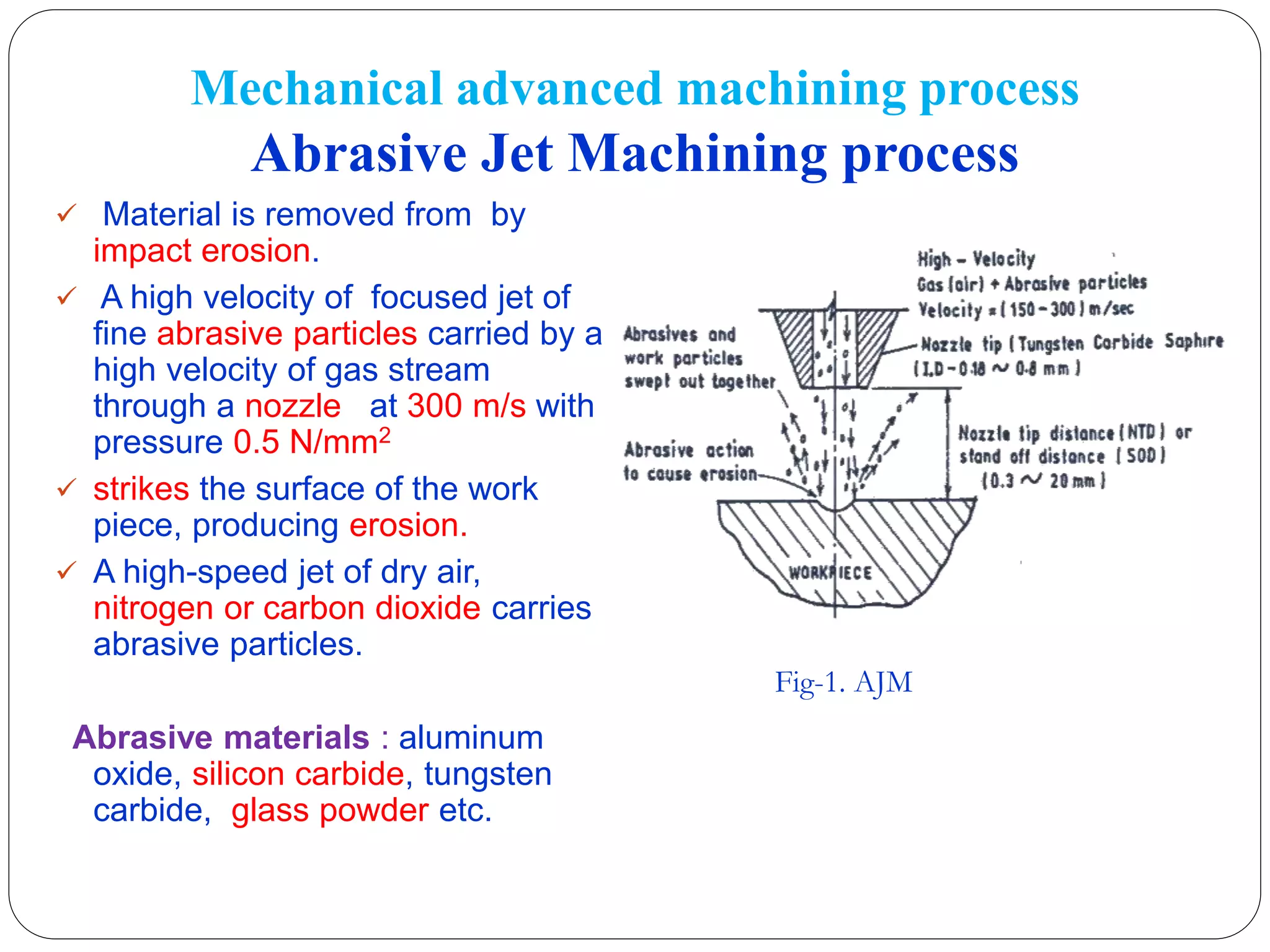
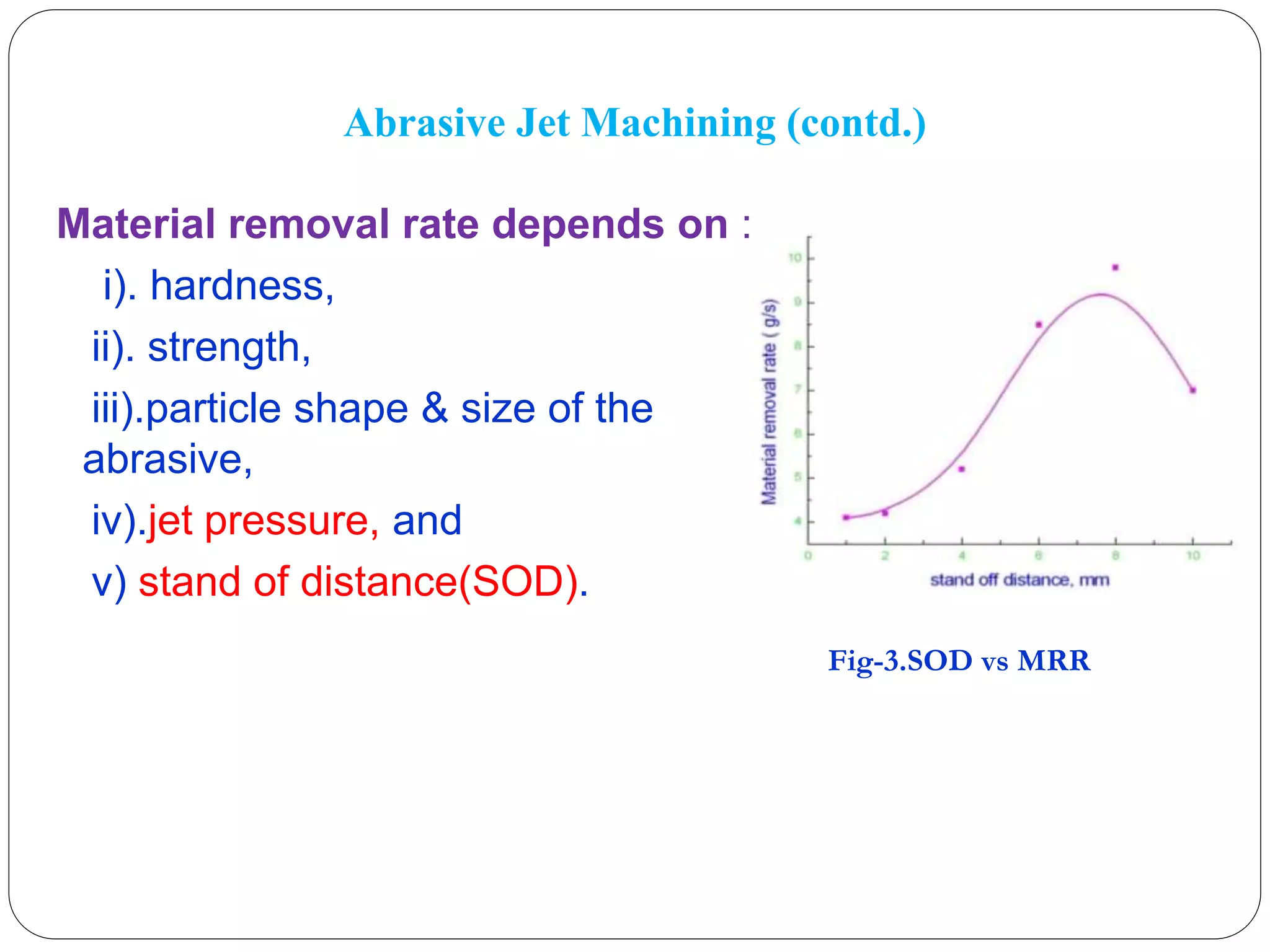
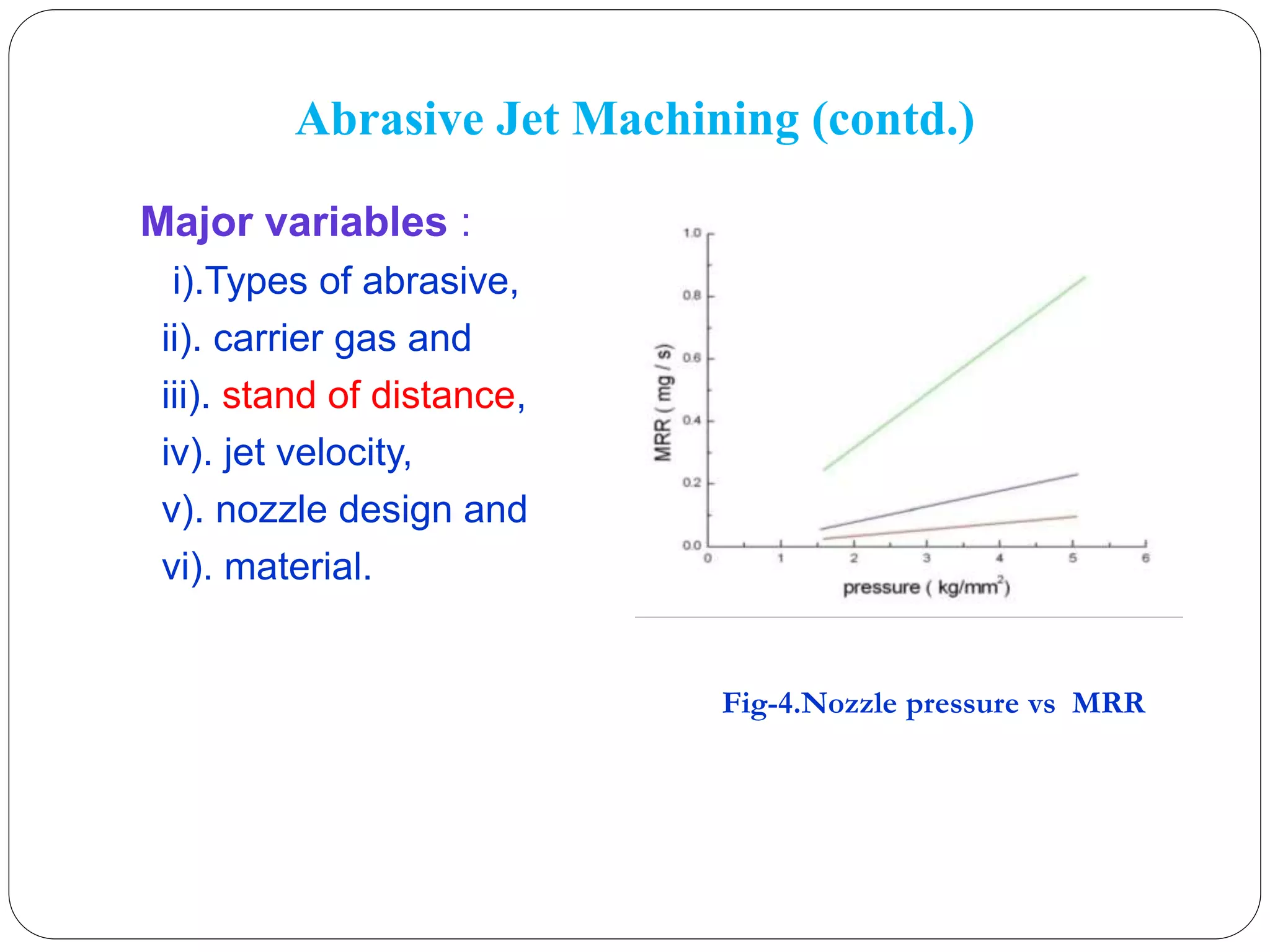
This seminar presentation provides an overview of abrasive jet machining (AJM). AJM is a mechanical advanced machining process where material is removed through impact erosion from a high-velocity jet of abrasive particles carried by a pressurized gas. Key aspects of AJM covered include the process mechanics, factors that influence material removal rate, common applications for machining hard or brittle materials, and advantages over traditional machining methods. The objectives are to educate about the AJM process and its ability to manufacture complex parts from difficult-to-machine materials for industries like aerospace and nuclear engineering.