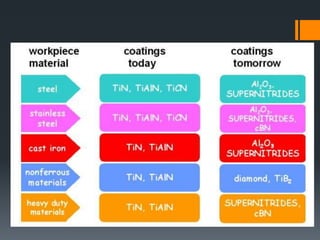
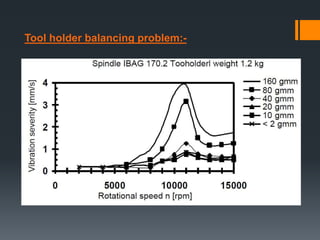
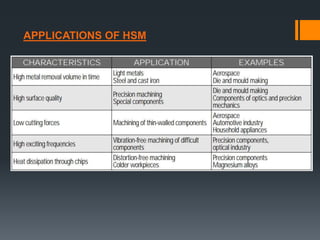
The document provides an overview of high speed machining (HSM), including its history, definitions, process parameters, machine details, advantages/disadvantages, applications, and conclusions. It discusses how HSM uses high spindle speeds and feed rates with specific tools and tool motions. Key benefits of HSM include improved accuracy, efficiency, reduced machining times, and decreased costs compared to conventional machining. The document also compares HSM to conventional machining and EDM.




















![The technical papers referred for this seminar are listed below.
[1] PASKO, R. - PRZYBYLSKI, L. & SLODKI, B, High Speed Machining
(HSM) – the effective way of modern cutting, Cracow University of
Technology.
[2] M.A. DAVIES, T. J. BURNS, T. L. SCHMITZ, High-Speed
Machining Processes: Dynamics on Multiple Scales, National Institute
of Standards and Technology, USA.
[3] J. KOPAC, Advanced tool materials for high-speed machining, 12th
international science conference paper, Faculty of Mechanical
Engineering, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia.
[4] HERBERT SCHULZ, The History of High-Speed Machining,
Darmstadt University of Technology, Germany.
REFERENCES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/highspeedmachininghsm-141224141229-conversion-gate01/85/High-speed-machining-HSM-36-320.jpg)
