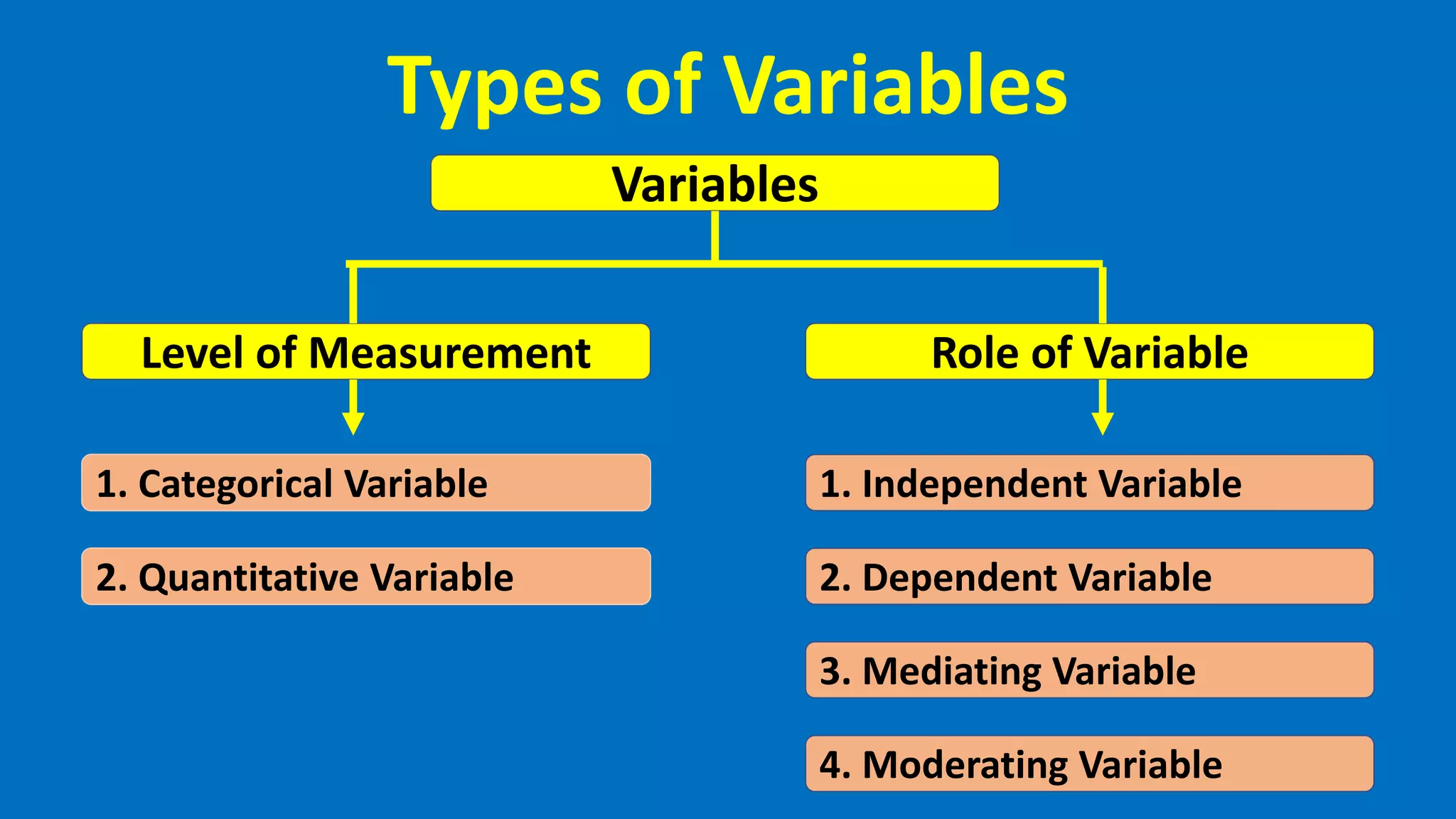
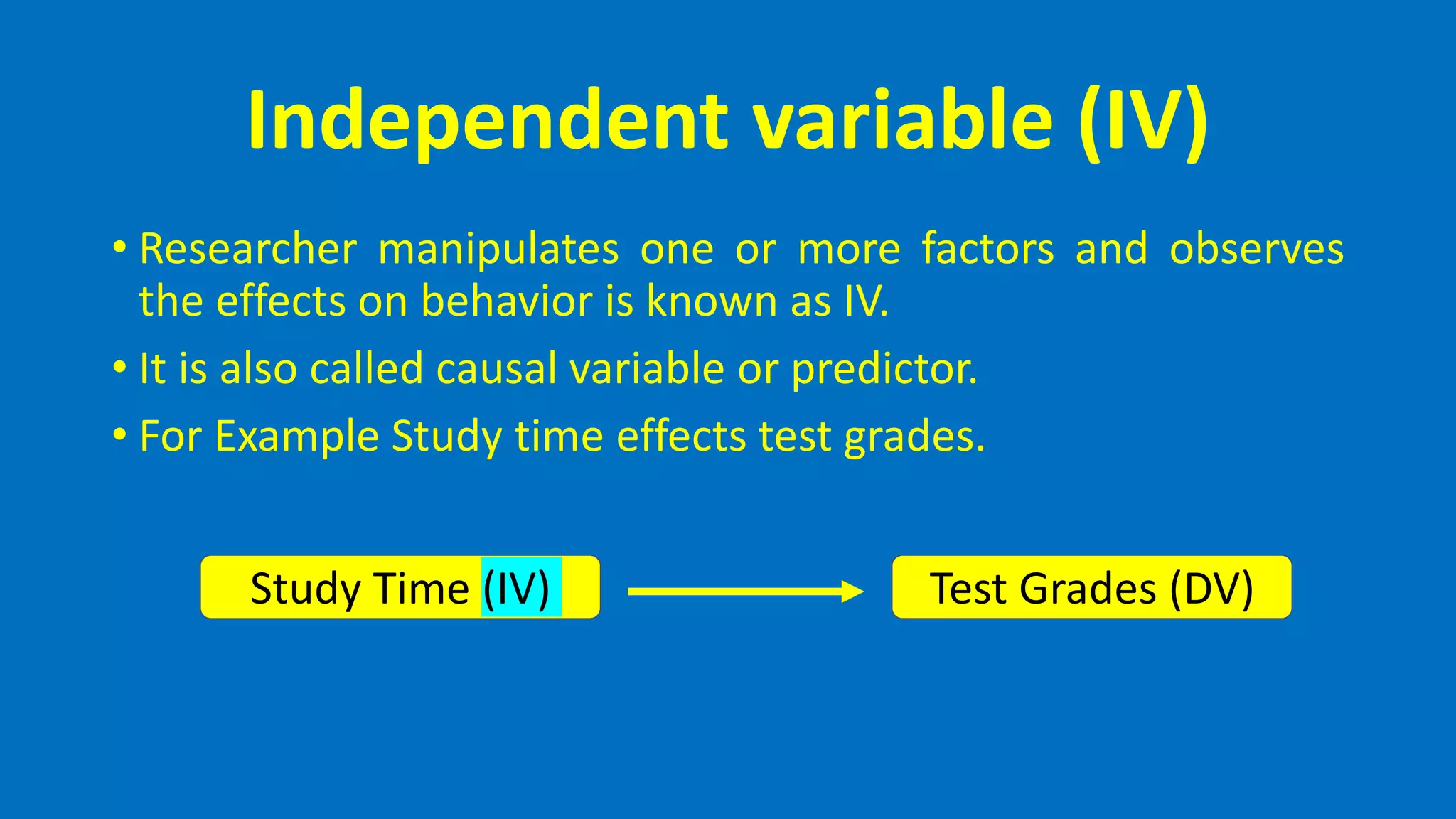
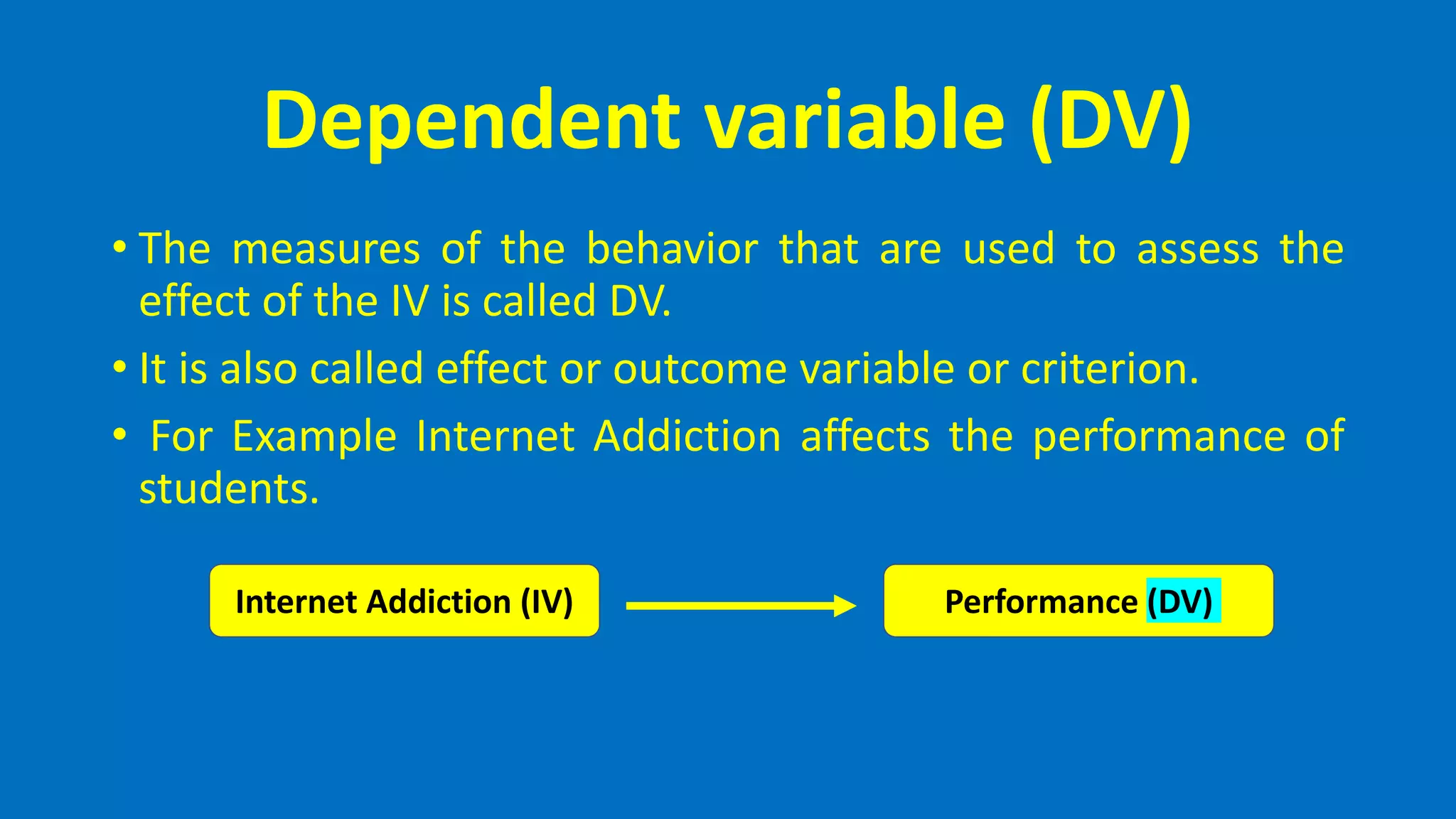
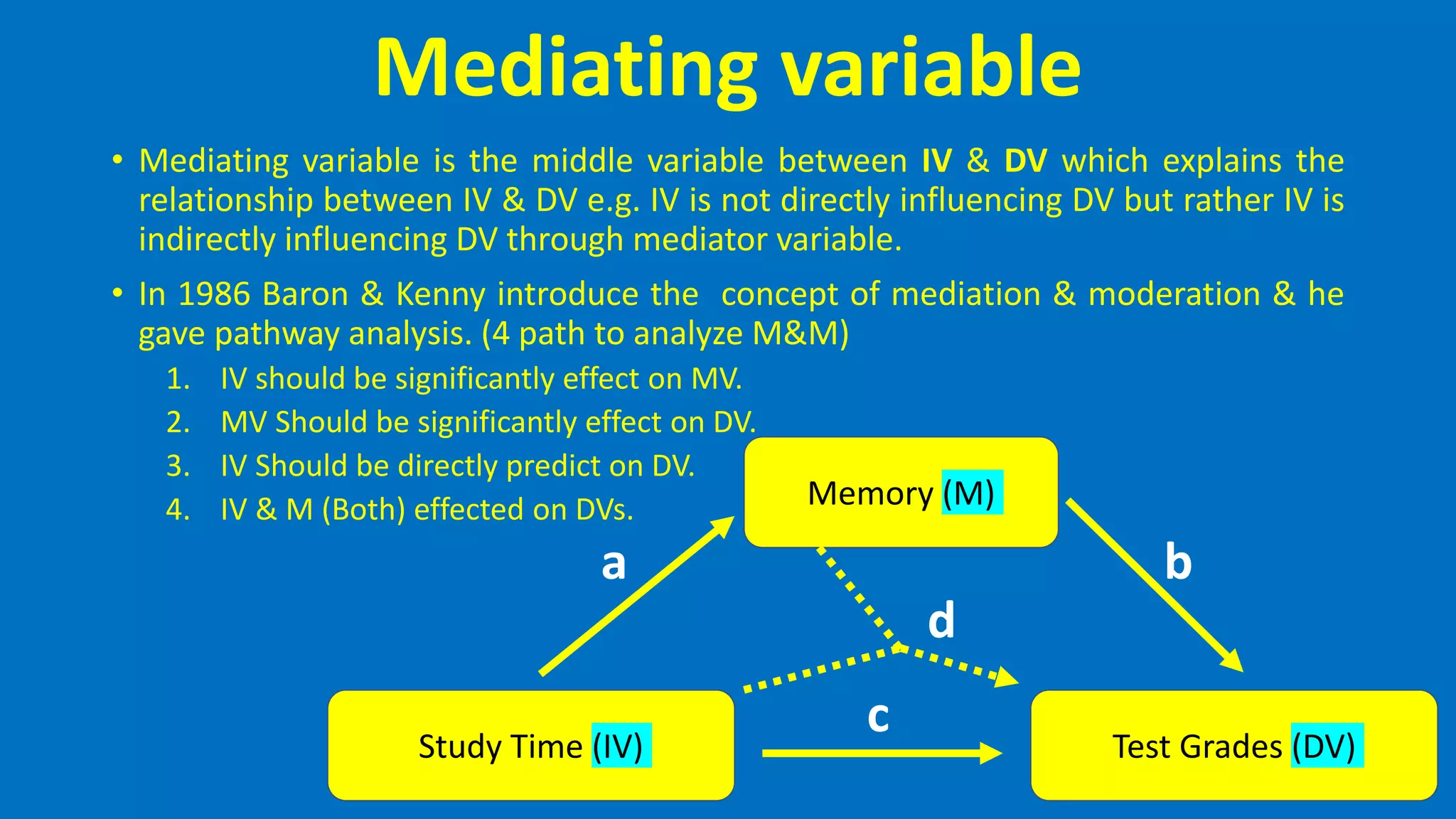
This document defines and describes different types of variables that are commonly used in quantitative research. It discusses categorical and quantitative variables, as well as independent, dependent, mediating, moderating, intervening, and extraneous variables. Categorical variables divide phenomena into categories, while quantitative variables vary in degree. Independent variables are manipulated by researchers, dependent variables are measured outcomes, and mediating/moderating variables explain relationships between independent and dependent variables.