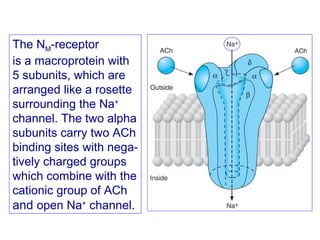
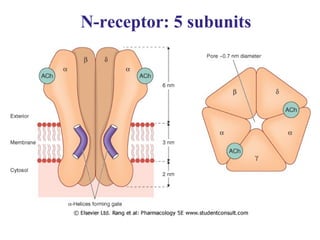
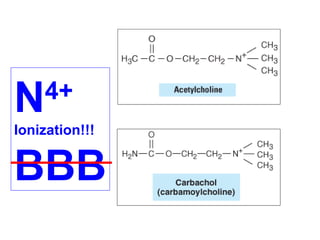
This document discusses cholinomimetic drugs and acetylcholine (ACh) signaling in the nervous system. It begins by describing the autonomic and somatic divisions of the nervous system. It then discusses how ACh acts as a neurotransmitter at cholinergic synapses in both divisions. Cholinomimetic drugs can be direct agonists that mimic ACh or indirect inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) to prolong the actions of endogenous ACh. Examples of direct agonists include pilocarpine and nicotine. Indirect agonists like galantamine and donepezil inhibit AChE. The document provides detailed information on the mechanisms and clinical uses of various cholinomime













![50
100
150
200
A B C D1 min
M- и N-effects of ACh
Bloodpressure[mmHg]
ACh
2 mcg i.v.
ACh
50 mcg
ACh
50 mcg
ACh
5 mg
M-
effect
M-
effect
N-
effect
Atropine
2 mg i.v.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-171029150845/85/Cholinergic-drugs-26-320.jpg)