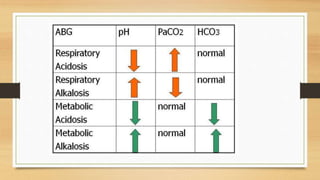
ABG analysis measures levels of oxygen, carbon dioxide, pH and bicarbonate in arterial blood to diagnose acid-base imbalances and respiratory issues. Normal values include a pH of 7.35-7.45, PaCO2 of 35-45 mm Hg, PaO2 of 75-100 mm Hg, and HCO3 of 22-26 meq/L. Respiratory failure occurs when blood gas levels fall outside normal ranges, and is classified as type I (low PaO2) or type II (low PaO2 and high PaCO2). Causes include lung diseases, infections, injuries or disorders that impact breathing. Treatment focuses on addressing underlying causes, improving oxygen levels and managing complications through