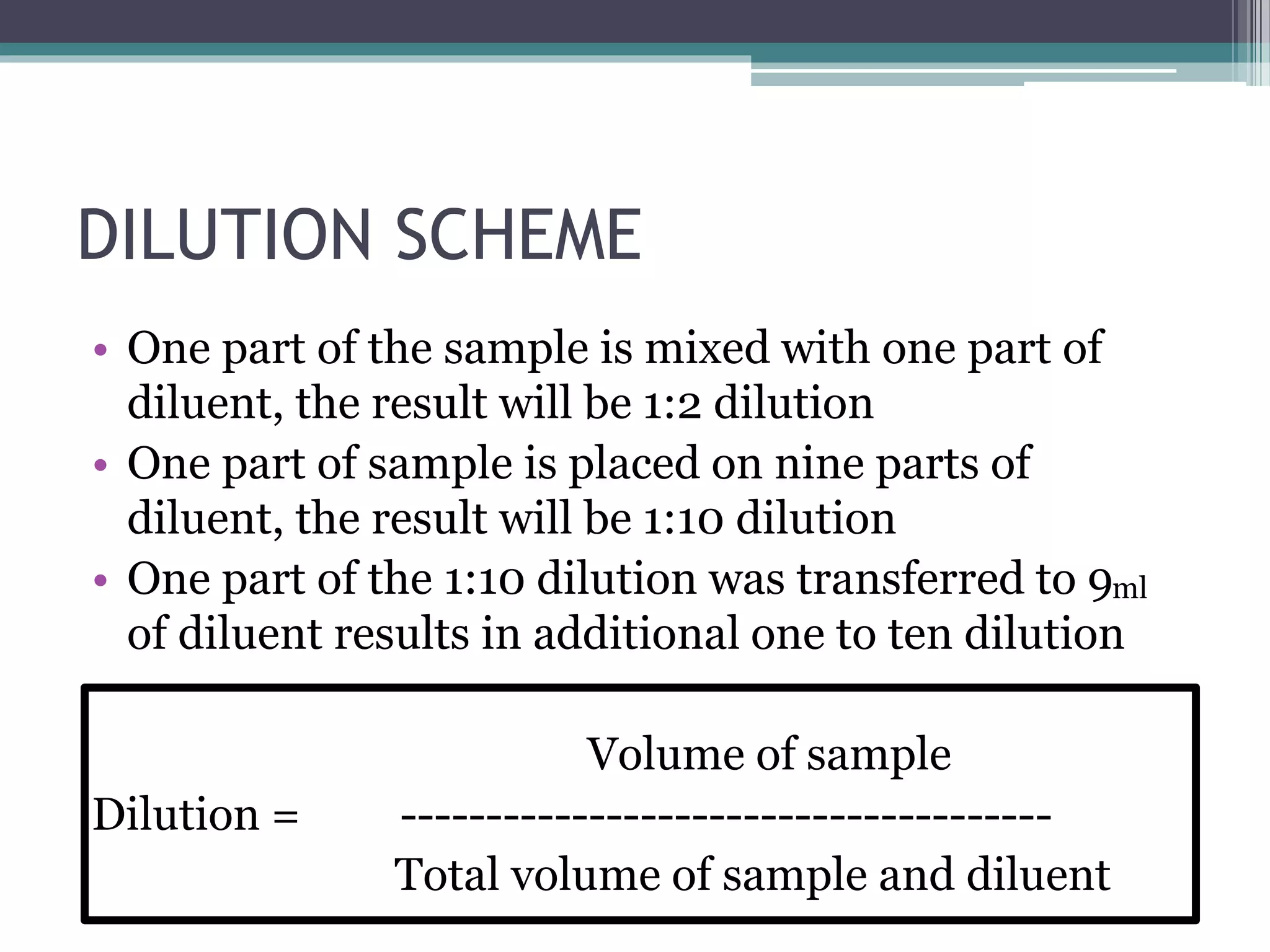
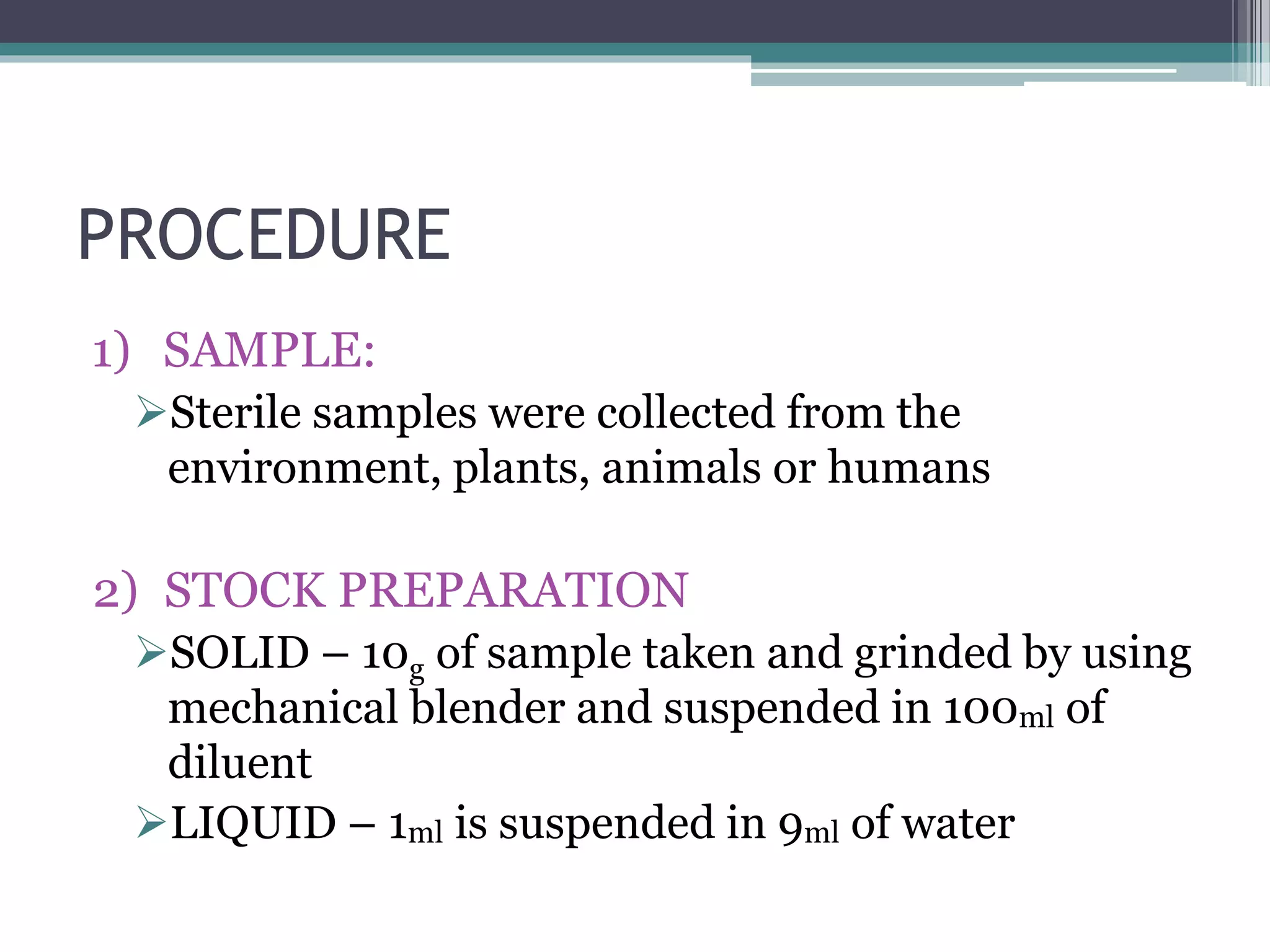
The serial dilution technique is used to count microbial colonies in environmental samples. It involves mixing a sample with diluent at ratios of 1:2 or 1:10 to reduce the microbial concentration to a countable level. The sample is serially diluted up to 10-8 and plated using the pour plate method. The plates are incubated and colonies are counted. The number of colonies per gram of sample is then calculated using the dilution factor. This technique allows microbiologists to study the number and types of microorganisms present in various environmental sources.