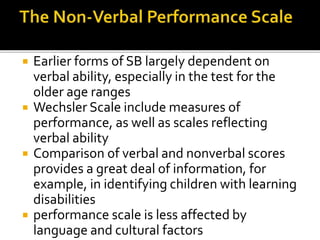
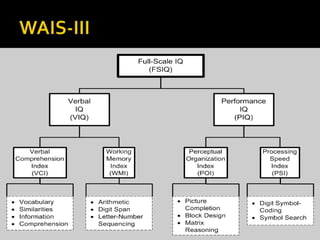
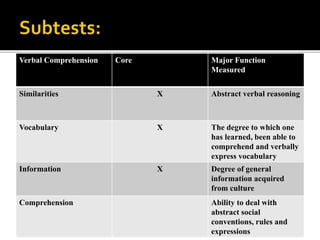
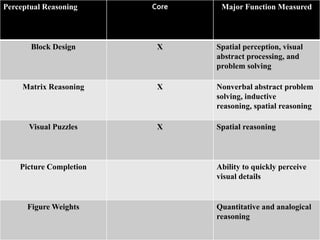
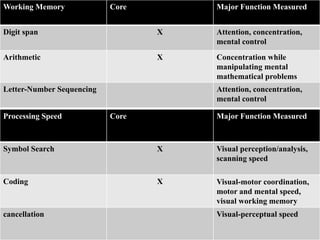
The California Personality Inventory (CPI) is a self-reported personality test created in 1956 to assess normal personality and interpersonal behavior. It contains 260 or 434 true-false items and measures 20 scales. The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) is an individually administered intelligence test for adults aged 16-90. It was created in 1939 as an alternative to the Stanford-Binet test for adults. The WAIS measures intelligence through verbal reasoning, working memory, perceptual reasoning, and processing speed subtests. It has been revised over time, with the current version being the WAIS-IV from 2008.