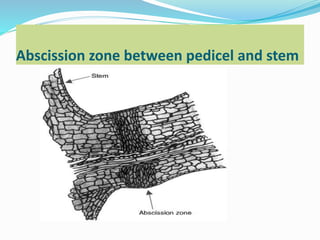
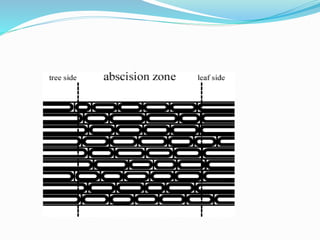
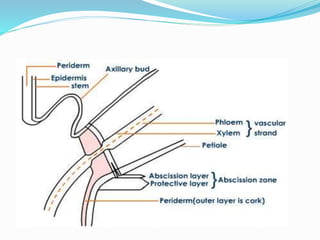
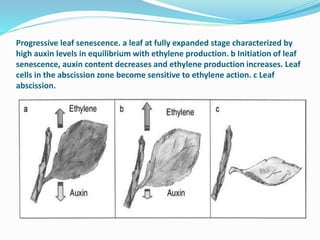
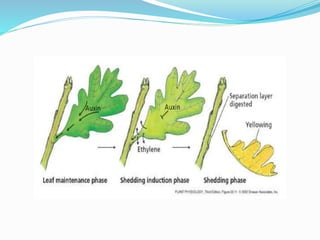
Abscission is the process by which plant organs such as leaves, flowers, and fruits become detached from the plant in a controlled manner. It occurs through the formation of an abscission zone, a layer of weak-walled cells located at the base of the petiole or other structure. Abscission is controlled by the plant hormones auxin and ethylene, with decreasing auxin and increasing ethylene levels initiating cell wall degradation in the abscission zone. This allows separation of plant organs through a combination of enzymatic breakdown and mechanical forces. Abscission aids in shedding organs no longer needed by the plant and occurs in response to environmental and developmental signals.