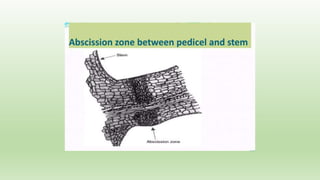
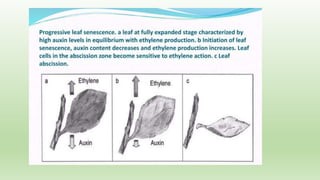
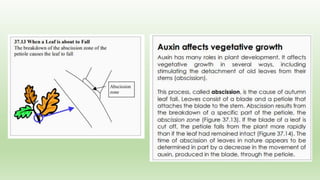
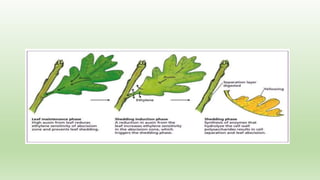
Abscission refers to the normal separation of senescent plant organs like leaves. It is a controlled process initiated during organ development with the formation of an abscission zone, a distinct layer of cells formed transversally across the petiole base. The abscission zone contains two layers - the abscission layer and protective layer. During abscission, the cells of the abscission layer separate due to dissolution of middle lamellae and cell walls by enzymes. Physiological changes also occur like chlorophyll degradation, decreased auxin, and increased ethylene production, which promote formation of cell wall degrading enzymes and abscission layer separation.