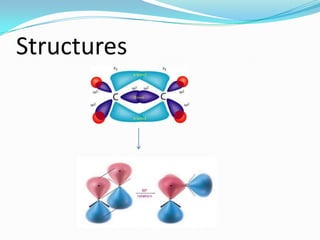
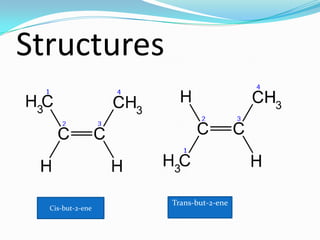
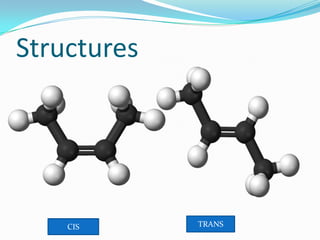
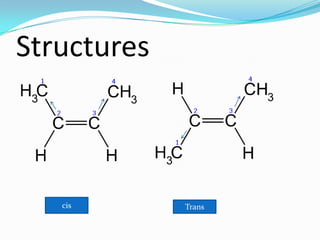
This document discusses geometrical isomerism in 2-butene. It defines cis-trans isomerism as a type of stereoisomerism that occurs when double bonds or ring structures prevent bond rotation. The structures of cis-but-2-ene and trans-but-2-ene are presented, and it is explained that cis means "on the same side" and trans means "on the opposite side." Key differences in their physical and chemical properties are described, including higher dipole moment and reactivity toward addition reactions in the cis isomer. The trans isomer is more stable due to less steric strain between groups on opposite sides of the double bond.




![Physical Property
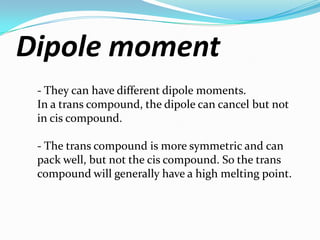
Cis-2-butene have high boiling point [4(3.73)] because
they have high dipole moment.
Trans-2-butene have high melting point [1(0.9)] due to
less dipole moment.
Cis M.P (- 139)
Trans B.P(-105.5)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/97-130831065430-phpapp01/85/Geometric-Isomerism-11-320.jpg)